garage crane Safety Certifications
When utilizing a garage crane, ensuring safety is paramount. Various certifications and standards exist to guarantee that the equipment meets stringent safety requirements. Here are some key certifications to consider:
1. OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration): OSHA oversees workplace safety in the United States. Compliance with OSHA standards ensures that the crane meets federal safety requirements concerning operation, maintenance, and training.
2. ANSI (American National Standards Institute): ANSI provides guidelines that are widely accepted in the industry. For garage cranes, ANSI standards, particularly B30 for cranes and related equipment, are crucial.
3. ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers): ASME B30.2 covers the rules for overhead and gantry cranes. Compliance with ASME standards ensures that the crane adheres to rigorous safety and performance criteria.
4. ISO (International Organization for Standardization): For global safety standards, ISO certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 13849 for safety-related parts of control systems are significant. They ensure that the crane operates safely within international safety guidelines.
5. CE Marking: For cranes used within Europe, CE marking indicates conformity with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards. The Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC is particularly relevant.
6. CSA (Canadian Standards Association): In Canada, CSA standards like CSA B167 cover the safety of cranes, ensuring that the equipment complies with national safety regulations.
By ensuring your garage crane meets these certifications, you minimize the risk of accidents and injuries while maintaining equipment integrity. Always check for these certifications and consult user manuals and professional guidelines to guarantee safe and efficient use.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “garage crane”
Certainly! Below is a list of reference technical parameters for a garage crane, which are essential for determining its suitability for various lifting applications:
1. Load Capacity:
– Specifies the maximum weight a crane can safely lift.
– Typically measured in kilograms (kg) or tons.
2. Lift Height:
– The maximum vertical distance the crane can lift a load from the floor.
– Measured in meters (m).
3. Boom Length:
– The length of the crane’s extendable arm.
– Can be measured in collapsed and extended positions, in meters (m).
4. Electric Motor Power:
– For electric garage cranes, specifies the power rating of the motor.
– Measured in kilowatts (kW) or horsepower (hp).
5. Hydraulic Pressure:
– Relevant for hydraulic garage cranes.
– Denoted in bars or Pascals (Pa).
6. Rotation Angle:
– Indicates the rotational range of the crane arm.
– Measured in degrees (°).
7. Weight of the Crane:
– The total weight of the crane itself.
– Measured in kilograms (kg).
8. Base Dimensions:
– The size of the crane’s base, which influences stability.
– Measured in meters (m) for width and length.
9. Hook Reach:
– The horizontal distance from the crane’s base to the hook in extended position.
– Measured in meters (m).
10. Lift Speed:
– The speed at which the crane can lift or lower a load.
– Measured in meters per minute (m/min).
11. Control System:
– Describes whether the crane is manually operated, electrically controlled, or remote-controlled.
12. Safety Features:
– Includes overload protection, emergency stop buttons, and safety latches on hooks.
13. Duty Cycle:
– Refers to the operational period and rest period required to prevent overheating.
– Expressed as a percentage.
14. Material of Construction:
– The type of materials used, which impacts durability and weight.
These parameters offer a comprehensive understanding of a garage crane’s technical specifications, ensuring you can match the crane to your specific lifting needs effectively.
List Product features of “garage crane”
A garage crane, often referred to as an engine hoist or shop crane, is an essential tool for mechanics and automotive enthusiasts. Here are the key features:
1. Load Capacity: Typically ranges from 1 to 3 tons, allowing it to lift heavy engines and other components.
2. Adjustable Boom: The boom can often be adjusted to different lengths to accommodate various lifting needs, providing versatility in different garage setups.
3. Hydraulic System: Equipped with a hydraulic jack or ram, requiring minimal physical effort to lift heavy objects smoothly and safely.
4. Foldable Design: Many models feature foldable legs and booms for easy storage when not in use, making them convenient for smaller spaces.
5. Dual-Action Pump: Some cranes come with dual-action pumps for faster lifting, increasing efficiency during use.
6. Heavy-Duty Construction: Usually built with high-strength steel to ensure durability and long service life, even under heavy-duty operations.
7. 360-Degree Rotating Hook: The hook often rotates to provide flexibility in positioning the lifted object precisely.
8. Sturdy Wheels and Casters: Equipped with strong, swivel casters for easy maneuverability around the garage, even when carrying heavy loads.
9. Safety Features: Includes overload valves and safety chains to prevent potential accidents and ensure secure lifting.
10. Adjustable Legs: Some models have adjustable-width legs to offer stability while accommodating various workspaces.
11. Ease of Assembly: Often designed with user-friendly assembly instructions and minimal tools required.
12. Versatile Applications: Useful for engine swaps, component lifts, and other heavy lifting tasks around the garage or workshop.
13. Coating and Finish: Typically coated with paint or powder coating to resist corrosion and wear, enhancing longevity.
14. Swivel Handle: For improved maneuvering and control when adjusting the load.
These features make a garage crane a flexible, robust, and indispensable tool for automotive work and other heavy lifting tasks in a garage setting.

List Various Types of “garage crane”
Sure, here are various types of garage cranes, each designed for specific tasks and different levels of capability:
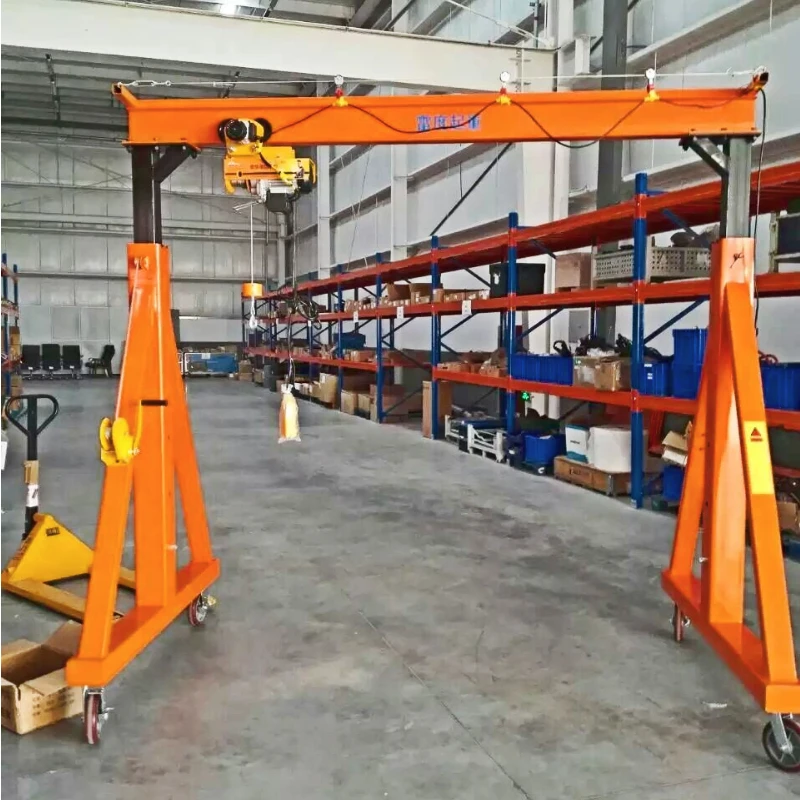
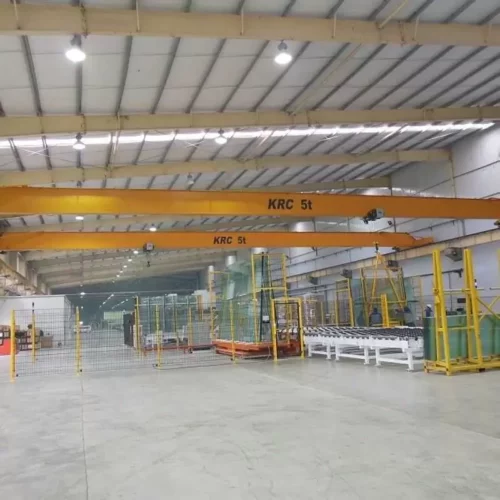
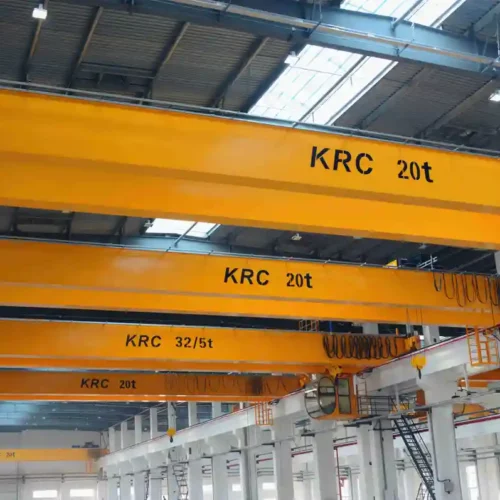
1. Overhead Garage Crane:
– Bridge Cranes: These consist of two parallel runways with a traveling bridge spanning the gap. They are ideal for heavy lifting and can be either fixed or mobile.
– Gantry Cranes: Similar to bridge cranes but supported by freestanding legs that move on wheels or along a track. Good for both indoor and outdoor use.
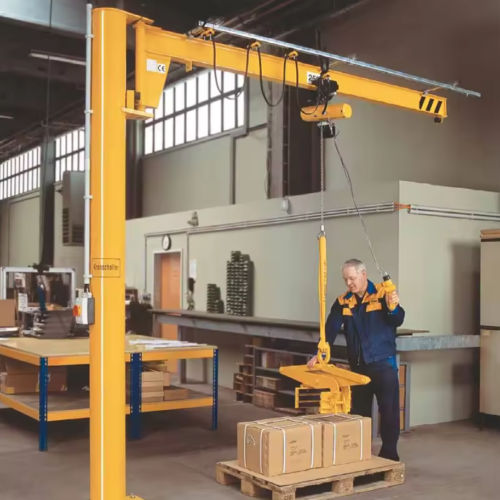
2. Jib Cranes:
– Wall-Mounted Jib Cranes: These are fixed to a wall or column and have a swinging arm to lift loads within a semi-circular area.
– Freestanding Jib Cranes: These stand alone and are ideal for areas where overhead mounting isn’t feasible.
3. Engine Hoists (Cherry Picker):
– Hydraulic Engine Hoists: Utilize a hydraulic mechanism for lifting engines and other heavy automotive parts. They are portable and commonly used in automotive repair.
4. Monorail Cranes:
– These feature a single rail that a trolley runs along, suitable for straight-line lifting tasks. Ideal for assembly lines or small workshops.
5. Portable Floor Cranes:
– Folding Floor Cranes: These can be folded for easy storage and are typically used for lifting heavy objects in garages, such as car engines.
– Counterbalance Floor Cranes: These offer greater reach and are often used in tight spaces where maneuverability is crucial.
6. Chain Hoists:
– Manual Chain Hoists: Operated by hand, these are cost-effective and useful for smaller lifting tasks.
– Electric Chain Hoists: Provide higher efficiency and are suitable for heavier loads and higher frequency of use.
7. Workbench Cranes:
– These small, versatile cranes are mounted on workbenches and are ideal for lifting lighter objects.
Each type of garage crane has its own specific advantages depending on the lifting requirements, space constraints, and type of tasks at hand.
List Application of “garage crane”
A garage crane, commonly found in automotive garages and workshops, has various practical applications:
1. Engine Lifting: One of the primary uses of a garage crane is to lift and maneuver heavy car engines for removal or installation. This is crucial for engine repairs, replacements, or modifications.
2. Transmission Handling: Similar to engine work, garage cranes assist in lifting and positioning transmissions, enabling easier access for repairs, maintenance, or replacements.
3. Vehicle Restoration: During car restoration projects, garage cranes help lift large vehicle components such as frames, axles, and chassis elements. This aids in detailed work without straining the mechanics.
4. Heavy Parts Installation: Installation of other heavy parts, such as differentials, fuel tanks, and exhaust systems, is simplified with the precise lifting capabilities of a garage crane.
5. Parts Transportation: Moving heavy parts around the workshop or garage without physical strain or risk of damage is another important application of garage cranes.
6. Motorcycle Repair: For motorcycle enthusiasts, garage cranes can lift bikes for easier access to the undercarriage, facilitating repairs, maintenance, or part swaps.
7. Industrial Equipment Maintenance: Beyond automotive use, garage cranes can aid in lifting and maintaining heavy industrial equipment found in workshops, such as lathes or milling machines.
8. Material Handling: In garages that also function as general workshops, garage cranes can help in handling and lifting building materials, machinery, and other heavy items.
9. Safety Assurance: By using garage cranes, workers can handle heavy loads safely, reducing the risk of injuries and enhancing overall workplace safety.
In conclusion, garage cranes provide versatile, practical solutions for handling heavy components and machinery with precision and safety in automotive and industrial settings.

List Buyer Types of “garage crane”
When considering the buyer types for a garage crane, it’s crucial to recognize that such equipment serves a wide variety of purposes across different sectors. Here are some primary buyer types:
1. Automotive Enthusiasts and Hobbyists:
– Use Case: These individuals often work on car maintenance, repairs, or restoration projects in their home garages.
– Requirements: Typically seek compact, efficient, and easy-to-operate cranes that can handle smaller, lighter tasks like lifting engines or heavy car parts.
2. Professional Mechanics and Automotive Shops:
– Use Case: These buyers are involved in regular, heavy-duty lifting tasks and require reliable, durable, and powerful cranes.
– Requirements: Prefer industrial-grade equipment with higher lifting capacities and enhanced safety features to handle a wide range of vehicles and components.
3. DIY Homeowners:
– Use Case: These are individuals engaged in diverse DIY projects which might require lifting heavy objects such as construction materials, gardening equipment, or household items.
– Requirements: Look for affordable, user-friendly cranes that provide versatility for various home improvement and maintenance tasks.
4. Small Manufacturers and Workshops:
– Use Case: These businesses need to move heavy materials or equipment within their production spaces.
– Requirements: Need robust cranes with moderate to high lifting capacities, reliability, and efficiency to improve operational workflow.
5. Construction and Renovation Professionals:
– Use Case: Involved in building or remodeling projects where lifting heavy construction materials is necessary.
– Requirements: Demand sturdy, portable cranes that can be easily transported and set up on different job sites, with sufficient lifting power to handle construction materials.
6. Farmers and Agricultural Operations:
– Use Case: Utilize cranes for maintaining and repairing farm machinery, and handling heavy livestock feed or other materials.
– Requirements: Seek durable cranes that can operate in rugged conditions with moderate lifting capacities and ease of use.
Each buyer type has distinct needs and priorities, making it essential for suppliers to offer a range of garage cranes to meet these varied demands.

List “garage crane” Project Types for Different Industries
1. Automotive Industry: In automotive shops, garage cranes are essential for lifting engines, transmissions, and other heavy components. Mobile gantry cranes, engine hoists, and overhead bridge cranes are commonly used for maintenance, repair, and assembly tasks.
2. Construction Industry: Garage cranes are employed for lifting heavy construction materials such as steel beams, concrete blocks, and machinery. Telescoping cranes and portable gantry cranes facilitate material handling on construction sites, improving efficiency and safety.
3. Manufacturing Industry: In manufacturing plants, garage cranes enable the movement of raw materials, heavy equipment, and finished products. Overhead cranes, jib cranes, and workstation bridge cranes are integral to assembly lines, machining centers, and manufacturing cells.
4. Aerospace Industry: The aerospace sector utilizes garage cranes for the precise handling and assembly of aircraft components. Overhead bridge cranes and jib cranes assist in lifting large aircraft parts such as wings and fuselage sections in production and maintenance facilities.
5. Warehouse and Logistics: For warehouses and distribution centers, garage cranes aid in the efficient movement of large and bulky items. Overhead cranes and gantry cranes streamline the process of loading and unloading goods, improving inventory management and reducing manual labor.
6. Marine Industry: In shipyards and marine service shops, garage cranes handle engines, anchors, and other heavy marine equipment. Gantry cranes and hoists are essential for the repair, maintenance, and construction of ships and boats.
7. Mining Industry: Heavy-duty garage cranes are crucial in mining operations for lifting heavy machinery, repairing equipment, and handling extracted minerals. Gantry cranes and monorail hoists ensure operational efficiency and worker safety in rugged mining environments.
8. Agricultural Industry: Agricultural operations employ garage cranes for maintaining heavy farm equipment such as tractors, combine harvesters, and irrigation systems. Portable cranes and engine hoists facilitate repair work and equipment handling on farms.
9. Energy Sector: In energy production facilities, especially in wind and solar power plants, garage cranes are used for installing and maintaining heavy components like wind turbine blades and solar panels. Gantry cranes and mobile cranes support these large-scale installations and servicing tasks.
10. Entertainment and Events: For large events, concerts, and shows, garage cranes assist in setting up heavy stage equipment, light rigs, and sound systems. Portable gantry cranes and lightweight mobile hoists enhance efficiency in event setup and teardown.
In summary, garage cranes adapt to diverse industrial needs by providing tailored lifting solutions that enhance operational efficiency, safety, and productivity across various sectors.

garage crane Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Garage cranes are powerful tools for lifting and maneuvering heavy loads, but their functionality can be significantly enhanced with the right accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options. Here’s a brief overview:
Accessories:
1. Load Levelers: Allow for balanced lifting of uneven loads, preventing sway and ensuring safety.
2. Remote Controls: Enhance operational convenience and safety by allowing maneuvering from a distance.
3. Slings and Straps: Offer additional stability for various load shapes and sizes.
4. Trolleys and Hoists: Facilitate smooth horizontal movement along beams, increasing versatility.
5. Safety Latches and Hooks: Ensure secure connections between the crane and the load, minimizing the risk of accidents.
Upgrades:
1. Electric Motors: Upgrade from manual operation to electric for increased lifting speed and reduced physical effort.
2. Enhanced Jib Arms: Opt for adjustable or longer jib arms to increase reach and flexibility.
3. Higher Capacity Winches: Upgrade to winches with larger capacity to handle heavier loads.
4. Swivel Bases: Integrate swivel bases for 360-degree rotation, improving maneuverability in tight spaces.
5. Wireless Connectivity: Implement wireless systems for remote monitoring and control, boosting operational efficiency.
Custom Manufacturing Options:
1. Tailored Load Capacities: Customize your crane to handle specific weight requirements beyond standard models.
2. Adjustable Height: Design cranes with adjustable height capabilities to accommodate various work environments.
3. Specialized Attachments: Develop custom attachments for unique load shapes or specific industrial tasks.
4. Material Choices: Select specialized materials for durability, such as stainless steel for corrosive environments.
5. Ergonomic Designs: Customize controls and structural features for improved user ergonomics and safety.
By integrating these accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options, garage cranes can be tailored to meet specific needs, enhancing both performance and safety.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “garage crane”
Quality Control of Garage Crane
1. Material Inspection: Raw materials like steel are checked for compliance with quality standards and specifications.
2. Dimensional Accuracy: Each component is measured to ensure it meets design tolerances, preventing assembly issues.
3. Load Testing: Finished cranes are subjected to load tests under various conditions to ensure they can handle specified weights safely.
4. Welding Quality: Welds are inspected using ultrasonic testing or x-rays for internal defects that could compromise structural integrity.
5. Paint and Coating: The paint and any protective coatings are inspected for uniformity and adhesion to prevent corrosion.
6. Operational Testing: The mechanical components such as winches and pulleys are tested for smooth operation.
7. Documentation and Compliance: Ensuring all processes and tests are documented for compliance with industry standards like ISO 9001.
The Manufacturing Process of Garage Crane
1. Design and Planning: Engineering team designs the crane using CAD software, considering load capacity, materials, and safety features.
2. Material Sourcing: High-quality materials are sourced from certified suppliers to ensure durability and performance.
3. Cutting and Shaping: Materials are cut and shaped using CNC machines, ensuring precision and uniformity in parts.
4. Welding and Assembly: Components are welded together by skilled technicians, followed by assembly of major parts like the jib and base.
5. Machining: Machined parts such as joints, pulleys, and fasteners are crafted with high precision to fit perfectly.
6. Surface Treatment: Assembled cranes undergo surface treatments like sandblasting and painting to enhance durability and appearance.
7. Quality Control Inspections: Comprehensive inspections are carried out at various stages to ensure each crane meets quality standards.
8. Load Testing and Fine-Tuning: Assembled cranes are load-tested and any necessary adjustments are made to ensure peak performance.
9. Packaging and Shipping: Finally, the cranes are securely packaged and shipped to distributors or end-users.
This structured approach ensures that garage cranes are manufactured to the highest standards of quality, safety, and reliability.

How to use “garage crane”
Using a garage crane, also known as an engine hoist, is essential for tasks like lifting engines or other heavy components in a garage. Here’s a step-by-step guide to using one safely and effectively:
1. Preparation:
– Inspect the Crane: Ensure that the crane is in good working condition. Check for any signs of damage or wear.
– Position the Crane: Place the crane on a flat, stable surface to prevent tipping.
2. Attaching the Load:
– Secure the Chains/Straps: Attach the hoist’s chains or straps to the load. If lifting an engine, connect the chains to the designated lifting points.
– Balance the Load: Ensure the load is balanced to prevent swinging or tipping during lifting.
3. Lifting:
– Pump the Handle: Slowly pump the hydraulic handle to raise the boom and lift the load. Keep an eye on the load to ensure it remains balanced.
– Adjust as Needed: If the load starts to shift, lower it slightly and adjust the chains/straps.
4. Moving the Load:
– Proceed with Caution: Carefully roll the crane to the desired location if it has wheels. Avoid sudden movements.
5. Lowering the Load:
– Release the Hydraulic Valve: Slowly open the hydraulic valve to lower the load gently.
– Ensure Safety: Keep hands and feet clear of the load’s path.
6. After Use:
– Store Properly: Once finished, retract the boom completely and store the crane in a secure location.
Safety Tips:
– Check Weight Limits: Never exceed the crane’s maximum load capacity.
– Use Protective Gear: Wear gloves and safety glasses to prevent injuries.
– Clear the Area: Ensure the workspace is free of obstacles and bystanders.
Following these steps ensures safe and efficient use of a garage crane.
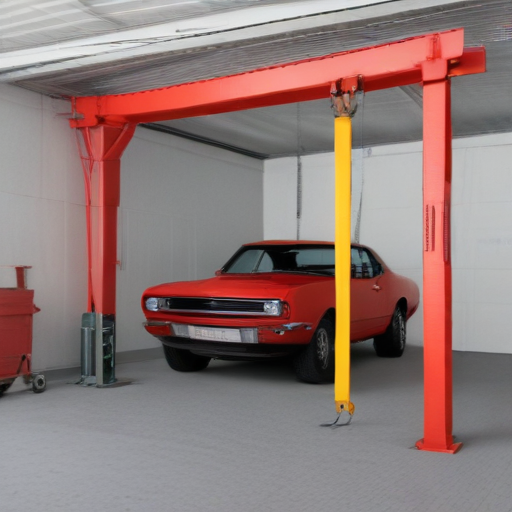

“garage crane” Comparative Analysis
A “garage crane” is a pivotal tool for lifting and moving heavy objects in automotive repair and home improvement settings. Let’s delve into a comparative analysis of two primary types: the engine hoist (shop crane) and the overhead garage crane.
1. Engine Hoist (Shop Crane):
– Design: Portable, floor-based structure with a hydraulic jack and boom. Often equipped with wheels for mobility.
– Capacity: Typically ranges from 1 to 3 tons, suitable for lifting car engines and other heavy components.
– Advantages: Highly versatile and mobile, can be positioned exactly where needed. It’s collapsible for easy storage.
– Disadvantages: Limited vertical height, can take up floor space, and may require more effort to maneuver in confined spaces.
– Use Cases: Ideal for automotive repair shops, home garages focusing on vehicle maintenance, and small-scale industrial uses.
2. Overhead Garage Crane:
– Design: Fixed or adjustable beam mounted to the ceiling, with a trolley and hoist system.
– Capacity: Ranges broadly, from 500 pounds to several tons, depending on the beam and hoist setup.
– Advantages: Saves floor space, offers greater lifting height, and can cover a larger area if the trolley system is extensive.
– Disadvantages: Installation can be complex and permanent. Limited to the structural support and space of the garage ceiling.
– Use Cases: Suitable for permanent repair shops, large home garages, and any facility requiring consistent overhead lifting.
Comparative Summary:
– The engine hoist is excellent for mobility and versatility, particularly in scenarios where the lifting points change frequently. It’s a cost-effective option but can be cumbersome in a cluttered workspace.
– The overhead garage crane excels in maximizing vertical space and providing extensive reach. It’s ideal for heavier and more frequent lifting tasks but requires a sturdy installation.
Conclusion:
Choosing between an engine hoist and an overhead garage crane depends on the specific needs, such as mobility, space availability, lifting capacity, and frequency of use. For dynamic, varied tasks, the engine hoist is preferable, while the overhead crane suits more static, consistent operations.
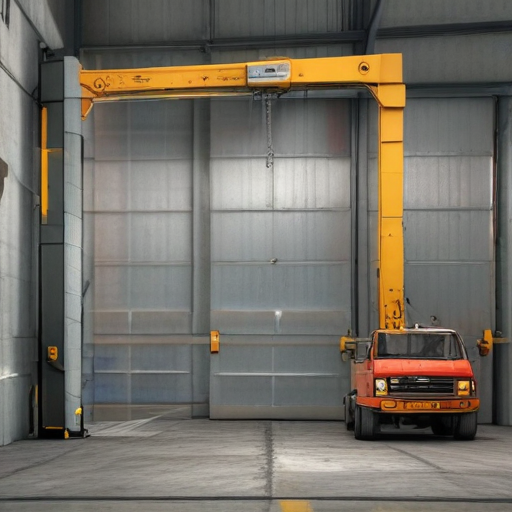

“garage crane” Warranty and Support
Garage Crane Warranty and Support
When investing in a garage crane, understanding the warranty and support offered is crucial to ensure long-term reliability and peace of mind.
Warranty:
Most reputable manufacturers provide a standard warranty period, typically ranging from one to three years. This warranty often covers defects in materials and workmanship under normal use conditions. Some brands may offer extended warranties or additional coverage for an extra cost.
Key Points:
1. Coverage: Ensure the warranty covers essential components like the hydraulic system, motor, and structural parts.
2. Exclusions: Be aware of what is not covered, such as normal wear and tear, misuse, or improper maintenance.
3. Claim Process: Understand the procedure for filing a claim. This usually involves contacting the manufacturer or an authorized service center.
Support:
Customer support is vital for troubleshooting, repairs, and maintenance guidance.
1. Technical Support: Manufacturers typically offer technical support via phone, email, or online chat. They can assist with setup, troubleshooting, and operational questions.
2. Service Centers: Authorized service centers can perform repairs and maintenance. Check if there is a center near your location.
3. Manuals and Resources: Ensure you receive a comprehensive user manual. Many manufacturers also provide online resources such as FAQs, instructional videos, and downloadable manuals.
4. Replacement Parts: Confirm the availability of replacement parts and the ease of ordering them.
Additional Tips:
– Registration: Register your garage crane after purchase to activate the warranty and receive updates or recalls.
– Maintenance: Regular maintenance, as outlined in the user manual, can prevent issues and extend the lifespan of your crane.
By thoroughly understanding the warranty and support options, you can ensure that your garage crane remains a reliable tool in your workspace for years to come.
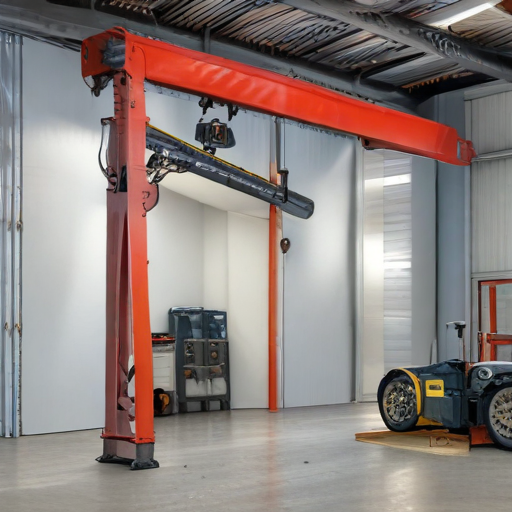

List “garage crane” FAQ
Garage Crane FAQ
1. What is a garage crane?
A garage crane is a piece of equipment used to lift and move heavy objects within a garage or workshop. It’s commonly used for lifting engines, vehicles, and other heavy machinery.
2. What types of garage cranes are available?
There are several types, including engine hoists, gantry cranes, and overhead cranes. Engine hoists are portable and have a hydraulic mechanism, while gantry cranes are typically stationary with adjustable heights.
3. What should I consider when choosing a garage crane?
Consider the weight capacity, lifting height, and the specific type of tasks you’ll be performing. Ensure the crane’s specifications match your requirements and that your garage has adequate space for its operation.
4. How much weight can a garage crane lift?
Weight capacities vary widely. Smaller engine hoists may lift up to 2 tons, while larger gantry cranes can lift several tons. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications.
5. How do you safely operate a garage crane?
Read the user manual thoroughly, follow all safety guidelines, inspect the crane before use, and never exceed the maximum weight capacity. Use proper lifting techniques and ensure the load is securely attached.
6. Do garage cranes require maintenance?
Yes, regular maintenance is essential. This includes checking for wear and tear, lubricating moving parts, and ensuring that all bolts and connections are secure. Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule.
7. Can I assemble the garage crane myself?
Most garage cranes come with detailed instructions, making self-assembly possible. However, if you’re not confident or the crane is particularly complex, consider professional assembly.
8. Where can I purchase a garage crane?
Garage cranes can be purchased at hardware stores, specialty equipment retailers, and online marketplaces. Make sure to buy from a reputable source to ensure quality and warranty support.
9. What are the storage requirements for a garage crane?
Garage cranes should be stored in a dry, secure area. Some are portable and can be folded for easier storage. Ensure the crane is clean and free from contaminants before storing.
10. How much do garage cranes cost?
Prices vary based on type, capacity, and brand. Smaller engine hoists may start around $200, while larger, more sophisticated models can cost several thousand dollars.
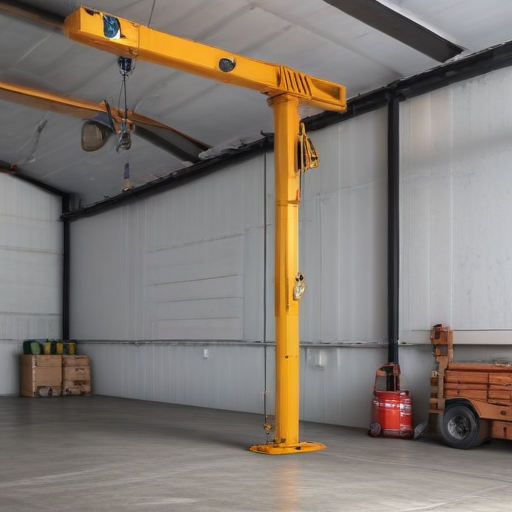

Top 10 FAQ with answer about garage crane for Buyer Sourcing from China
1. What is a garage crane?
– A garage crane is a lifting device used in garages and workshops to move heavy objects such as engines, transmissions, and other sizable components. They come in various forms like engine hoists, shop cranes, and gantry cranes.
2. What types of garage cranes are available?
– Options include hydraulic engine hoists, electric shop cranes, portable gantry cranes, and jib cranes. Each type serves different lifting needs and space constraints.
3. What is the lifting capacity of a typical garage crane?
– Lifting capacities range from 1 ton (2,000 lbs) to 3 tons (6,000 lbs) based on the crane type and model. Always verify the required capacity to ensure safety and efficiency.
4. What safety features should I look for?
– Look for features such as overload protection, secure locking mechanisms, stabilizing bases or legs, and robust construction. These features help prevent accidents and ensure the crane operates smoothly.
5. What is the average cost of a garage crane sourced from China?
– Prices vary widely depending on the type and capacity, ranging from $100 for basic models to over $1,000 for more advanced, high-capacity cranes. Shipping and customs duties may also influence the cost.
6. What certifications should a quality garage crane have?
– Ensure the crane complies with international safety standards such as CE (Conformité Européenne), ISO 9001, and other relevant industrial certifications. These guarantee quality and safety.
7. How long is the delivery time from China?
– Delivery time typically ranges from 20 to 45 days, depending on the manufacturer, custom procedures, and shipping method. Delays could occur, so plan accordingly.
8. What are the shipping costs?
– Shipping costs vary by weight, dimensions, and shipping method (sea freight or air freight). It’s essential to get a quote from the manufacturer or freight forwarder for accurate estimates.
9. Do Chinese manufacturers offer warranties and after-sales service?
– Reputable manufacturers generally provide a warranty period ranging from 1 to 3 years. Clarify the terms of the warranty and after-sales services, including spare parts availability and technical support.
10. How do I verify the reliability of a Chinese supplier?
– Check the supplier’s credentials, ask for customer references, read reviews, and consider using sourcing platforms like Alibaba or Made-in-China, which offer buyer protection services. Verification methods such as on-site factory audits can also ensure reliability.





