Here are the top 10 frequently asked questions about indoor crane applications, types, manufacturing processes, and more, along with their answers:
1. What types of indoor cranes are commonly used in manufacturing facilities?
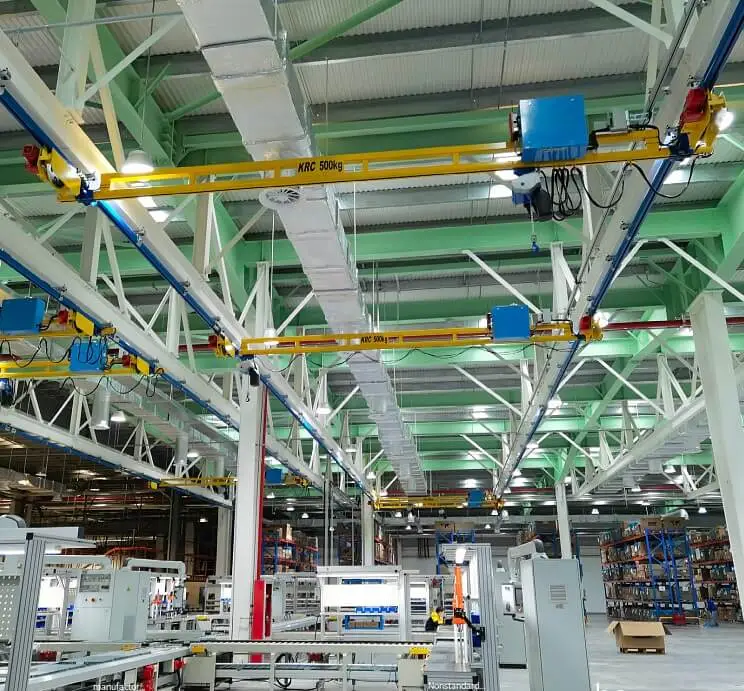
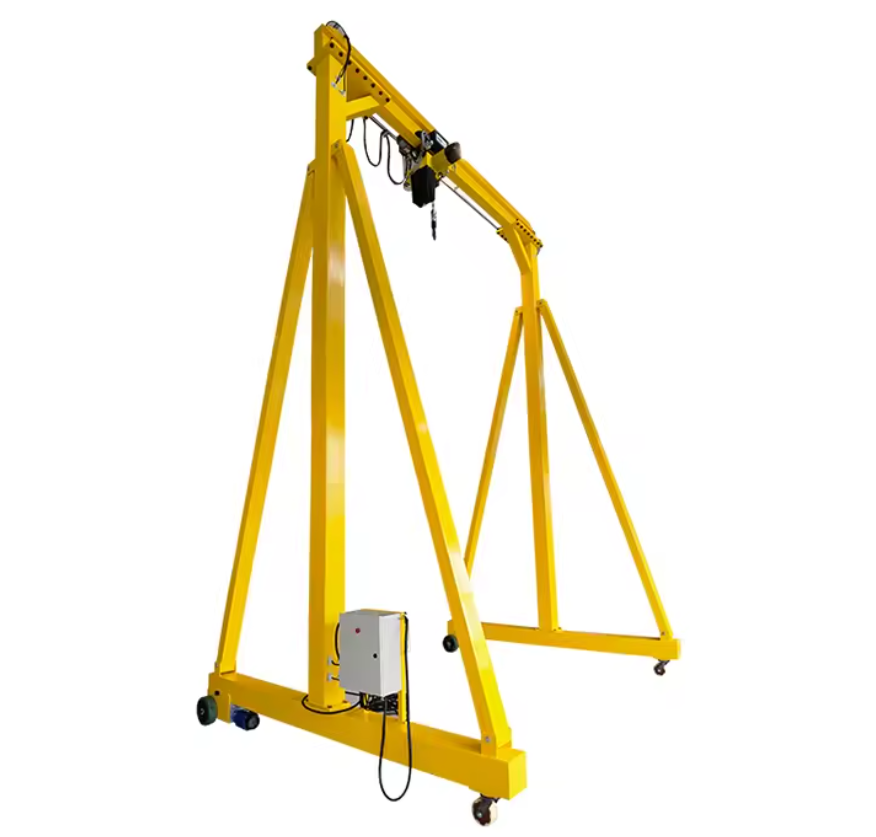
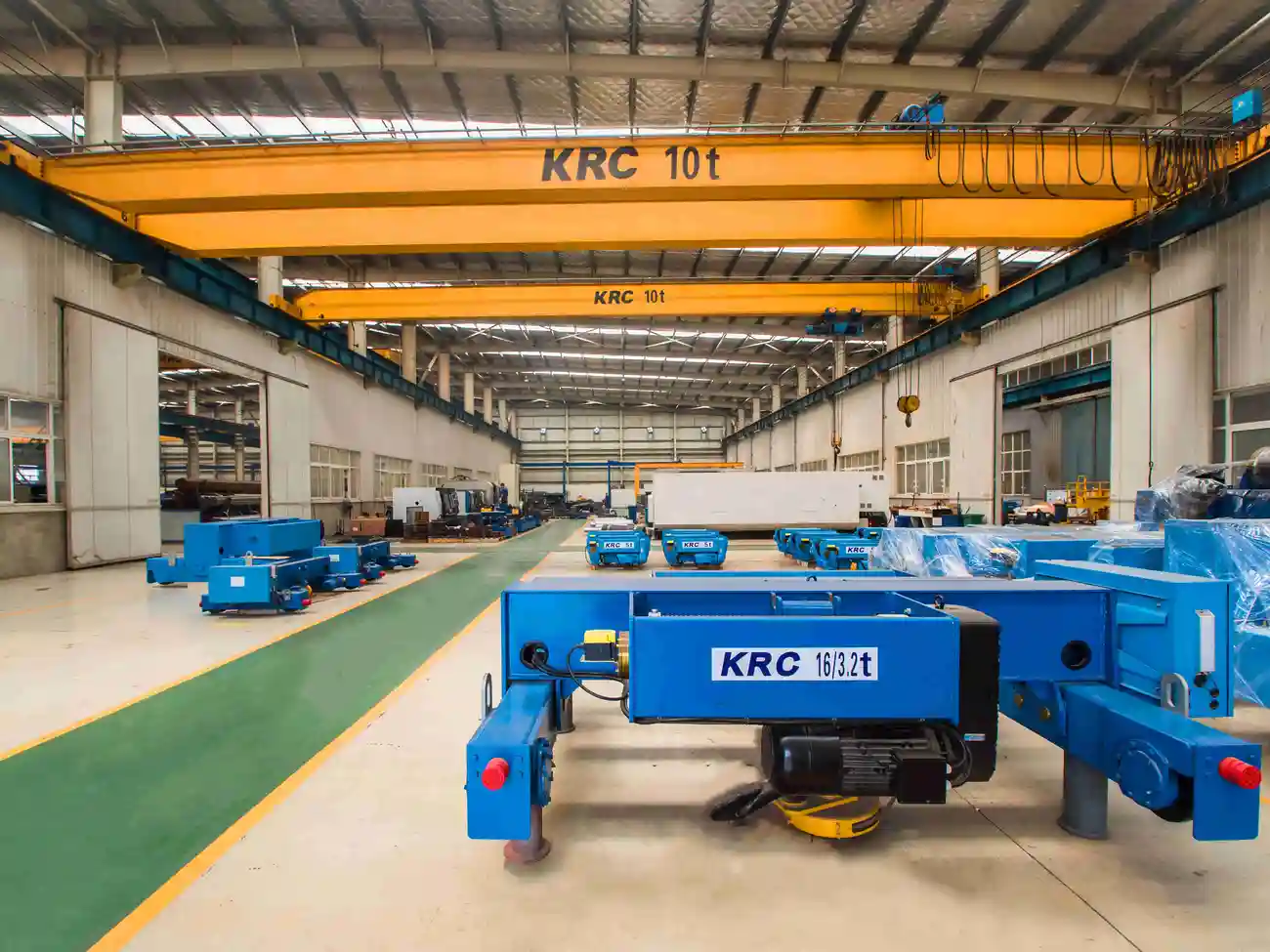
Answer: Common types of indoor cranes used in manufacturing include overhead bridge cranes, jib cranes, gantry cranes, and monorail cranes. Each type serves different purposes based on the layout and requirements of the facility.
2. How do I determine the right crane capacity for my application?
Answer: To determine the right crane capacity, assess the maximum weight of loads you plan to lift, including the weight of any rigging or lifting attachments. It’s advisable to choose a crane with a capacity slightly higher than the maximum load to ensure safety and longevity of the crane.
3. What safety features should I consider when installing an indoor crane?
Answer: Important safety features for indoor cranes include overload protection, emergency stop buttons, limit switches to prevent over-travel, and anti-collision devices if multiple cranes operate in the same space. Regular inspections and maintenance are also crucial for safety.
4. Can indoor cranes be customized for specific industrial applications?
Answer: Yes, indoor cranes can be highly customized with various hoists, trolleys, beam sizes, and control options to meet specific operational needs. Manufacturers often work closely with clients to tailor cranes to specific applications and environments.
5. What are the maintenance requirements for indoor cranes?
Answer: Maintenance requirements for indoor cranes include regular inspections of mechanical and electrical components, lubrication of moving parts, checking wire ropes and chains for wear, and ensuring all safety devices are functional. Maintenance schedules can vary based on the crane’s usage and environment.
6. How does the installation environment affect the choice of an indoor crane?
Answer: The installation environment influences the choice of crane type, material, and protective coatings. Factors such as ceiling height, floor space, ambient conditions (like temperature and humidity), and the presence of corrosive substances can dictate the specifications of the crane.
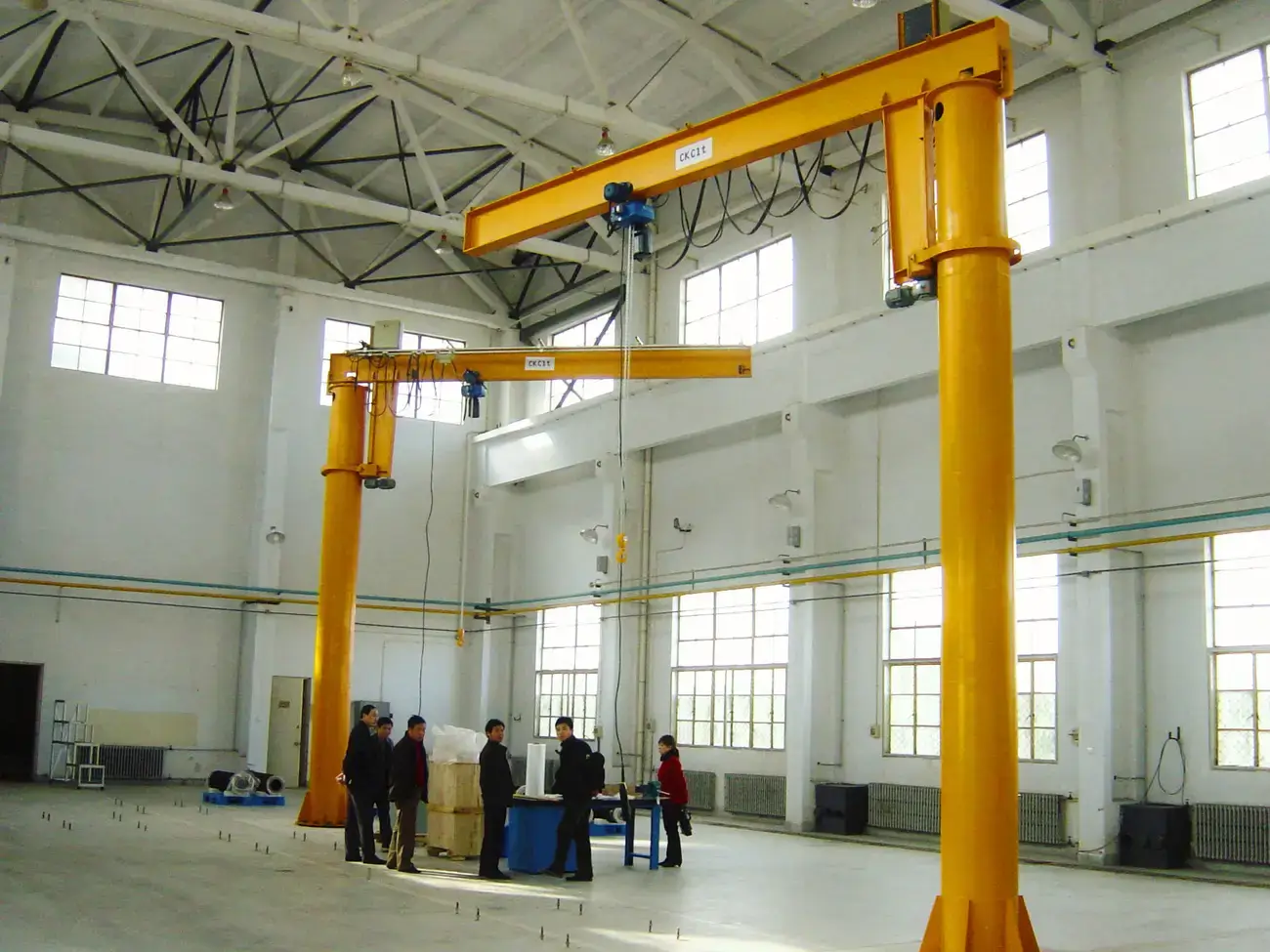
7. What are the advantages of using a jib crane in workshops?
Answer: Jib cranes offer high maneuverability and efficient use of space, making them ideal for workshops where materials need to be lifted and moved within a limited area. They are relatively simple to install and can be mounted on walls or floors.
8. How does an overhead crane differ from a gantry crane?
Answer: Overhead cranes are typically mounted on fixed structures and run along a rail or beam at a higher elevation within a facility. Gantry cranes, on the other hand, are supported by legs and move on wheels, making them more flexible and suitable for operations where overhead installations are not feasible.
9. What training is required for indoor crane operators?
Answer: Crane operators must undergo specific training to handle different types of cranes, focusing on operational techniques, safety protocols, and emergency procedures. This training is crucial for compliance with occupational health and safety regulations.
10. How do telescopic cranes function within confined spaces?
Answer: Telescopic cranes have booms that extend and retract to adjust their length, allowing them to operate in confined spaces. This feature makes them particularly useful in indoor environments where space is limited and precision handling is required.
These FAQs cover a range of topics that help in understanding the complexities and requirements when considering the deployment of cranes in indoor environments.