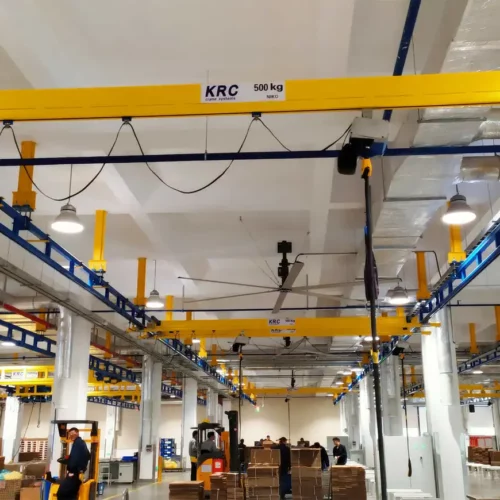
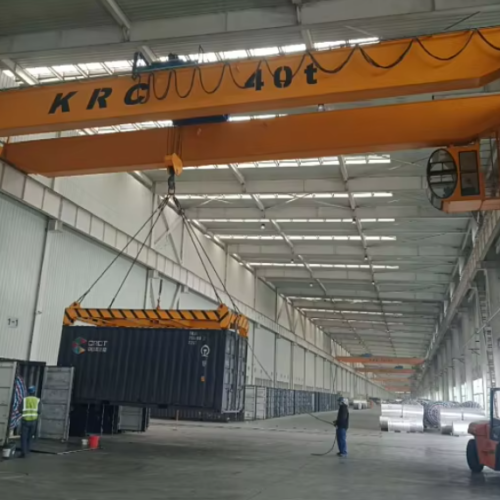
12 types of crane Safety Certifications
Sure, here’s a brief overview of 12 types of crane safety certifications:
1. OSHA Crane Operator Certification: Ensures operators meet Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards for crane operation.
2. NCCCO (National Commission for the Certification of Crane Operators): Offers certification for various types of cranes, including mobile, tower, and overhead cranes.
3. CIC (Crane Institute Certification): Provides certification for crane operators, riggers, and signalpersons with a focus on practical and written exams.
4. NCCER (National Center for Construction Education and Research): Offers crane operator certification that includes written and practical exams.
5. CPCS (Construction Plant Competence Scheme): UK-based certification that includes a Red Trained Operator Card and a Blue Competent Operator Card.
6. API (American Petroleum Institute) RP 2D Certification: Specific to offshore crane operators, ensuring safety and competence in the oil and gas industry.
7. TÜV SÜD Crane Operator Certification: An internationally recognized certification focusing on safety and operational efficiency.
8. ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) B30.5 Certification: Certification aligning with ASME standards for mobile and locomotive cranes.
9. Lifting Equipment Engineers Association (LEEA) Certification: Provides training and certification for various lifting equipment, including cranes.
10. ISO 23813:2007 Certification: International certification for the competence of crane operators.
11. IPAF (International Powered Access Federation) Certification: Certification for operators of powered access equipment, including mobile cranes.
12. CITB (Construction Industry Training Board) Certification: Offers a range of training and certification options for crane operators in the construction industry.
These certifications ensure that crane operators are skilled, knowledgeable, and compliant with safety standards, reducing the risk of accidents and improving overall site safety.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “12 types of crane”
Certainly! Here are the reference technical parameters for 12 types of cranes, summarized concisely:
1. Tower Crane:
– Max Load: 20 tons
– Max Height: 265 feet
– Max Jib Length: 230 feet
2. Mobile Crane:
– Max Load: 1,200 tons
– Boom Length: 200 feet
– Travel Speed: 40-60 mph
3. Rough Terrain Crane:
– Max Load: 150 tons
– Boom Length: 160 feet
– Max Speed: 25 mph
4. Crawler Crane:
– Max Load: 3,500 tons
– Boom Length: 300 feet
– Movement Speed: 1-2 mph
5. All Terrain Crane:
– Max Load: 1,200 tons
– Boom Length: 220 feet
– Max Speed: 50 mph
6. Truck-Mounted Crane:
– Max Load: 1,300 tons
– Boom Length: 250 feet
– Max Speed: 55 mph
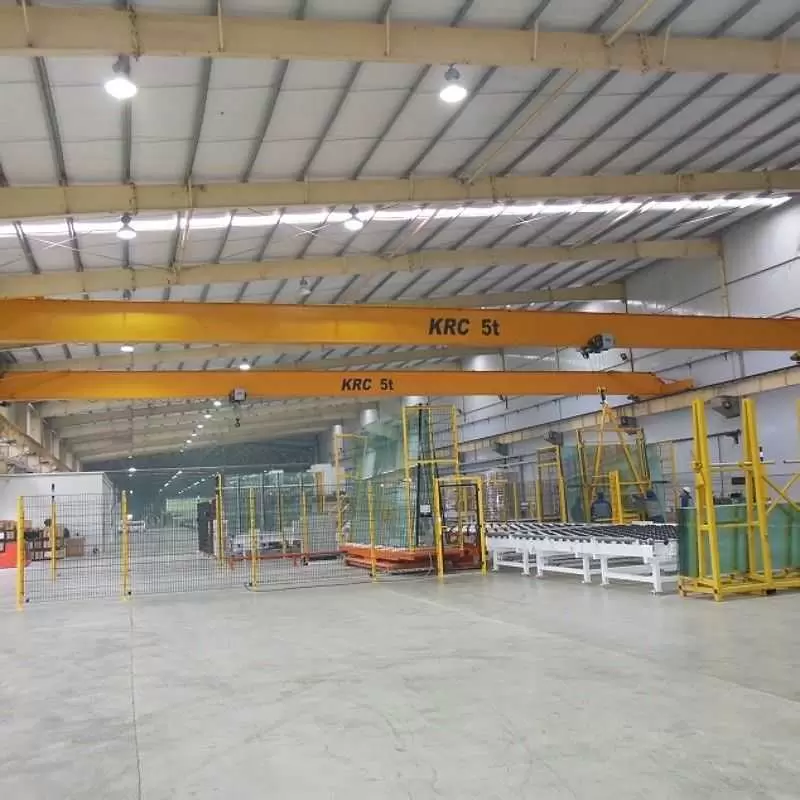
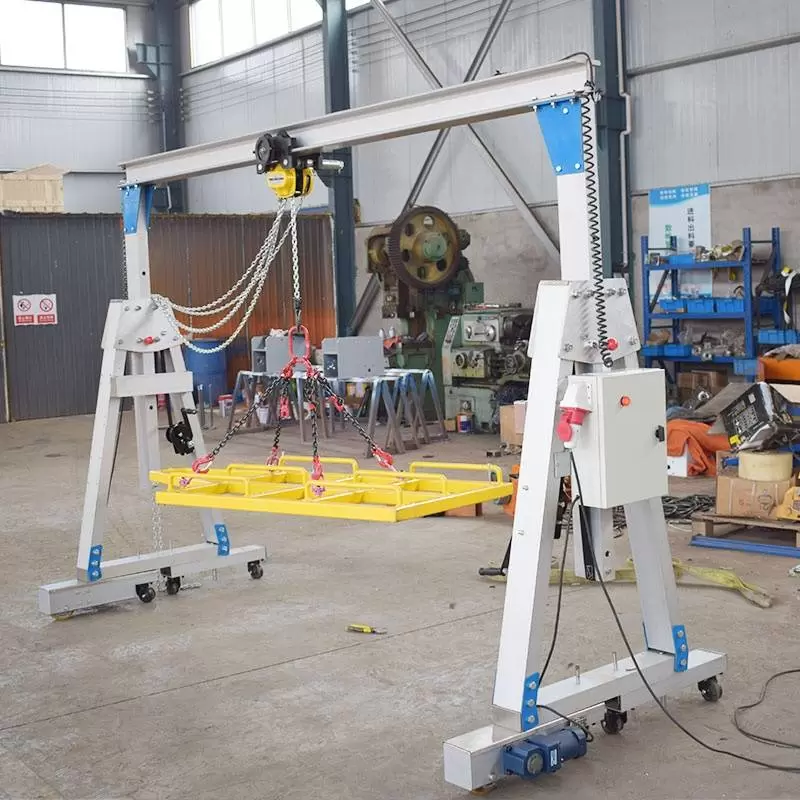
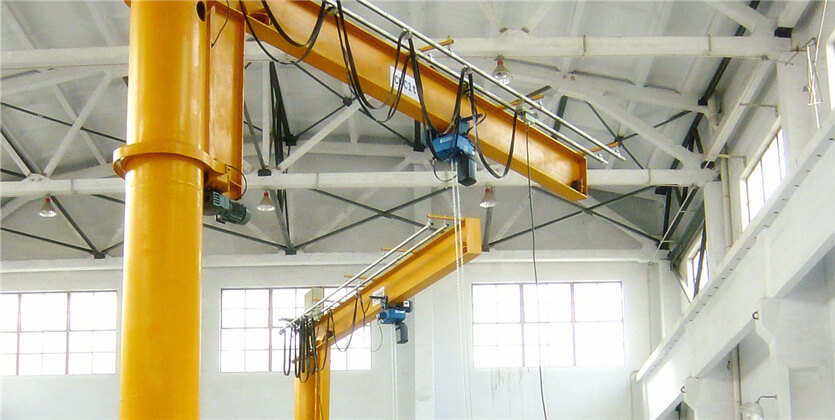
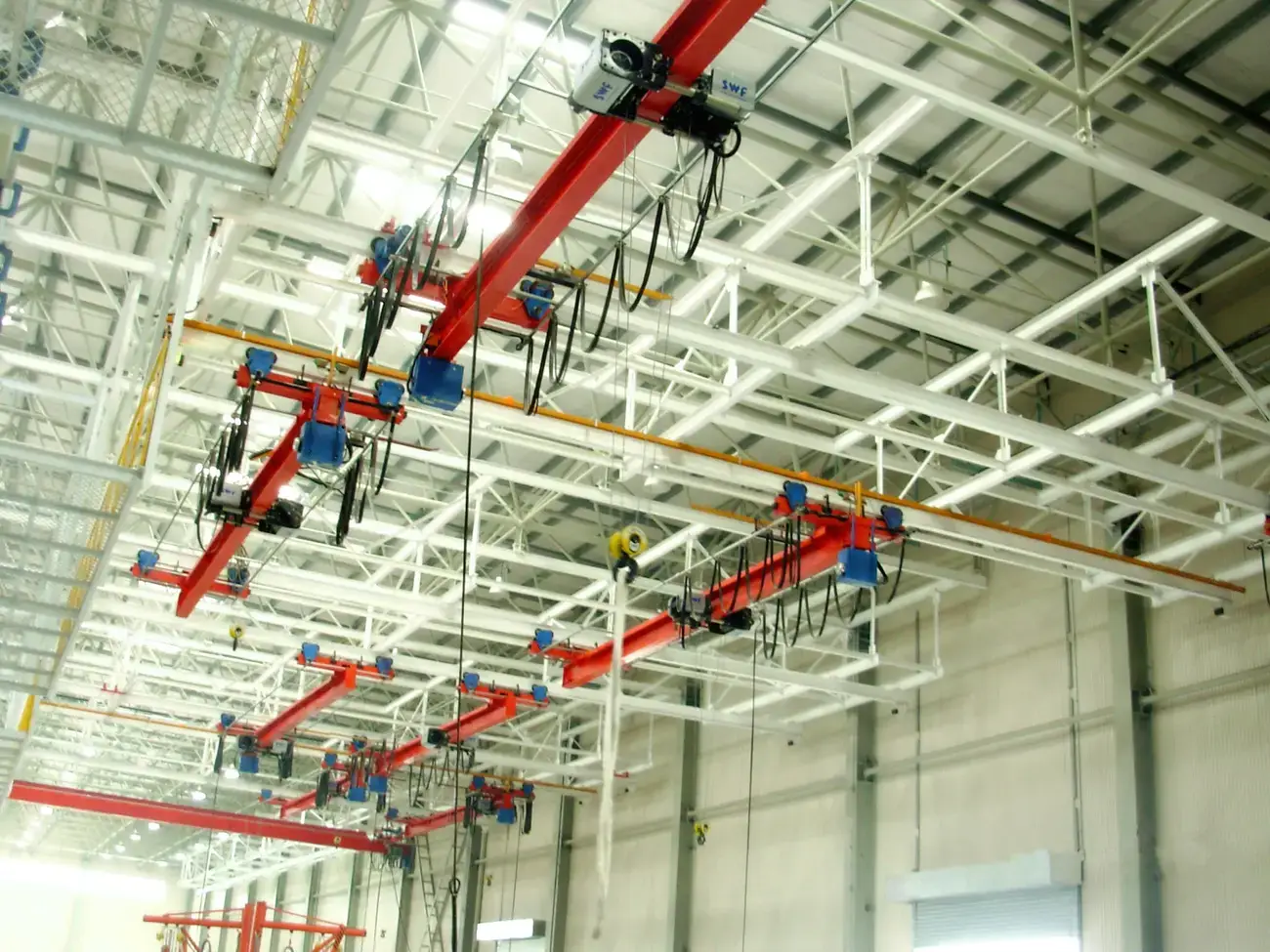
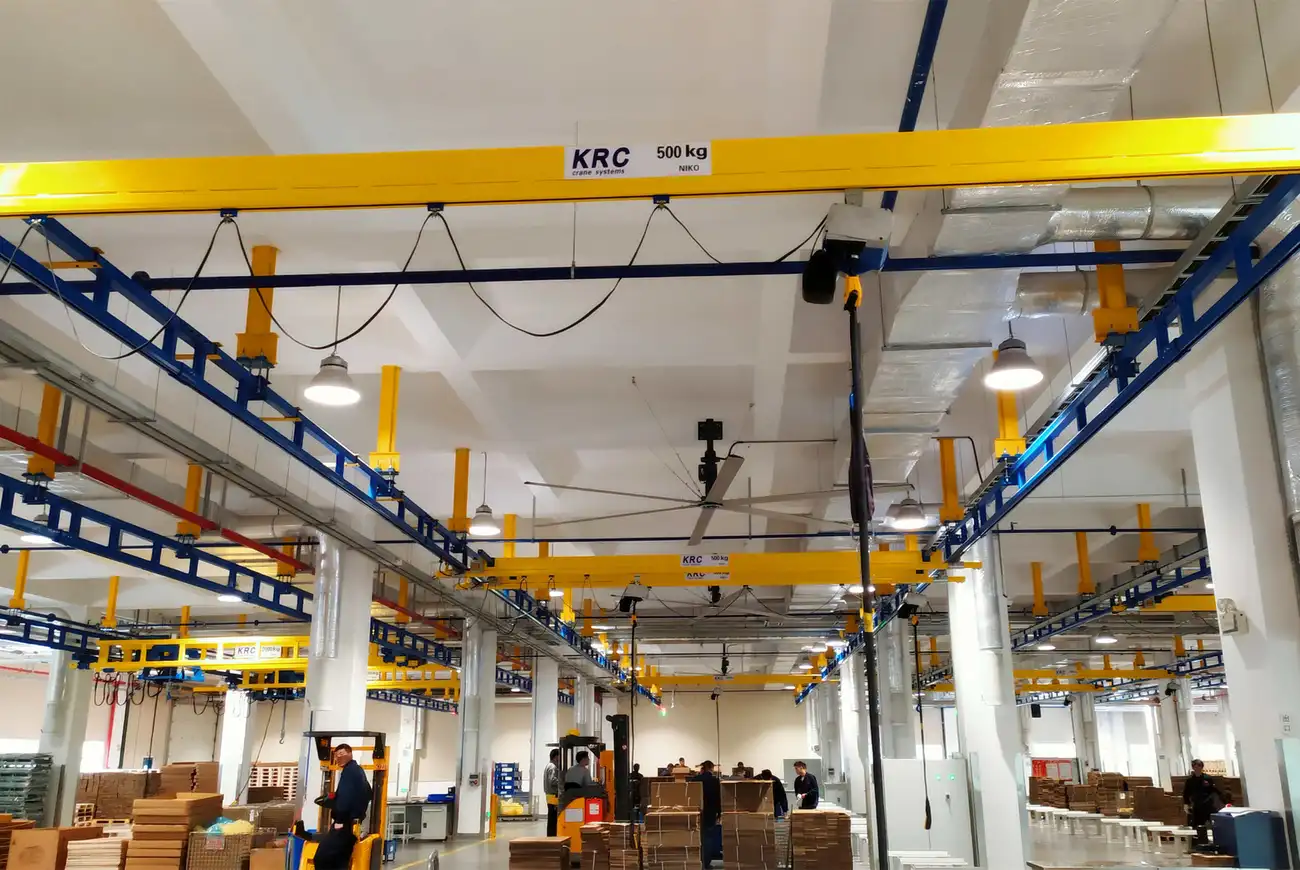
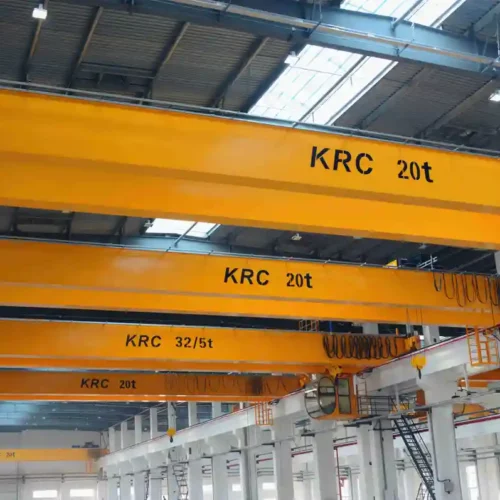
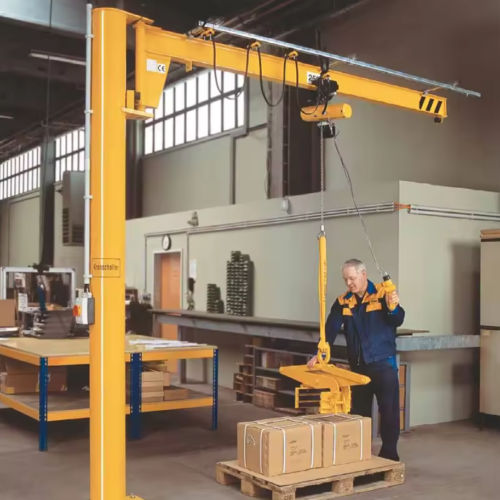
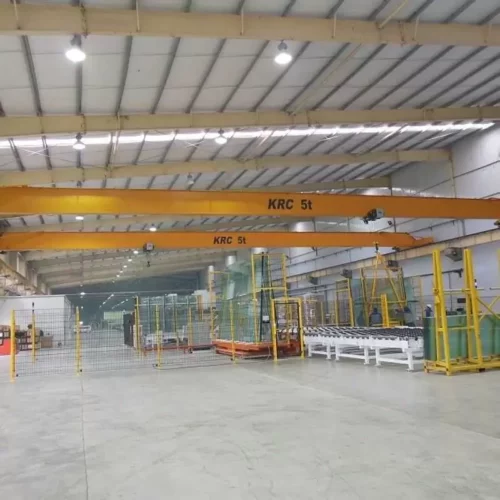
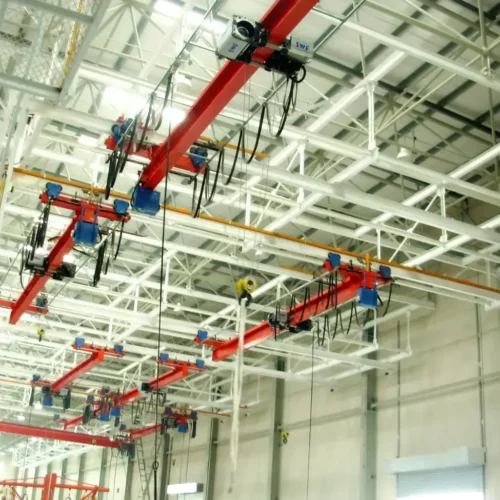
7. Overhead Crane:
– Max Load: 100 tons
– Span: 100 feet
– Lift Height: 50 feet
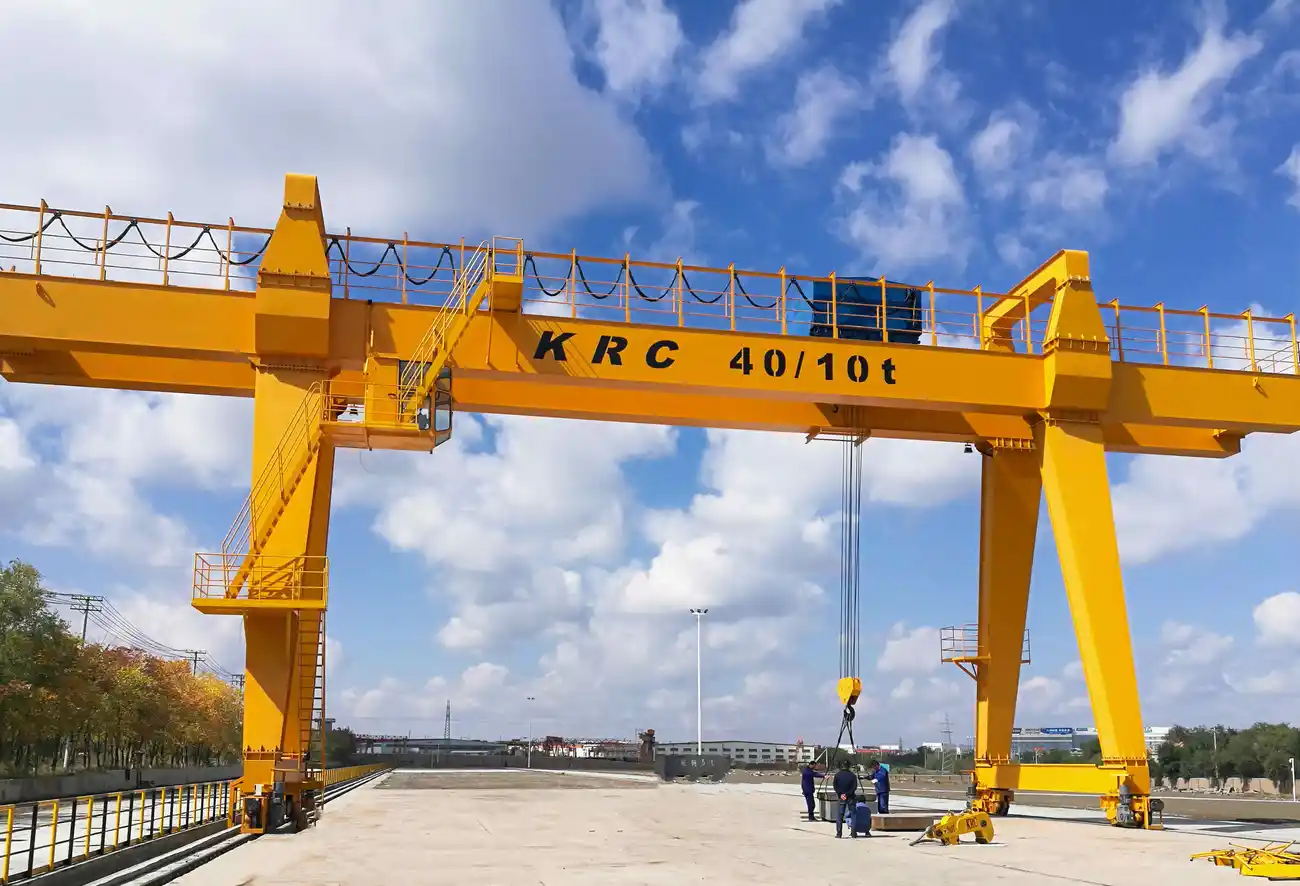
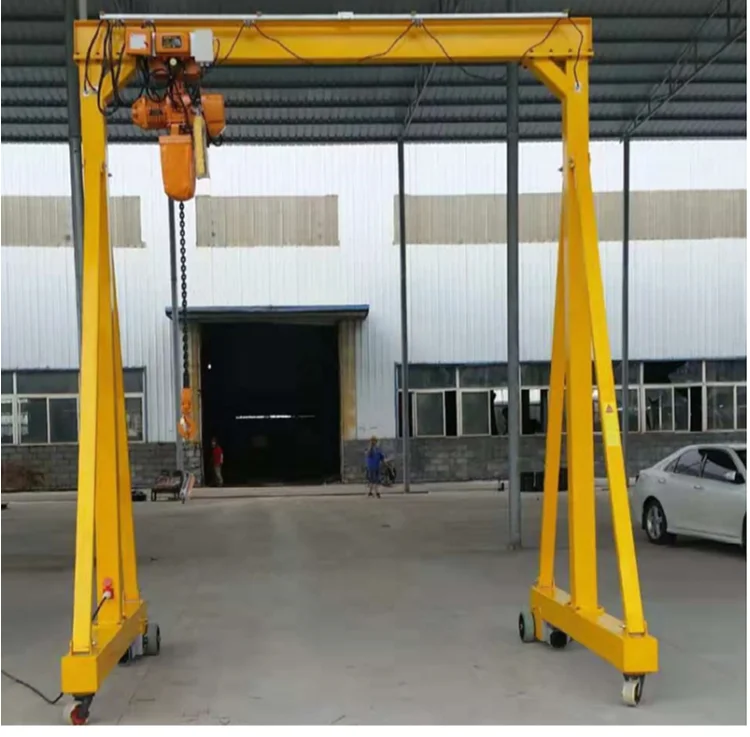
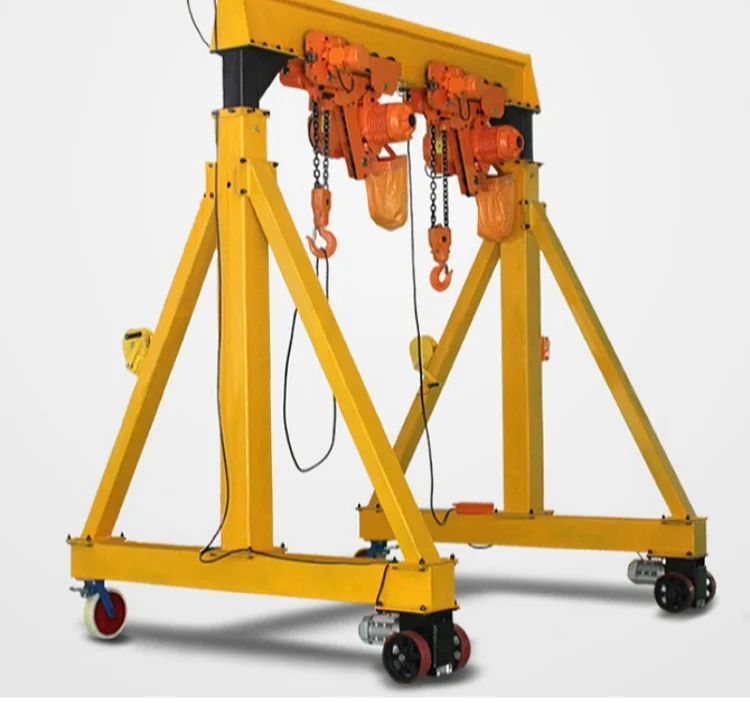
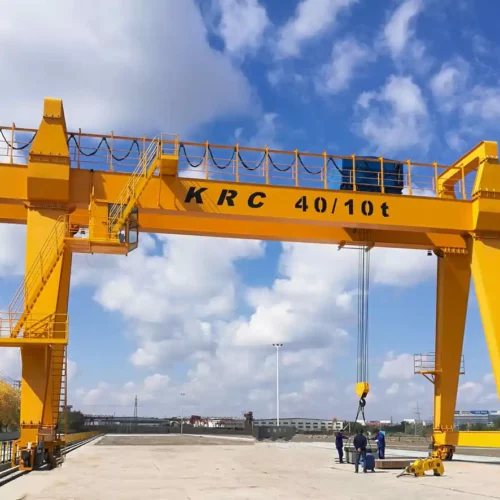
8. Gantry Crane:
– Max Load: 900 tons
– Span: 150 feet
– Lift Height: 60 feet
9. Floating Crane:
– Max Load: 10,000 tons
– Boom Length: 200 feet
– Draft: 30 feet
10. Telescopic Crane:
– Max Load: 1,200 tons
– Boom Length: 200 feet
– Sections: 4-5
11. Hammerhead Crane:
– Max Load: 350 tons
– Max Height: 100 feet
– Max Jib Length: 250 feet
12. Level Luffing Crane:
– Max Load: 100 tons
– Boom Length: 200 feet
– Luffing Speed: 10 feet/min
These parameters cover the essential technical aspects such as maximum load capacity, boom or jib length, and operational heights, providing a clear snapshot of the capabilities of each crane type.

List Product features of “12 types of crane”
Product Features of “12 Types of Crane”
1. Tower Crane
– Height: Reaches up to 265 feet.
– Lifting Capacity: Can lift up to 20 tons.
– Usage: Ideal for constructing tall buildings.
2. Mobile Crane
– Versatility: Easily moved to different locations.
– Lifting Capacity: Typically lifts 10 to 60 tons.
– Usage: Suitable for various construction tasks.
3. Crawler Crane
– Mobility: Tracks allow movement on rough terrain.
– Lifting Capacity: Can lift up to 3,500 tons.
– Usage: Heavy lifting in large construction projects.
4. Rough Terrain Crane
– Mobility: Designed for off-road sites.
– Lifting Capacity: Generally lifts up to 150 tons.
– Usage: Construction sites with uneven ground.
5. All Terrain Crane
– Versatility: Suitable for both off-road and paved surfaces.
– Lifting Capacity: Can lift up to 1,200 tons.
– Usage: Multi-purpose construction projects.
6. Truck-mounted Crane
– Mobility: Easily transported on highways.
– Lifting Capacity: Typically lifts up to 1,300 tons.
– Usage: Quick setup and use in various sites.
7. Floating Crane
– Specialty: Operates on water.
– Lifting Capacity: Can lift up to 10,000 tons.
– Usage: Ports and shipbuilding.
8. Overhead Crane
– Precision: Operates on a fixed rail system.
– Lifting Capacity: Usually lifts up to 20 tons.
– Usage: Factories and warehouses.
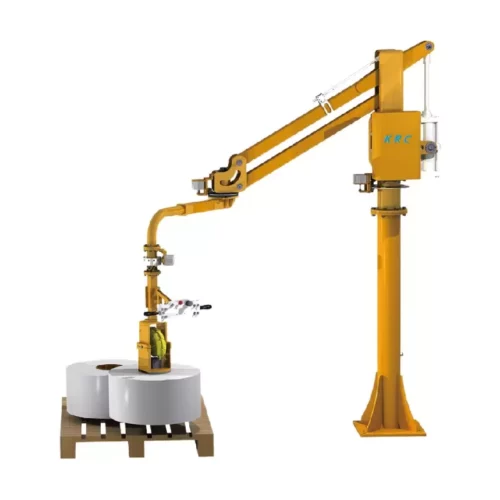
9. Loader Crane
– Compactness: Mounted on a truck.
– Lifting Capacity: Lifts up to 200 tons.
– Usage: Loading and unloading cargo.
10. Gantry Crane
– Structure: Supported by freestanding legs.
– Lifting Capacity: Lifts up to 900 tons.
– Usage: Shipyards and outdoor yards.
11. Deck Crane
– Placement: Installed on ships.
– Lifting Capacity: Can lift up to 30 tons.
– Usage: Loading and unloading cargo at sea.
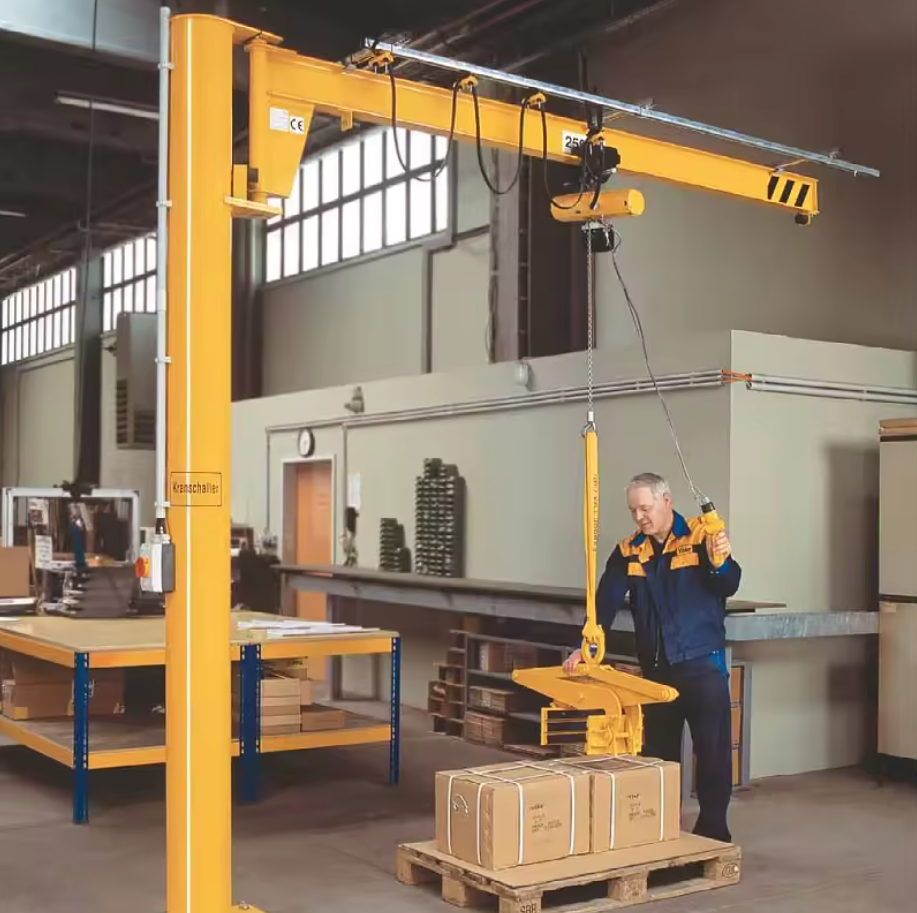
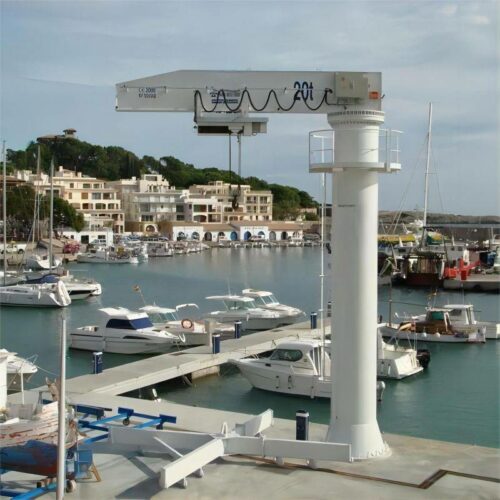
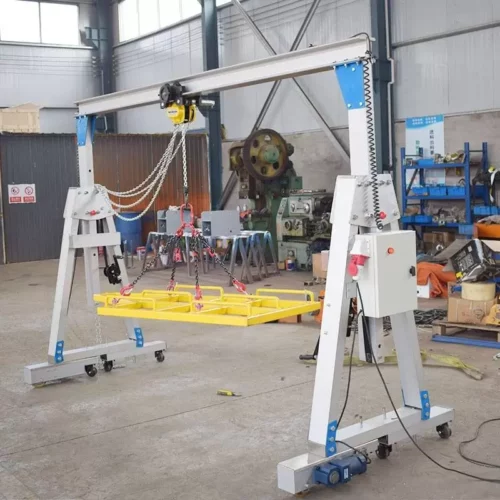
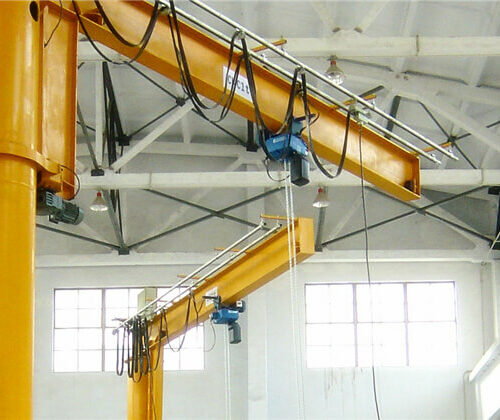
12. Jib Crane
– Flexibility: Rotating arm for specific areas.
– Lifting Capacity: Lifts up to 15 tons.
– Usage: Workshops and manufacturing floors.
These cranes vary in their mobility, lifting capacities, and specific applications, ensuring the right equipment for different construction needs.

List Various Types of “12 types of crane”
Sure! Here are twelve different types of cranes, focusing on their distinct features and applications:
1. Tower Crane: These are fixed to the ground on a concrete slab and are commonly used in the construction of tall buildings. They offer excellent height and lifting capabilities.
2. Mobile Crane: Versatile and flexible, mobile cranes can be transported to different sites. They come with various attachments, making them suitable for multiple lifting tasks.
3. Truck-Mounted Crane: Mounted on a truck, these cranes can travel on highways, providing easy mobility to and from job sites. They are used for various construction and transport tasks.
4. Rough Terrain Crane: Built for off-road applications, rough terrain cranes are equipped with large tires and four-wheel drive, making them ideal for construction sites with difficult terrains.
5. All-Terrain Crane: Combining the roadability of truck-mounted cranes with the off-road capability of rough terrain cranes, these are versatile for various job sites.
6. Crawler Crane: Mounted on tracks, crawler cranes offer excellent stability and are used for heavy lifting tasks, particularly on soft ground.
7. Floating Crane: These cranes are mounted on barges and are used for construction and maintenance work in ports, bridges, and offshore projects.
8. Gantry Crane: With a bridge supported by legs that move on wheels or along a track, gantry cranes are often used in shipyards, rail yards, and industrial plants.
9. Overhead Crane: Also known as a bridge crane, this type runs on elevated tracks along the facility’s ceiling, commonly used in manufacturing and assembly plants.
10. Loader Crane: These are hydraulic cranes fitted to trucks, used for loading and unloading cargo. They are compact and highly maneuverable.
11. Telescopic Crane: Featuring a boom with multiple sections that can extend and retract, telescopic cranes are used for lifting operations where varying boom lengths are required.
12. Hammerhead Crane: These have a horizontal, swiveling lever that rests on a fixed tower. They are used in shipbuilding and other heavy-duty industrial applications.
These cranes each serve unique purposes across various industries, enhancing efficiency and capability in lifting and transporting heavy loads.

List Application of “12 types of crane”
Sure, here’s a list of applications for 12 different types of cranes:
1. Mobile Cranes:
– Construction sites for lifting heavy materials.
– Maintenance tasks in urban areas where space is limited.
2. Tower Cranes:
– High-rise building construction for moving large and heavy materials.
– Used in assembling large structures like bridges.
3. Rough Terrain Cranes:
– Construction projects on uneven or rough terrain.
– Oil refineries and power plants for equipment maintenance.
4. Crawler Cranes:
– Heavy-duty construction tasks, such as bridge building and wind farm construction.
– Handling large-scale infrastructure projects.
5. All-Terrain Cranes:
– Versatile use in various terrains for construction and maintenance.
– Used in rescue operations and disaster relief.
6. Overhead Cranes:
– Factories and warehouses for moving heavy materials along a fixed path.
– Used in steel and automobile manufacturing plants.
7. Gantry Cranes:
– Shipyards for loading and unloading ships.
– Container terminals for moving containers efficiently.
8. Floating Cranes:
– Offshore construction projects, such as building oil rigs.
– Salvage operations for sunken ships and large underwater objects.
9. Railroad Cranes:
– Railway construction and maintenance.
– Used for lifting and placing railway tracks.
10. Loader Cranes:
– Transport and delivery trucks for loading and unloading goods.
– Used in forestry to load logs onto transport vehicles.
11. Stacker Cranes:
– Automated warehouses for storing and retrieving items efficiently.
– Distribution centers to streamline logistics operations.
12. Telescopic Cranes:
– Rescue missions and emergency services to reach high or difficult locations.
– Construction and maintenance of power lines and wind turbines.
These applications highlight the versatility and specialized use of different crane types across various industries, making them indispensable tools for construction, manufacturing, logistics, and emergency operations.

List Buyer Types of “12 types of crane”
Here are the buyer types for the “12 types of cranes”:
1. Mobile Cranes:
– Construction Companies: For flexible lifting on varied sites.
– Rental Services: To provide short-term lifting solutions.
2. Tower Cranes:
– High-Rise Builders: For skyscraper and tall building projects.
– Urban Developers: To support dense city construction.
3. Overhead Cranes:
– Manufacturing Plants: For material handling within production lines.
– Warehouses: To move heavy inventory efficiently.
4. Gantry Cranes:
– Shipyards: For loading and unloading ships.
– Rail Yards: To handle cargo containers and heavy materials.
5. Loader Cranes:
– Logistics Companies: For loading and unloading goods from trucks.
– Forestry Operations: To handle logs and timber.
6. Jib Cranes:
– Workshops: For localized lifting tasks.
– Repair Shops: To move heavy equipment and parts.
7. Floating Cranes:
– Port Authorities: For harbor construction and maintenance.
– Marine Salvage Companies: For underwater recovery operations.
8. Crawler Cranes:
– Large Construction Firms: For heavy-duty lifting on difficult terrains.
– Mining Operations: To move heavy materials in open pits.
9. Rough Terrain Cranes:
– Oil & Gas Companies: For rugged and remote site lifting.
– Construction Firms: For off-road construction sites.
10. All Terrain Cranes:
– Infrastructure Builders: For versatile lifting across varied environments.
– Utility Companies: To maintain power lines and facilities.
11. Telescopic Cranes:
– Rescue Operations: For reach in emergency situations.
– Construction Companies: For projects needing adjustable height.
12. Aerial Cranes (Helicopter Cranes):
– Disaster Relief Agencies: For remote area access and aid delivery.
– Forestry Departments: For firefighting and timber lifting.
These buyer types leverage the specific capabilities of each crane type to meet their operational needs and project requirements.

List “12 types of crane” Project Types for Different Industries
Sure, here are 12 types of cranes used across different industries, explained concisely:
1. Tower Cranes: Predominantly used in the construction of tall buildings. These cranes offer height and lifting capacity, making them essential for high-rise projects.
2. Mobile Cranes: Versatile and able to move around the site. Used in various construction projects, maintenance tasks, and transportation of heavy materials.
3. Crawler Cranes: Equipped with tracks, they provide stability and can move on soft ground. Ideal for large-scale construction and heavy lifting tasks in diverse terrains.
4. Overhead Cranes: Also known as bridge cranes, these are used in manufacturing and assembly lines. They are perfect for lifting heavy loads across a fixed path.
5. Gantry Cranes: Similar to overhead cranes but supported by freestanding legs. Commonly used in shipyards, rail yards, and large outdoor manufacturing areas.
6. Floating Cranes: Mounted on barges, these cranes are used for marine construction, salvage operations, and loading/unloading ships.
7. Telescopic Cranes: Feature a boom with multiple sections that can extend. Used in short-term construction projects, logistics, and emergency situations for their ease of transport and setup.
8. Truck-Mounted Cranes: A crane mounted on a truck for easy mobility. Used for lifting tasks in urban construction projects and logistics.
9. Rough Terrain Cranes: Designed for off-road construction sites. These cranes have large tires and four-wheel drive to navigate difficult terrains.
10. Loader Cranes: Small cranes mounted on trailers or trucks. Used for loading and unloading goods, particularly in the transport and logistics industry.
11. Stacker Cranes: Employed in automated warehouses and distribution centers. These cranes move along aisles to retrieve and store goods efficiently.
12. Level Luffing Cranes: The jib arm remains level while it luffs (moves up and down). Typically used in shipbuilding and port operations for precise load positioning.
These diverse crane types serve specific purposes across various industries, enhancing efficiency and productivity in their respective domains.

12 types of crane Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Sure, here are 12 types of crane accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options:
1. Hooks and Lifting Attachments: Customized hooks and lifting devices to handle various load shapes and weights, ensuring safe and efficient lifting.
2. Spreader Beams: Adjustable and fixed spreader beams to distribute the load evenly, reducing stress on the lifting points.
3. Load Cells and Scales: Integrated load cells for accurate weight measurement and overload protection systems, ensuring safety and compliance with regulations.
4. Jib Extensions: Extendable jibs to increase the reach of the crane, allowing for more versatile handling of materials in confined spaces.
5. Remote Controls: Wireless remote control systems for better maneuverability and safety, enabling operators to control the crane from a distance.
6. Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): VFDs for smooth and precise control of crane movements, reducing wear and tear on mechanical components.
7. Anti-Collision Systems: Advanced sensors and software to prevent collisions between cranes or with other objects, enhancing workplace safety.
8. Cameras and Monitoring Systems: High-definition cameras and monitoring systems for better visibility of the load and surrounding area, improving operational accuracy and safety.
9. Operator Cabs: Ergonomically designed operator cabs with climate control and enhanced visibility for improved operator comfort and efficiency.
10. Power Supply Systems: Custom power supply options like festoon systems, conductor bars, and battery packs to suit various operational environments.
11. Specialty Slings: Custom-designed slings made from materials like nylon, wire rope, or chain, tailored to handle specific types of loads and lifting conditions.
12. Automation and Smart Features: Integration of IoT and automation technologies for remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized operational efficiency.
These accessories and upgrades enhance the functionality, safety, and efficiency of cranes, allowing for tailored solutions to meet specific industrial needs.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “12 types of crane”
Quality Control in Crane Manufacturing
1. Material Inspection: Raw materials are inspected for quality, ensuring they meet the specified standards. This includes checking for defects, verifying certifications, and testing mechanical properties.
2. Precision Machining: Components are machined with high precision to meet design specifications. This involves CNC machining, grinding, and other techniques to ensure accuracy and consistency.
3. Welding Quality: Welded joints are inspected using non-destructive testing (NDT) methods like ultrasonic testing, X-ray inspection, and dye penetrant testing to detect any flaws.
4. Assembly Verification: During assembly, components are checked for proper fit and alignment. Torque specifications are verified to ensure fasteners are correctly tightened.
5. Load Testing: Cranes undergo load testing to verify their lifting capacity. This includes static and dynamic tests to simulate operational conditions and ensure the crane can handle maximum loads safely.
6. Functional Testing: All operational functions, such as lifting, lowering, slewing, and travel, are tested. Controls, safety devices, and emergency systems are checked for proper operation.
7. Final Inspection: A comprehensive final inspection ensures all components and systems meet quality standards. Documentation and certification are reviewed, and any issues are addressed before delivery.
Manufacturing Process of 12 Types of Cranes
1. Mobile Cranes: Assembled on truck or crawler chassis; involves integrating hydraulic systems for mobility.
2. Tower Cranes: Erected on-site using sections transported separately; involves high-altitude assembly and rigging.
3. Overhead Cranes: Built with structural beams and runways; requires precise alignment of tracks and hoists.
4. Gantry Cranes: Similar to overhead cranes but supported by ground structures; involves heavy-duty fabrication and assembly.
5. Jib Cranes: Manufactured with a rotating arm fixed on a vertical mast; involves robust welding and machining.
6. Floating Cranes: Assembled on a floating platform; requires marine-grade materials and corrosion-resistant coatings.
7. Loader Cranes: Mounted on trucks for loading/unloading; involves compact design and hydraulic integration.
8. Rough Terrain Cranes: Built on off-road chassis; requires heavy-duty suspension and all-terrain tires.
9. Railroad Cranes: Mounted on railcars; involves specialized couplings and rail compatibility checks.
10. Telescopic Cranes: Feature extendable booms; involves precision hydraulic engineering.
11. Level Luffing Cranes: Designed for horizontal load movement; involves complex counterbalance systems.
12. Deck Cranes: Installed on ships; requires marine certification and weatherproofing measures.
Quality control and meticulous manufacturing processes ensure cranes are safe, reliable, and efficient for various applications.

How to use “12 types of crane”
Sure, here’s a concise guide on how to use the “12 types of crane”:
1. Overhead Crane
– Use: Move heavy loads horizontally in warehouses.
– Best For: Manufacturing and maintenance operations.
2. Mobile Crane
– Use: Transport and lift materials across job sites.
– Best For: Construction projects with varying locations.
3. Tower Crane
– Use: Construct tall buildings by lifting steel, concrete, and large tools.
– Best For: Skyscraper and high-rise building construction.
4. Truck-Mounted Crane
– Use: Quick setup and mobility for lifting heavy loads.
– Best For: Infrastructure projects and road construction.
5. Rough Terrain Crane
– Use: Lift materials on uneven or rough ground.
– Best For: Off-road construction and rough terrains.
6. Crawler Crane
– Use: Lift heavy materials with stability on soft grounds.
– Best For: Long-term projects on unpaved surfaces.
7. Floating Crane
– Use: Load and unload ships at docks or offshore construction.
– Best For: Marine construction and port operations.
8. Gantry Crane
– Use: Lift containers and heavy materials in open areas.
– Best For: Shipping yards and outdoor storage areas.
9. Telescopic Crane
– Use: Extend and retract to reach different heights.
– Best For: Precise lifting in urban environments.
10. Level Luffing Crane
– Use: Maintain a horizontal load while moving.
– Best For: Dockside unloading and shipbuilding.
11. Loader Crane
– Use: Load equipment onto trailers.
– Best For: Transportation and logistics.
12. Bulk-Handling Crane
– Use: Lift bulk materials like coal or minerals.
– Best For: Mining and material handling industries.
Each type of crane serves specific purposes, offering unique advantages based on the environment and the nature of the job. Selecting the appropriate crane ensures efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness in various industrial and construction applications.
“12 types of crane” Comparative Analysis
Certainly! Here’s a comparative analysis of 12 types of cranes, focusing on their key features and applications:
1. Tower Crane
– Use: Construction of tall buildings.
– Features: Fixed to the ground, has a long horizontal jib.
– Advantages: High lifting capacity and height reach.
2. Mobile Crane
– Use: Versatile, used in construction, transportation, and utilities.
– Features: Mounted on a truck, can travel on roads.
– Advantages: Easy to move and set up.
3. Rough Terrain Crane
– Use: Construction sites with uneven ground.
– Features: Mounted on four rubber tires, all-wheel drive.
– Advantages: Can operate on rough terrains.
4. Crawler Crane
– Use: Heavy lifting on construction sites.
– Features: Tracks for mobility on soft ground.
– Advantages: High stability and lifting capacity.
5. All-Terrain Crane
– Use: Diverse construction sites.
– Features: Combination of rough terrain and mobile crane features.
– Advantages: Versatile with high mobility.
6. Floating Crane
– Use: Harbor and offshore construction.
– Features: Mounted on a barge.
– Advantages: Can handle heavy loads over water.
7. Gantry Crane
– Use: Shipyards and large industrial sites.
– Features: Bridge-like structure on rails.
– Advantages: Can handle extremely heavy loads.
8. Overhead Crane
– Use: Factories and warehouses.
– Features: Fixed track, travels along the ceiling.
– Advantages: Efficient for indoor lifting.
9. Telescopic Crane
– Use: Various construction and transport applications.
– Features: Extendable boom.
– Advantages: Adjustable length, easy to transport.
10. Loader Crane
– Use: Loading and unloading goods.
– Features: Mounted on a trailer or truck.
– Advantages: Compact and versatile.
11. Aerial Crane (Helicopter)
– Use: Remote or inaccessible locations.
– Features: Suspended from a helicopter.
– Advantages: Can reach difficult locations.
12. Railroad Crane
– Use: Railroad maintenance.
– Features: Mounted on a railroad car.
– Advantages: Specialized for rail applications.
Comparative Insights
– Mobility: Mobile, rough terrain, all-terrain, and crawler cranes offer high mobility, with crawler cranes being excellent for soft ground stability.
– Height Reach: Tower cranes excel in height reach, making them ideal for skyscrapers.
– Load Capacity: Gantry and floating cranes handle the heaviest loads, essential for shipyards and offshore work.
– Versatility: All-terrain and mobile cranes provide versatility across different sites.
– Specialized Use: Floating, railroad, and aerial cranes are highly specialized for specific environments.
Each crane type has unique advantages, making them suitable for particular applications based on terrain, load requirements, and operational context.

“12 types of crane” Warranty and Support
12 Types of Crane: Warranty and Support
When purchasing a crane, understanding the warranty and support provided by manufacturers is crucial. Here’s a detailed look at the warranty and support for 12 common types of cranes:
1. Tower Crane: Typically, a 1-2 year warranty on parts and labor. Support includes on-site inspections and 24/7 customer service.
2. Mobile Crane: Often comes with a 1-year warranty. Manufacturers offer regular maintenance checks and emergency repair services.
3. Crawler Crane: A standard 1-2 year warranty. Support involves remote diagnostics and technical assistance.
4. Rough Terrain Crane: Usually a 1-year warranty. Includes training programs and preventive maintenance plans.
5. All-Terrain Crane: Standard warranty is 1-2 years. Comprehensive support with dedicated service teams and spare parts availability.
6. Overhead Crane: Generally, a 1-2 year warranty. Extensive support with periodic inspections and operator training.
7. Gantry Crane: Comes with a 1-year warranty. Support includes installation assistance and regular service visits.
8. Jib Crane: Typically has a 1-year warranty. Manufacturers provide technical support and routine maintenance services.
9. Floating Crane: Warranty varies from 1-2 years. Support features on-site service and specialized training for operators.
10. Railroad Crane: Usually a 1-year warranty. Includes on-call support and maintenance scheduling.
11. Deck Crane: Standard 1-year warranty. Comprehensive support with emergency repair services and technical consultations.
12. Telescopic Crane: Typically comes with a 1-2 year warranty. Support includes troubleshooting and regular maintenance checks.
General Support Highlights:
– Technical Support: 24/7 availability for troubleshooting and assistance.
– Maintenance: Scheduled inspections and preventive maintenance.
– Training: Operator training programs and safety certifications.
– Spare Parts: Quick access to genuine spare parts and components.
Always check with the manufacturer for specific warranty terms and support services to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your crane.

List “12 types of crane” FAQ
Sure! Here are FAQs about 12 types of cranes commonly used in construction and other industries:
1. Tower Crane
Q: What is a tower crane?
A: A tall, fixed crane often used in the construction of tall buildings. It has a long horizontal jib for lifting materials to great heights.
2. Mobile Crane
Q: What defines a mobile crane?
A: A versatile crane mounted on a mobile platform, such as a truck, allowing it to travel to different job sites easily.
3. Crawler Crane
Q: How does a crawler crane operate?
A: It moves on tracks (crawlers) and is known for its stability and ability to lift heavy loads on rough terrain.
4. Rough Terrain Crane
Q: Where is a rough terrain crane used?
A: Designed for off-road applications, this crane has large tires and is used in rugged conditions where other cranes might not be able to go.
5. All Terrain Crane
Q: What are the features of an all terrain crane?
A: Combines the capabilities of a rough terrain crane and a mobile crane, suitable for both on-road and off-road conditions.
6. Floating Crane
Q: What is a floating crane used for?
A: Mounted on a vessel, it is used for lifting heavy loads in ports, offshore constructions, and shipbuilding.
7. Gantry Crane
Q: What distinguishes a gantry crane?
A: It spans across an open space and moves along tracks. Often used in shipyards and large factories.
8. Overhead Crane
Q: Where would you find an overhead crane?
A: Commonly found in industrial environments, it runs on elevated tracks along the ceiling.
9. Loader Crane
Q: What is a loader crane’s primary function?
A: Mounted on a truck, it loads and unloads materials from the truck bed, typically used for smaller loads.
10. Telescopic Crane
Q: What is special about a telescopic crane?
A: Features a boom with several sections that can extend and retract, providing flexibility in reach.
11. Stiff Boom Crane
Q: How does a stiff boom crane operate?
A: Known for its rigid boom, it provides precise lifting and is often used in loading and unloading ships.
12. Deck Crane
Q: What is the purpose of a deck crane?
A: Mounted on a ship, it assists in loading and unloading cargo from the deck of the vessel.
These cranes serve diverse functions and environments, showcasing the variety of lifting solutions available for different tasks.

Top 10 FAQ with answer about 12 types of crane for Buyer Sourcing from China
Sure, here’s a detailed yet concise FAQ for buyers sourcing 12 types of cranes from China:
1. What are the main types of cranes available from China?
The main types include Tower Cranes, Mobile Cranes, Overhead Cranes, Gantry Cranes, Crawler Cranes, Telescopic Cranes, Loader Cranes, Rough Terrain Cranes, All Terrain Cranes, Floating Cranes, Aerial Cranes, and Bridge Cranes.
2. What is the typical lead time for crane orders from China?
Lead times vary by type and customization, generally ranging from 30 to 90 days.
3. How do I ensure the quality of cranes from Chinese manufacturers?
Verify certifications (ISO, CE), request factory audits, and ask for previous client references.
4. What certifications should I look for when sourcing cranes from China?
Key certifications include ISO 9001, CE, CCC, and sometimes ANSI or ASME depending on your region.
5. Are Chinese cranes compliant with international safety standards?
Many manufacturers comply with international safety standards like EN 14439 for tower cranes and ISO 23815 for mobile cranes.
6. Can I get customization on cranes from Chinese suppliers?
Yes, most suppliers offer customization in terms of load capacity, boom length, and additional features.
7. What is the typical warranty period for cranes sourced from China?
Warranties typically range from 1 to 2 years, but it’s crucial to clarify this with the supplier.
8. How do I handle spare parts and maintenance for cranes from China?
Ensure the supplier provides a comprehensive spare parts list and offers after-sales service support.
9. What is the process for shipping and logistics?
Shipping is usually done via sea freight. Ensure your supplier handles the necessary export documentation, and consider hiring a freight forwarder.
10. How can I manage communication effectively with Chinese crane suppliers?
Use clear and precise language, utilize translators if needed, and maintain regular updates via emails and video calls to avoid misunderstandings.
This compact FAQ covers essential questions buyers might have when sourcing cranes from China, ensuring clarity and addressing common concerns succinctly.
































