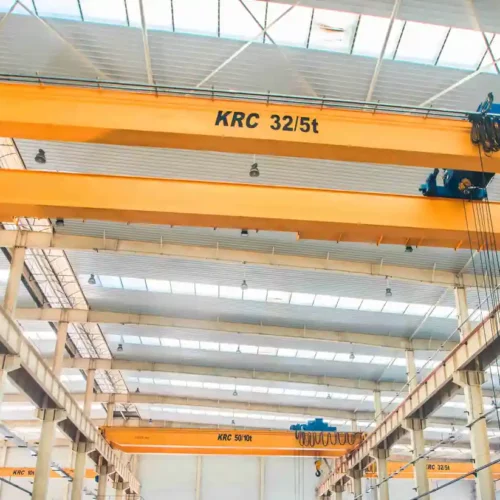
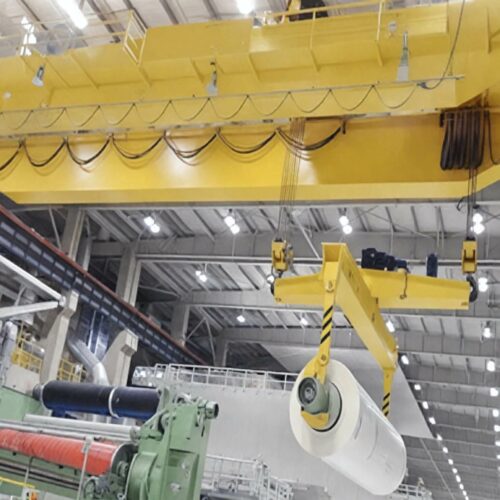
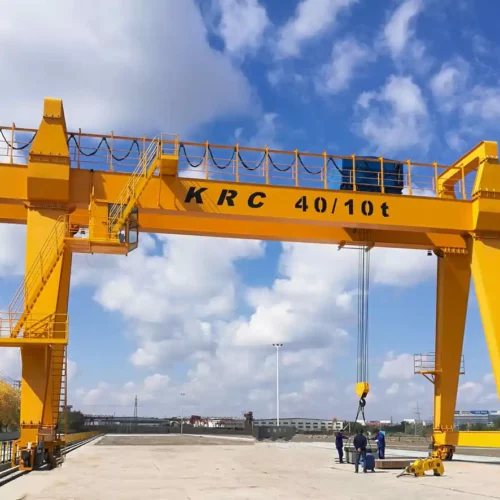
electric crane Safety Certifications
Electric cranes are pivotal in various industrial applications, making safety certifications essential to ensure operational safety and reliability. Here are some key safety certifications for electric cranes:
1. OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration):
– OSHA sets comprehensive standards for crane safety in the United States, including operator qualifications and safety protocols. Compliance with OSHA guidelines helps ensure a safe working environment.
2. ANSI/ASME (American National Standards Institute/American Society of Mechanical Engineers):
– ASME B30.2 covers overhead and gantry cranes, ASME B30.3 addresses tower cranes, and ASME B30.17 pertains to overhead and gantry cranes for special applications. These standards focus on design, inspection, testing, and maintenance.
3. CE Marking (Conformité Européenne):
– For cranes used in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental requirements. Relevant directives include the Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC.
4. ISO (International Organization for Standardization):
– ISO 4301 specifies classifications for lifting equipment. ISO 9927 outlines inspection requirements, while ISO 10245 sets forth safety requirements for mobile cranes.
5. CMAA (Crane Manufacturers Association of America):
– CMAA specifications 70 and 74 provide guidelines for the construction, installation, and maintenance of cranes, emphasizing safety and performance.
6. LOLER (Lifting Operations and Lifting Equipment Regulations):
– In the UK, LOLER sets forth specific obligations for crane operators regarding safe lifting practices and regular equipment inspections.
Acquiring and maintaining these certifications are paramount for ensuring that electric cranes operate safely and efficiently, protecting both personnel and assets. Regular safety audits and training further reinforce compliance with these standards.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “electric crane”
Sure, here are the reference technical parameters for an electric crane:
1. Lifting Capacity: The maximum weight the crane can lift, typically measured in tons (e.g., 5 tons, 10 tons).
2. Span: The horizontal distance between the rails or tracks on which the crane operates, measured in meters or feet.
3. Lift Height: The maximum vertical distance that the crane can lift its load, measured in meters or feet.
4. Hook Approach: The minimum distance from the centerline of the hook to the nearest obstruction, measured in side and end directions.
5. Hoisting Speed: The speed at which the hook can be raised or lowered, usually measured in meters per minute (m/min).
6. Travel Speed: The speed at which the entire crane can travel along its rails, generally measured in meters per minute (m/min).
7. Duty Cycle: Defined by the classification of crane operation such as A1 to A8 or equivalent, indicating the frequency and intensity of crane usage.
8. Power Supply: Voltage and frequency the crane operates on, typically 3-phase AC power like 380V/50Hz or 460V/60Hz.
9. Control System: Type of system used to control crane operations, such as pendant control, wireless remote control, or cabin control.
10. Motor Power: The power output of the hoisting motor and travel motor, measured in kilowatts (kW).
11. Trolley Dimensions: Dimensions of the trolley on which the hoist is mounted, critical for fitting in specific spaces.
12. Operational Temperature Range: The temperature range within which the crane can safely operate, important for specific working environments.
13. Protection Class: The ingress protection rating (e.g., IP54, IP65) indicating the level of protection against dust and water ingress.
14. Brake System: Type and capacity of the braking system employed to ensure load stoppage and safety.
15. Load Limiter: Safety devices that prevent overloading by cutting off operation when maximum capacity is exceeded.
These parameters define the capabilities and suitability of an electric crane for specific tasks and environments.
List Product features of “electric crane”
An electric crane boasts an array of impressive features that make it indispensable for lifting and transporting heavy loads efficiently in various industrial, construction, and logistics applications. Below are key product features of an electric crane:
1. High Lifting Capacity: Designed to handle substantial weights, electric cranes can lift loads ranging from a few hundred kilograms to several tons.
2. Electric Motor: Powered by robust electric motors, these cranes provide consistent and reliable performance, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing operational efficiency.
3. Precision Control: Advanced control systems, such as variable frequency drives (VFD), provide smooth and precise movements, which are essential for delicate operations or complex installations.
4. Safety Mechanisms: Equipped with numerous safety features including overload protection, emergency stop buttons, limit switches, and anti-sway mechanisms to ensure safe operation.
5. Versatile Design: Can be integrated into different types of crane systems such as overhead bridge cranes, gantry cranes, jib cranes, and workstation cranes, making them adaptable to specific application needs.
6. Remote Control Operation: Many electric cranes come with wireless remote controls, enabling operators to control the crane from a safe distance, thereby enhancing safety and convenience.
7. Durability and Construction: Built with high-quality materials and robust construction to ensure long-term durability and reliability even in harsh working environments.
8. Efficiency: Electric cranes are usually more energy-efficient compared to their diesel or hydraulic counterparts, which reduces operational costs and environmental impact.
9. Quiet Operation: The electric motor allows quieter operation, contributing to a less noisy work environment, which is beneficial for worker comfort and communication.
10. Enhanced Mobility: Some models offer wheel or track systems to provide improved mobility, allowing the crane to be easily relocated within the worksite.
In summary, an electric crane is a versatile, efficient, and safe solution for heavy lifting needs, integrating advanced technologies and robust construction to meet the demanding requirements of various industries.
List Various Types of “electric crane”
Electric cranes are versatile pieces of equipment utilized in various industries for lifting and moving heavy loads. Here are some common types of electric cranes:
1. Overhead Cranes:
– Single Girder Overhead Crane: Features one girder mounted on the crane’s structure, suitable for lighter loads and shorter spans.
– Double Girder Overhead Crane: Comprises two girders for added strength, ideal for heavy-duty lifting and longer spans.
2. Electric Jib Cranes:
– Wall-Mounted Jib Crane: Attached to a wall or vertical structure, suitable for confined spaces.
– Freestanding Jib Crane: Independent structure that offers flexibility in movement and can be installed almost anywhere.
3. Electric Hoists:
– Chain Hoist: Uses a chain to lift loads; commonly used for smaller and lighter loads.
– Wire Rope Hoist: Utilizes a wire rope for lifting; more robust and suitable for heavier loads.
4. Gantry Cranes:
– Full Gantry Crane: Features two legs that run on a track, supporting loads across a wide area.
– Portable Gantry Crane: Smaller and mobile, these can be easily moved around the workplace.
5. Monorail Cranes:
– Underhung Monorail Crane: Runs on a single rail, which is typically attached to the ceiling of the workspace.
6. Electric Tower Cranes:
– Primarily used in construction for lifting heavy materials to significant heights.
7. Electric Mobile Cranes:
– Electric Truck Cranes: These are mounted on trucks and offer mobility combined with electric functionality.
– All-Terrain Electric Cranes: Suitable for various terrains, providing versatility in construction and industrial applications.
These electric cranes not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute to safer handling of heavy loads, making them indispensable in construction, manufacturing, and logistics environments.
List Application of “electric crane”
Electric cranes are versatile lifting devices used across various industries to handle heavy loads efficiently and safely. Here are some key applications:
1. Construction:
– Building Materials: Electric cranes are used to lift and transport construction materials like steel beams, cement bags, and prefabricated components to desired heights or locations on construction sites.
– Assembly: They assist in the assembly of structures by positioning heavy components accurately.
2. Manufacturing:
– Production Line: In manufacturing plants, electric cranes move raw materials, components, and finished products along the production line.
– Maintenance: They facilitate maintenance tasks by lifting heavy machinery parts for repair or replacement.
3. Warehousing and Logistics:
– Loading/Unloading: Electric cranes aid in the loading and unloading of goods from trucks, trains, and ships.
– Storage: They help in stacking goods at various heights in warehouses, optimizing storage space.
4. Shipping and Ports:
– Container Handling: Electric cranes, specifically container cranes, are vital in loading and unloading shipping containers from cargo vessels.
– Bulk Handling: They are used to handle bulk materials like coal, ore, and grains.
5. Automotive Industry:
– Assembly Lines: Electric cranes lift and position heavy automotive parts, including engines and chassis, on assembly lines.
– Maintenance: They assist in lifting vehicles for maintenance and repairs.
6. Mining:
– Material Removal: Electric cranes efficiently remove extracted materials from mining sites.
– Equipment Handling: They manage the handling of heavy mining equipment and machinery.
7. Energy Sector:
– Wind Turbines: Used to install and maintain wind turbine components.
– Power Plants: Assist in the construction and maintenance of power plants, including handling heavy generators and turbines.
8. Railways:
– Track Maintenance: Electric cranes help lift and place railroad tracks and sleepers during construction and maintenance.
– Rolling Stock: They assist in assembling and maintaining railway carriages and engines.
Electric cranes are essential for improving operational efficiency, safety, and productivity across these diverse applications.
List Buyer Types of “electric crane”
Buyers of electric cranes can be categorized into several types based on their specific needs and industries they belong to. Here are the primary buyer types:
1. Construction Companies:
– Residential and Commercial: These buyers often use electric cranes for lifting materials at construction sites.
– Infrastructure Projects: Used for large-scale projects like bridges and highways, where precise and efficient lifting is crucial.
2. Manufacturing and Industrial Plants:
– These facilities utilize electric cranes for moving heavy items, parts, and equipment across the factory floor.
– Common in automotive, aerospace, and machinery manufacturing industries.
3. Warehousing and Logistics Companies:
– Electric cranes assist in loading and unloading goods, organizing inventory, and streamlining supply chain operations.
4. Shipping Ports and Shipyards:
– Essential for handling cargo, containers, and heavy ship components.
5. Mining Operations:
– Used to lift and move raw materials, machinery, and mined products.
6. Energy Sector:
– Includes wind farms, oil rigs, and pipeline projects where large and heavy components require precise placement.
7. Public Utilities:
– Electric cranes are used for maintenance and construction of utility infrastructure like power lines and water treatment facilities.
8. Railroad Companies:
– For maintenance of tracks and moving heavy rail components.
9. Automotive Repair Shops and Garages:
– Use smaller electric cranes for lifting engines, vehicle parts, and other heavy components.
10. Scrap and Recycling Companies:
– Essential in handling large volumes of scrap metals and materials.
11. Rental Companies:
– Purchase electric cranes to rent out to other businesses on short-term or long-term contracts.
12. Event Management Companies:
– Utilize cranes for setting up stages, lighting, and other large structures.
Understanding these buyer types help manufacturers and suppliers tailor their products and marketing strategies effectively, addressing the distinct needs of each sector.
List “electric crane” Project Types for Different Industries
Electric cranes are versatile tools that cater to a wide variety of industries. Here are some project types for different sectors:
1. Construction Industry:
– High-Rise Building Assembly: Electric tower cranes are essential for lifting heavy construction materials to great heights.
– Bridge Construction: Specialized electric gantry cranes enable the precise placement of bridge segments.
– Residential Development: Small electric mobile cranes provide maneuverability for lifting materials in confined spaces.
2. Manufacturing Industry:
– Assembly Line Work: Overhead electric cranes aid in the seamless movement of heavy components along the production line.
– Warehouse Logistics: Electric stacker cranes manage the organization and retrieval of materials.
– Heavy Equipment Manufacturing: Jib cranes facilitate the assembly of bulky machinery parts.
3. Shipping and Logistics:
– Port Operations: Electric container cranes, such as ship-to-shore (STS) cranes, handle container loading and unloading.
– Rail Yard Management: Mobile gantry cranes lift and position containers onto railway wagons.
– Inland Storage Facilities: Straddle carriers provide efficient stacking and sorting of containers.
4. Automotive Industry:
– Production Lines: Semi-gantry cranes assist with engine and body part assembly.
– Parts Storage: Automated electric monorail systems streamline the transport of components.
– Maintenance Facilities: Portable electric gantry cranes support vehicle repairs and maintenance.
5. Mining Industry:
– Underground Operations: Compact electric overhead cranes handle equipment and material movement in constrained environments.
– Surface Mining: Large electric rope shovels facilitate the extraction and loading of ore.
– Material Processing Plants: Specialized cranes handle the transport of heavy mineral processing equipment.
6. Renewable Energy:
– Wind Farm Construction: Electric crawler cranes erect wind turbines and handle nacelle, blade, and tower assembly.
– Solar Panel Installation: Lightweight mobile cranes assist in the placement of solar panels.
– Hydropower Facility Maintenance: Bridge cranes perform routine maintenance of hydropower plant equipment.
By leveraging electric cranes tailored to specific industry needs, projects can achieve greater efficiency, safety, and precision.
electric crane Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Electric cranes are pivotal in modern material handling tasks, offering efficiency and safety. To enhance their functionality, various accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options are available.
Accessories:
1. Remote Controls: Enable precise and safe operation from a distance.
2. Load Indicators: Provide real-time feedback on weight, ensuring safe load handling.
3. Anti-Sway Systems: Reduce load swing, enhancing control and safety.
4. Limit Switches: Prevent over-travel of the crane, protecting both the machinery and the load.
5. Hoist Units: Offer various lifting capacities and speeds for diverse applications.
Upgrades:
1. Variable Frequency Drives (VFD): Improve control over crane speed and movement, enhancing efficiency.
2. Modernization Kits: Upgrade older cranes with the latest technology to improve performance and safety.
3. Automated Systems: Integrate automation for enhanced precision and reduced human intervention.
4. Energy Recovery Systems: Recycle energy from crane movements back into the system, improving energy efficiency.
Custom Manufacturing Options:
1. Tailored Load Capacities: Cranes can be built with specific load capacities to meet unique application needs.
2. Specialized Lifting Attachments: Custom hooks, grabs, and spreader beams for handling unique materials.
3. Extended Reach: Custom boom lengths for applications requiring longer reach.
4. Environmental Adaptations: Design modifications for usage in extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or corrosive environments.
5. Integration with Existing Systems: Custom solutions to seamlessly integrate with pre-existing infrastructure and workflows.
Conclusion:
Enhancing electric cranes with the right accessories, upgrades, and custom options can significantly improve their performance, safety, and versatility. Whether through remote controls, anti-sway systems, VFDs, or bespoke manufacturing, these enhancements ensure cranes meet specific operational requirements efficiently.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “electric crane”
Quality Control in Electric Crane Manufacturing:
1. Material Inspection: Raw materials are inspected for compliance with specifications regarding strength, durability, and other relevant properties.
2. Component Testing: Individual components such as motors, cables, hooks, and controls are rigorously tested to ensure they meet industry standards.
3. Dimensional Checks: Precision measurements are taken to verify that components are within acceptable tolerances.
4. Assembly Monitoring: Continuous monitoring during assembly helps ensure that all parts fit correctly and function as intended.
5. Load Testing: The fully assembled crane is tested under various load conditions to ensure it can handle its rated capacity safely.
6. Electrical Safety and Performance Testing: Electrical systems are tested for safety, efficiency, and adherence to regulations.
7. Final Inspection: A comprehensive final inspection is conducted to verify that the crane meets all design specifications and safety standards.
8. Documentation and Traceability: Detailed records are kept for all processes, tests, and inspections to ensure traceability and accountability.
—
Manufacturing Process of Electric Crane:
1. Design and Engineering: Engineers create detailed specifications and designs based on customer requirements and regulatory standards.
2. Procurement: High-quality raw materials and components are sourced from reliable suppliers.
3. Fabrication: Structural components like the crane frame, jib, and beams are cut, welded, and machined to precise dimensions.
4. Component Manufacturing: In-house or outsourced manufacturers produce motors, control systems, cables, and other essential parts.
5. Pre-Assembly: Major components are pre-assembled to ensure fitment and functionality before final assembly.
6. Final Assembly: All pre-assembled parts are put together, integrating the mechanical and electrical systems.
7. Quality Control and Testing: The assembled electric crane undergoes rigorous testing, including load and performance tests, as described in the quality control section.
8. Painting and Finishing: The crane is painted and coated for corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
9. Packaging and Shipping: The crane is safely packaged for transport and shipped to the customer.
10. Installation and Customer Support: Installation support and after-sales service ensure the crane operates efficiently and safely on-site.
This manufacturing workflow ensures that electric cranes are produced efficiently, meet high-quality standards, and fulfill customer requirements.
How to use “electric crane”
Using an electric crane involves several steps to ensure safety and efficiency. Below is a concise guide within a 300-word limit.
1. Familiarize Yourself with the Equipment:
– Read the operator’s manual.
– Understand all controls and warning signals.
2. Pre-Operational Checks:
– Inspect the crane for any visible damage or wear.
– Check the electric power source and connections.
– Ensure all safety devices are working correctly (e.g., limit switches, emergency stop).
3. Power-Up Sequence:
– Turn on the electric power.
– Allow systems to perform self-checks.
4. Load Considerations:
– Verify the load weight doesn’t exceed the crane’s capacity.
– Use appropriate rigging and slings.
5. Operating the Crane:
– Use the control panel or remote to maneuver the crane.
– Start with slow, deliberate movements.
– Raise the load just enough to clear the ground and verify stability.
– Guide the load to the desired location carefully.
6. Safety Precautions:
– Maintain a clear area around the crane.
– Avoid abrupt movements.
– Never leave a suspended load unattended.
– Use spotters if necessary.
7. Shut Down and Maintenance:
– Lower the load to a secure position.
– Turn off the power.
– Perform any needed maintenance.
– Report any malfunctions to your supervisor.
By following these steps, you can safely and effectively operate an electric crane. Always prioritize safety and adhere to your specific crane’s operating guidelines.
“electric crane” Comparative Analysis
Electric cranes represent a significant evolution in material handling equipment, offering distinct advantages and some limitations compared to traditional fuel-powered and hydraulic cranes. Here, we compare key aspects of electric cranes with their conventional counterparts:
1. Efficiency and Operating Costs:
Electric cranes are generally more efficient, converting roughly 90-95% of energy into mechanical work compared to about 35-45% for internal combustion engines. This leads to lower operational costs due to cheaper electricity rates and reduced fuel consumption.
2. Environmental Impact:
Electric cranes produce zero emissions on-site, making them environmentally friendly and suitable for indoor use or pollution-sensitive areas. In contrast, diesel or gas-powered cranes generate emissions, contributing to air pollution and carbon footprint.
3. Maintenance:
Electric cranes often require less maintenance, as they have fewer moving parts and no engine oil, fuel filters, or exhaust systems. Traditional cranes, especially those running on diesel, necessitate regular checks and more frequent part replacements.
4. Power and Performance:
While electric cranes excel in providing consistent power and smooth operation, they may be limited by battery life and recharging needs. However, emerging technologies in battery storage and quick-charging capabilities are mitigating these limitations. Traditional cranes can operate as long as fuel is available but are subject to fluctuations in power and emissions regulations.
5. Noise Levels:
Electric cranes operate much more quietly, reducing noise pollution and improving working conditions for operators and nearby workers. Conversely, diesel engines are notably louder and can contribute to noise pollution, requiring additional measures for noise management.
6. Initial Investment:
The initial cost of electric cranes can be higher due to advanced technology and battery systems. Over time, however, the lower operating and maintenance costs can offset these initial expenses, proving cost-effective in the long run.
In summary, electric cranes are increasingly becoming the crane of choice for many industries due to their operational efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and lower long-term costs. While they may require higher initial investment and face battery-related limitations, technological advancements are rapidly bridging these gaps, making them a competitive and sustainable alternative to traditional cranes.
“electric crane” Warranty and Support
Warranty and Support for Electric Cranes
When investing in an electric crane, understanding the warranty and support options is crucial for ensuring longevity and reliability. Most manufacturers offer a comprehensive warranty that typically spans between one to three years, depending on the model and brand. This warranty generally covers defects in materials and workmanship, ensuring that any malfunction deriving from these issues is addressed without additional costs to the owner.
However, it’s important to review the specific terms and conditions, as some warranties may have limitations or exclusions, such as normal wear and tear, misuse, or inadequate maintenance. Manufacturers often recommend a schedule for maintenance checks and part replacements, which should be strictly adhered to in order to keep the warranty valid.
In addition to the warranty, robust customer support is a key factor. Leading electric crane manufacturers provide 24/7 customer service, offering immediate assistance for troubleshooting and technical issues. This support is available via multiple channels, including phone, email, and online chat, ensuring help is readily accessible whenever needed.
Many companies also offer extended support packages, which can include routine inspections, preventive maintenance services, and even operator training programs. These additional services can significantly enhance the operational efficiency and safety of the crane, and help in identifying potential issues before they lead to costly repairs or downtime.
It is advisable to choose a manufacturer with a strong reputation for after-sales service and a wide network of service centers. Timely access to genuine spare parts and experienced technicians can make a significant difference in minimizing downtime and ensuring safe, uninterrupted operations.
In summary, a solid warranty and reliable support network are essential when purchasing an electric crane. They not only protect your investment but also ensure the crane operates efficiently and safely throughout its lifespan.
List “electric crane” FAQ
Electric Crane FAQs
1. What is an electric crane?
An electric crane is a type of lifting device powered by electric motors, designed to move heavy loads vertically and horizontally within a workspace. It is commonly used in manufacturing, construction, and warehousing.
2. How does an electric crane work?
Electric cranes use electric motors to drive the hoist mechanism and the crane’s movement. The motor operates through a control system that allows precise handling of loads.
3. What are the benefits of using an electric crane?
Electric cranes offer several advantages, including:
– High efficiency and reliability
– Low operating and maintenance costs
– Precise control and smooth operation
– Reduced environmental impact due to lower emissions
4. What types of electric cranes are available?
There are various types, including:
– Overhead cranes (bridge cranes)
– Gantry cranes
– Jib cranes
– Monorail cranes
5. What are the typical applications of electric cranes?
Electric cranes are used in manufacturing plants, warehouses, shipyards, construction sites, and automotive industries for moving heavy materials and equipment.
6. What safety features are included in electric cranes?
Standard safety features may include:
– Overload protection
– Emergency stop buttons
– Limit switches
– Safety interlocks
7. How do I choose the right electric crane for my needs?
Consider factors such as load capacity, lift height, span, working environment, and specific application requirements. Consulting with a crane manufacturer or supplier can help you make an informed decision.
8. What maintenance is required for an electric crane?
Regular maintenance includes:
– Inspecting mechanical components
– Lubricating moving parts
– Checking electrical connections
– Testing safety features
9. Are there any regulatory standards for electric cranes?
Yes, electric cranes must comply with industry-specific standards such as OSHA, ANSI, and ISO regulations to ensure safety and reliability.
10. How do I install an electric crane?
Installation should be performed by qualified professionals following the manufacturer’s guidelines and local regulations. Proper installation ensures safe operation and longevity of the crane.
This concise set of FAQs provides an overview for those interested in understanding or purchasing an electric crane, highlighting key aspects, benefits, and considerations.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about electric crane for Buyer Sourcing from China
Certainly! When sourcing an electric crane from China, buyers have a variety of questions. Here’s a list of the top 10 frequently asked questions along with concise answers:
1. What certifications should I look for?
– When sourcing from China, ensure the crane has CE, ISO, and CCC certifications. These indicate compliance with industrial standards and safety regulations.
2. What is the typical lead time?
– Lead times can vary, but typically expect around 30-60 days from order confirmation to delivery. This timeframe includes manufacturing and shipping.
3. What are the payment terms?
– Common payment terms are a 30% deposit with the balance paid before shipment or via Letter of Credit. Always negotiate and confirm terms directly with the supplier.
4. Can I request customization?
– Yes, many Chinese manufacturers offer customization based on your specifications, including capacity, lifting height, and control systems.
5. What is the warranty period?
– Standard warranties range from 12 to 24 months. Verify what the warranty covers and if there are options to extend it.
6. How do I ensure quality control?
– Engage third-party inspection services to conduct pre-shipment inspections. Request quality assurance documentation and visit the factory if possible.
7. What about after-sales service?
– Confirm the availability of after-sales services, including troubleshooting, maintenance support, and spare parts availability.
8. What are the shipping costs?
– Shipping costs depend on crane size, weight, and destination. Request freight quotes and consider both sea and air options based on urgency and budget.
9. How do I handle installation?
– Some manufacturers offer on-site installation services, while others provide detailed manuals and remote support. Ensure you clarify this aspect beforehand.
10. Are there any hidden fees?
– Be aware of potential additional costs such as customs duties, local taxes, packaging, and insurance. Discuss these details upfront to avoid surprises.
By addressing these FAQs, buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing electric cranes from China.










