magnetic crane Safety Certifications
Magnetic cranes, used extensively in industries to lift and transport ferrous materials, must adhere to strict safety standards and certifications to ensure operational safety and efficiency. Below are some of the essential safety certifications and standards:
1. ISO 9001: This standard is crucial for quality management systems. Manufacturers of magnetic cranes must comply with ISO 9001 to ensure consistent product quality and continuous improvement in their production processes.
2. CE Marking: Compliance with the European Union CE marking ensures that the magnetic crane meets the EU’s stringent health, safety, and environmental requirements. This certification is mandatory for cranes operating within the EU.
3. ASME B30.20: The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) B30.20 addresses the safety requirements for below-the-hook lifting devices, including magnet systems used in magnetic cranes. It sets forth criteria for construction, maintenance, and operational functions.
4. OSHA Standards: The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides guidelines to ensure workplace safety and health. Magnetic cranes must comply with OSHA’s relevant standards, such as proper training for operators and regular equipment inspections.
5. CMAA Specifications: The Crane Manufacturers Association of America (CMAA) outlines specifications for the design, manufacturing, and testing of cranes, ensuring reliability and safety in industrial applications.
6. UL Certification: Underwriters Laboratories (UL) certification verifies the electrical safety of magnetic cranes, ensuring components meet US safety standards for electrical systems.
7. IEC 61508 / IEC 62061: These international standards for functional safety ensure that magnetic cranes’ electrical and electronic programmable systems operate safely and error-free.
Adherence to these certifications not only ensures operational safety but also enhances reliability and efficiency. Regular audits, inspections, and maintenance based on these standards are crucial to prevent failures and ensure the longevity of magnetic cranes.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “magnetic crane”
Certainly! Here’s a concise list of reference technical parameters for a magnetic crane:
Load Capacity
– Maximum Lifting Capacity: The upper limit of weight the crane can handle, often measured in metric tons (MT).
– Rated Load: The optimal weight that can be lifted safely and efficiently.
Magnetic Specifications
– Magnet Type: Permanent or Electro-magnetic.
– Force: Pull-off force indicating the magnetic strength, usually in Newtons (N).
– Duty Cycle: Percentage of time the magnet can be operational in a given period.
Lifting Height
– Maximum Lifting Height: Maximum vertical distance the crane can move a load.
Speed
– Hoisting Speed: Speed at which the crane can lift and lower loads.
– Trolley Speed: Speed of the trolley that moves the load horizontally.
– Crane Travel Speed: The speed at which the entire crane setup moves along the rails or ground.
Power Requirements
– Electric Power Supply: Voltage and phase, typically 220V, 380V, or 415V; single-phase or three-phase.
– Power Consumption: Measured in kilowatts (kW), indicating energy used by the crane.
Mechanical Specifications
– Span: Distance between the two rails the crane operates on.
– Outreach: Horizontal distance from the jib crane’s vertical support to the end of the boom.
– Rotation Angle: For jib cranes, usually up to 360 degrees.
Safety Features
– Overload Protection: Prevents the crane from lifting loads beyond its capacity.
– Emergency Stop: Immediate halt mechanism.
– Limit Switches: Prevents the crane from exceeding its operational zones.
Control Systems
– Manual Control: Lever or button-operated.
– Remote Control: Wireless operation via remote.
– Automated Systems: Pre-programmed lifting operations using PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers).
Environmental Parameters
– Temperature Range: Operating temperature limits.
– Humidity Range: Permissible humidity for safe operation.
– Corrosion Protection: Anti-corrosive features for specific environmental conditions.
Standards and Compliance
– Certification: Compliance with standards such as ISO, CE, or ANSI.
These parameters help in evaluating the operational capabilities, technical limits, and safety features of a magnetic crane.
List Product features of “magnetic crane”
A magnetic crane is a versatile piece of lifting equipment extensively used in various industries for handling heavy and ferrous materials. Here are some of the key product features:
1. Electromagnet or Permanent Magnet: Many magnetic cranes come equipped with powerful electromagnets or permanent magnets that provide strong adhesion for lifting metal objects securely.
2. Load Capacity: They have a broad range of load capacities, which can vary from a few hundred kilograms to several tons, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
3. Adjustable Electromagnetic Force: In electromagnet models, the magnetic force can often be adjusted to match the weight and type of the material being handled.
4. Remote Control Operation: Some models come with remote control features, enabling operators to control the crane from a safe distance, enhancing operational safety.
5. Battery Backup System: To ensure uninterrupted operation, especially during power outages, some magnetic cranes come with integrated battery backup systems.
6. Safety Features: Many magnetic cranes include safety features such as fail-safe mechanisms, automatic demagnetization in case of power loss, and overload protection systems.
7. Rotational Capability: Advanced models offer 360-degree rotation, allowing for precise positioning of materials, thereby increasing operational efficiency.
8. Durability: Typically constructed from robust materials like high-grade steel, ensuring the crane can withstand harsh industrial environments.
9. Ease of Maintenance: Designed for easy maintenance, with accessible components and user-friendly diagnostic systems to minimize downtime.
10. Versatility: Suitable for various industries including scrap yards, shipyards, construction sites, warehouses, and manufacturing plants.
11. Energy Efficiency: Modern magnetic cranes are designed with energy efficiency in mind, often featuring energy-saving modes and low power consumption during idle periods.
12. User Interface: Often equipped with an intuitive user interface that provides real-time data on operational status, load weight, and system diagnostics.
13. Compatibility: Can be integrated with existing crane systems for enhanced functionality and efficiency.
These features make magnetic cranes indispensable for efficient, safe, and precise handling of heavy and ferrous materials in diverse industrial settings.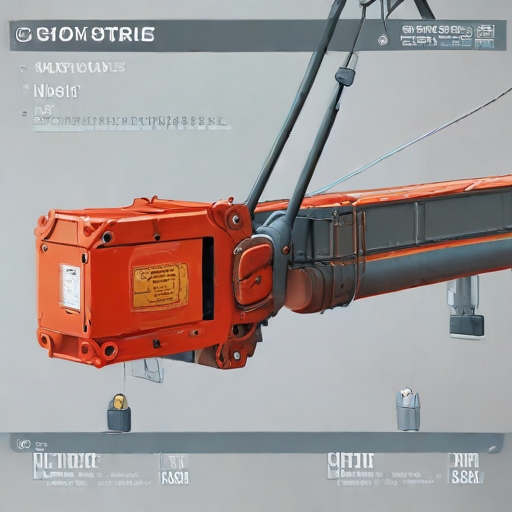
List Various Types of “magnetic crane”
Magnetic cranes are specialized lifting devices that use magnetic fields to hoist and transport ferrous materials. These cranes are commonly employed in warehouses, shipyards, and scrap yards for handling steel products, machinery, and scrap metal. Below are the different types of magnetic cranes:
1. Electromagnetic Cranes
– Description: These cranes utilize an electromagnet that can be switched on and off via an electric current. They are highly versatile and popularly used in various industries.
– Applications: Scrap yards, steel mills, loading docks.
2. Permanent Magnetic Cranes
– Description: Using permanent magnets, these cranes do not require an electric power source to maintain their magnetic field. This makes them energy-efficient and dependable.
– Applications: Smaller lifting tasks, workshops, and lifting finished products.
3. Battery-Operated Magnetic Cranes
– Description: These cranes use a battery to power their magnet, providing mobility and flexibility without relying on a constant power supply.
– Applications: Remote locations, mobile operations, intermittent lifting tasks.
4. Hydraulic Magnetic Cranes
– Description: These incorporate hydraulic systems to enhance lifting capabilities and often include electromagnetic or permanent magnetic units.
– Applications: Heavy-duty lifting, construction sites, and industrial applications.
5. Mobile Magnetic Cranes
– Description: Mounted on trucks or other mobile platforms, these cranes can be easily transported to different sites for on-the-go lifting operations.
– Applications: Construction, road clearing, shipyards.
6. Overhead Magnetic Cranes
– Description: Often found in industrial settings, these cranes move along overhead rails, allowing for extensive coverage of the floor area.
– Applications: Warehouses, manufacturing facilities, assembly lines.
7. Gantry Magnetic Cranes
– Description: Similar to overhead cranes but supported by freestanding legs that can either be fixed or mobile.
– Applications: Ports, outdoor storage yards, construction sites.
8. Jib Magnetic Cranes
– Description: Featuring a horizontal beam (jib) that can swing in an arc or be fixed, these cranes are suitable for localized lifting.
– Applications: Workshops, assembly lines, smaller industrial tasks.
Conclusion
Each type of magnetic crane has specific attributes that cater to distinct industrial needs, making them indispensable tools in material handling and transport operations.
List Application of “magnetic crane”
A magnetic crane, also known as an electromagnetic crane, leverages the power of electromagnets to lift and transport heavy ferrous materials. Here are some key applications:
1. Scrap Yards: Magnetic cranes are prominently used in scrap yards to handle and sort large quantities of ferrous scrap metal. The electromagnet can easily pick up and release metal scraps, facilitating efficient recycling operations.
2. Steel Mills: In steel mills, magnetic cranes transport large and heavy steel plates, slabs, and coils. They streamline the handling process, enhance safety, and improve operational efficiency.
3. Automotive Industry: These cranes are essential in automotive manufacturing and dismantling facilities. They assist in moving parts and components, and in scrapping and recycling end-of-life vehicles.
4. Construction Sites: Magnetic cranes are utilized to lift and position steel structures and rebar. This speeds up the construction process and ensures precision in placing heavy steel elements.
5. Shipyards: In shipbuilding and repair, magnetic cranes handle steel plates and sections, aiding in the assembly and maintenance of ships. They are critical for lifting and aligning large steel parts.
6. Railway Yards: Railway yards employ magnetic cranes to manage and maintain rails and other steel components. They enhance the efficiency of loading and unloading rail cars.
7. Foundries: In foundries, magnetic cranes transport heavy molds, castings, and raw materials. They are crucial for maintaining workflow in manufacturing processes that involve heavy metal parts.
8. Warehousing and Logistics: These cranes help in the storage and retrieval of heavy metal items. They are commonly used in warehouses dealing with bulky metal goods to improve storage efficiency and safety.
9. Demolition Sites: During demolition, magnetic cranes pick up and sort ferrous materials from the rubble. This aids in the recycling process and reduces the manual effort involved in material segregation.
Magnetic cranes thus play a vital role in sectors that require the handling, transportation, and recycling of heavy steel and ferrous materials, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and worker safety.
List Buyer Types of “magnetic crane”
When considering buyers for magnetic cranes, understanding the diverse sectors and specific applications of these machines is crucial. The primary types of buyers include:
1. Manufacturing Industries: Factories and production facilities, especially those involved in metalworking, automotive, and heavy machinery, frequently use magnetic cranes for lifting and transporting ferrous materials efficiently. They minimize manual labor and improve safety during operations involving heavy metal parts.
2. Scrap Yards and Recycling Centers: These facilities deal extensively with metallic scrap. Magnetic cranes are indispensable for sorting, moving, and loading scrap metal. Their ability to lift heavy, irregularly shaped metal pieces makes the recycling process more efficient.
3. Construction Companies: Large-scale construction projects often involve the handling and positioning of steel beams and other metal structures. Magnetic cranes streamline this process, making them highly valuable for construction firms aiming to improve productivity and safety on site.
4. Warehousing and Distribution Centers: Facilities that store and distribute metal goods—especially bulk items—benefit from the efficiency that magnetic cranes provide. They help in the organized handling and storage of metal products, reducing the time and labor required for inventory management.
5. Railroads and Shipyards: Both sectors require the frequent movement of heavy metal parts and equipment. Magnetic cranes assist in loading and unloading metal cargo, maintaining operational flow, and reducing downtime.
6. Aerospace and Defense: Industries that handle large quantities of specialized metals and alloys for manufacturing aircraft and military equipment often need magnetic cranes. They offer precision in handling sensitive materials and parts essential for these high-stakes sectors.
7. Energy Sector: Companies in the oil, gas, and renewable energy sectors use magnetic cranes to handle large metal pipes, machinery components, and infrastructure elements in plants and fields.
In summary, magnetic cranes are versatile tools catering to industries prioritizing the safe, efficient, and precise handling of metal materials and components.
List “magnetic crane” Project Types for Different Industries
Magnetic Crane Project Types for Different Industries
1. Automotive Industry:
– Car Scrap Handling: Utilized to lift and move scrap metal and end-of-life vehicles in recycling yards.
– Assembly Line Support: Magnetic cranes assist in the assembly of heavy automotive parts, improving efficiency and safety.
2. Construction Industry:
– Steel and Iron Handling: Magnetic cranes can lift beams, girders, and panels, facilitating high-rise building construction.
– Concrete Formwork: Employed to move and position metal formwork panels used in concrete casting.
3. Shipping and Logistics:
– Port Operations: Magnetic cranes load and unload large quantities of scrap metal and other ferrous materials from ships.
– Container Handling: Specialized models can handle containers with metal contents, streamlining port workflows.
4. Metal Fabrication and Manufacturing:
– Sheet Metal Handling: Used to lift and stack large metal sheets, reducing manual labor and enhancing safety.
– Machinery Parts Movement: Helps in transporting heavy machine components within manufacturing plants.
5. Mining Industry:
– Ore Handling: Employed to move bulk quantities of ferrous ore from one location to another.
– Equipment Maintenance: Assist in the disassembly and reassembly of large mining equipment for maintenance purposes.
6. Railway Sector:
– Track Maintenance: Magnetic cranes facilitate the lifting and laying of railway tracks and related components.
– Freight Loading: Used to load and unload bulk metal freight on trains, enhancing operational efficiency.
7. Electronics Recycling:
– E-Waste Separation: Aids in the extraction of ferrous materials from electronic waste, making recycling processes more effective.
8. Heavy Engineering:
– Bridge and Infrastructure Projects: Magnetic cranes help in the positioning of steel components, expediting construction timelines.
– Energy Sector: Used in the assembly and maintenance of wind turbines and other large-scale energy infrastructure.
Each of these projects highlights the versatility and critical role magnetic cranes play across various industries, boosting productivity and ensuring safe handling of heavy and cumbersome materials.
magnetic crane Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
When optimizing a magnetic crane, selecting the right accessories and upgrades can significantly enhance performance and efficiency. Common accessories include specialized lifting magnets suited for various materials such as steel plates, pipes, or scrap. These magnets can be equipped with permanent or electromagnet capabilities based on the specific application needs.
Control systems can also be upgraded to advanced programmable logic controllers (PLCs), offering precise control and automation. Incorporating wireless remote control systems can improve safety and ease of operation by allowing operators to manage the crane from a distance.
Cameras and sensor systems are valuable upgrades, providing real-time monitoring and increasing operational accuracy. Load cells and weight measurement devices ensure proper load management, minimizing the risk of overloads and enhancing safety.
For specialized applications, custom manufacturing options are available. Cranes can be tailored with bespoke boom lengths, lifting capacities, and magnetic strengths to meet unique project requirements. Additionally, frames and structures can be modified to operate in harsh environments, such as extreme temperatures or corrosive atmospheres.
Integration of energy-efficient components, such as LED lighting and variable frequency drives (VFDs), can reduce operational costs and improve the crane’s environmental footprint.
Maintenance accessibility can be improved through custom designs that allow easier access to critical parts, reducing downtime and enhancing productivity. For increased versatility, interchangeable magnet heads can be installed, allowing the crane to switch between different types of magnetic attachments quickly.
In summary, enhancing a magnetic crane’s capabilities through targeted accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options can provide substantial benefits in terms of efficiency, safety, and specialized performance, meeting the diverse needs of various industries.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “magnetic crane”
Quality Control of Magnetic Cranes:
Quality control in manufacturing magnetic cranes involves rigorous procedures to ensure high performance, reliability, and safety. Key steps include:
1. Material Inspection: Raw materials, especially magnets and metals, are inspected for quality and consistency.
2. Component Testing: Crucial components like motors, wiring, and control systems undergo functional testing.
3. Assembly Verification: During the assembly process, checks are in place to ensure that components fit and function correctly.
4. Load Testing: Finished cranes are subjected to load tests to verify their lifting capacity and safety.
5. Magnetic Field Strength: The magnetic field strength is measured to ensure it meets design specifications.
6. Safety Compliance: Cranes are inspected to comply with relevant safety standards and regulations.
7. Final Inspection: A comprehensive final inspection is conducted, covering all aspects from aesthetics to functionality.
Manufacturing Process of Magnetic Cranes:
1. Design and Planning: Engineers create detailed designs using CAD software, specifying materials, dimensions, and performance criteria.
2. Procurement: High-quality raw materials and components are sourced according to the design specifications.
3. Fabrication: Metal parts are cut, machined, and welded to form the frame and structural components of the crane. Simultaneously, magnets are prepared and tested.
4. Assembly: The magnetic system, motors, electrical wiring, and control systems are assembled. This step requires precision to ensure all parts fit and function together.
5. Installation of Magnets: Magnets are strategically installed onto the crane, ensuring optimal magnetic field distribution for lifting.
6. Electrical Integration: Electrical systems, including control panels and safety mechanisms, are integrated and wired.
7. Testing: The assembled crane undergoes stringent testing, including load tests and safety checks, to ensure it operates correctly and safely under various conditions.
8. Finishing: The crane is painted or coated for corrosion resistance and given final aesthetic touches.
9. Packaging and Delivery: After passing all quality checks, the crane is packaged securely and delivered to the client with necessary documentation and user manuals.
These processes ensure that magnetic cranes are reliable, durable, and safe for industrial use.
How to use “magnetic crane”
Operating a magnetic crane involves several critical steps to ensure safety and efficiency. Below are concise instructions to help you get started:
1. Pre-Operation Inspection
– Check the Crane: Inspect the crane for any mechanical issues, including the wires, hook, and body.
– Assess the Magnet: Ensure the electromagnet is intact and its connections are secure.
– Safety Gear: Wear appropriate safety gear, including a hard hat, gloves, and steel-toed boots.
2. Setup
– Position the Crane: Maneuver the crane to align over the load.
– Power the Magnet: Ensure the electrical power supply to the magnet is properly connected.
3. Lifting Procedure
– Lower the Magnet: Use the crane controls to lower the electromagnet onto the load.
– Engage the Magnet: Activate the magnet switch to energize the electromagnet, causing it to attract and secure the load.
– Lift the Load: Gradually raise the load by operating the crane’s lifting mechanism.
4. Transporting the Load
– Move Smoothly: Carefully transport the load to the designated drop-off point using the crane controls.
– Observe Limits: Adhere to the crane’s weight and movement limitations to avoid accidents.
5. Releasing the Load
– Lower the Load: Slowly lower the load to the desired location.
– Disengage the Magnet: Deactivate the magnet to release the load from the electromagnet.
– Lift the Magnet: Raise the magnet back to a safe height.
6. Post-Operation Checklist
– Power Down: Turn off the crane and magnet power.
– Inspect for Damage: Check the equipment for any potential damage or wear.
– Store Properly: Ensure the crane is parked in a designated area and secured if necessary.
Safety Tips:
– Never stand under a lifted load.
– Ensure the work area is clear of unauthorized personnel.
– Follow manufacturer guidelines and local safety regulations.
By following these steps, you can safely and effectively use a magnetic crane.
“magnetic crane” Comparative Analysis
Magnetic cranes are pivotal in industries reliant on heavy material handling, such as construction, scrap processing, and steel production. They leverage electromagnetism to lift ferrous materials, offering advantages and posing certain limitations compared to traditional cranes.
Advantages:
1. Efficiency: Magnetic cranes can pick up multiple pieces of scrap or metal sheets in one go, drastically reducing operation time.
2. Precision: They offer high precision in material placement due to adjustable magnetic fields.
3. Safety: Reduces manual handling, minimizing the risk of worker injuries.
4. Versatility: Ideal for handling irregularly shaped or loose metals that traditional cranes struggle with.
5. Clean Operation: Eliminate the need for hooks or slings, decreasing potential damage to materials.
Limitations:
1. Power Dependency: Electromagnets require a constant power supply; any power interruption can cause load drops, necessitating fail-safes.
2. Material Restriction: Effective only with ferromagnetic materials like iron and steel; unusable for non-ferrous metals like aluminum or copper.
3. Cost: Generally more expensive initially due to the integration of electromagnets and associated control systems.
Comparison with Traditional Cranes:
Load Versatility: Traditional cranes can handle a broader range of materials (wood, concrete, non-ferrous metals) using different attachments, whereas magnetic cranes are limited to ferromagnetic materials.
Cost: Traditional cranes often have a lower initial investment but may incur higher operational costs over time due to the need for varied attachments and increased manual intervention.
Operational Safety: Magnetic cranes offer better safety for workers concerning ferrous materials, while traditional cranes may offer broader safety solutions for diverse materials via specialized attachments.
Energy Consumption: Traditional cranes typically consume less energy as they do not require a continuous electrical supply for magnetization.
In summary, the optimal choice between magnetic and traditional cranes largely hinges on the specific material handling needs of a project. Magnetic cranes excel in efficiency, safety, and precision for ferrous materials but come with higher costs and material limitations, whereas traditional cranes offer versatility and a lower initial cost, suitable for a wider range of applications.
“magnetic crane” Warranty and Support
Warranty and Support for Magnetic Cranes
Our magnetic cranes come with a comprehensive warranty and robust support services to ensure your operations run smoothly and efficiently. Below are the key aspects of our warranty and support offerings:
Warranty
1. Duration: Our magnetic cranes are covered by a two-year warranty from the date of purchase. This warranty covers any defects in materials or workmanship under normal use.
2. Coverage: The warranty includes free repairs or replacement of defective parts. This does not cover normal wear and tear, misuse, accidental damage, or unauthorized modifications.
3. Claim Process: To make a warranty claim, contact our customer support team with your purchase details and a description of the issue. Our team will guide you through the process, including inspection and repair or replacement procedures.
Support
1. Technical Assistance: Our engineers are available to provide technical support to troubleshoot any issues you may encounter with your magnetic crane. This can be done via phone, email, or through on-site visits if necessary.
2. Preventive Maintenance: We offer preventive maintenance packages to keep your crane in optimal working condition. These services help to identify and address potential issues before they lead to costly downtime.
3. Training: We provide comprehensive training for your operators to ensure they are fully equipped to use the crane safely and efficiently. Training includes online resources, in-person sessions, and detailed user manuals.
4. Spare Parts: We maintain an extensive inventory of spare parts to ensure quick replacements when needed, minimizing downtime for your operations.
5. Customer Support: Our dedicated customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you with any inquiries or issues. You can reach out via phone, email, or through our online support portal.
By choosing our magnetic cranes, you gain a reliable partner committed to ensuring the longevity and performance of your equipment through top-notch warranty and support services.
List “magnetic crane” FAQ
Magnetic Crane FAQ
1. What is a magnetic crane?
A magnetic crane is a type of lifting device that uses electromagnetic or permanent magnetic systems to lift and transport ferromagnetic materials like steel plates, pipes, and scrap metal.
2. How does a magnetic crane work?
Magnetic cranes utilize an electric current to generate a magnetic field, attracting and holding ferromagnetic materials. When the current is turned off, the magnetic field dissipates, releasing the materials.
3. What are the types of magnetic cranes?
– Electromagnetic Cranes: Use electric current to create a magnetic field.
– Permanent Magnetic Cranes: Use permanent magnets and generally include a mechanical switch to turn the magnetism on and off.
4. What are the key applications of magnetic cranes?
– Industrial manufacturing
– Scrap yards
– Metal fabrication shops
– Construction sites
5. What are the advantages of using a magnetic crane?
– Efficiency: Quick and easy lifting and moving of materials.
– Safety: Reduced need for manual handling and fewer risks associated with slings and hooks.
– Versatility: Can handle a variety of ferromagnetic materials.
6. Are there any limitations?
– Magnetic cranes cannot lift non-metallic or non-ferromagnetic materials.
– Overheating can be a concern in electromagnetic cranes if used continuously for extended periods.
– Requires a reliable power source (except permanent magnets).
7. What is the typical lifting capacity?
Lifting capacities vary widely depending on the model and application, ranging from a few hundred kilograms to several tons.
8. How are magnetic cranes powered?
Electromagnetic cranes need a continuous power source, typically electricity. Permanent magnetic cranes do not require ongoing power but may have batteries for mechanical operations.
9. Are there specific maintenance requirements?
– Regular inspection of electrical components and wiring.
– Checking and replacing magnets if they lose strength.
– Ensuring mechanical parts work smoothly.
10. What safety measures should be taken?
– Regular maintenance and inspection
– Operator training and certification
– Using safety locks and alarms to prevent accidents
By understanding these common questions, you can better decide if a magnetic crane is suitable for your specific needs.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about magnetic crane for Buyer Sourcing from China
Certainly! Here are the top 10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) with answers regarding sourcing magnetic cranes from China:
1. What are the key features of a magnetic crane?
– Answer: Key features include lifting capacity, magnetic force, crane span, control system, safety mechanisms, and energy efficiency. Ensure the specifications meet your operational needs.
2. How do I verify the quality of a magnetic crane from a Chinese supplier?
– Answer: Check for quality certifications such as ISO, CE, and inspect sample units. Conduct factory audits and seek reviews or references from previous buyers.
3. What is the typical lead time for manufacturing and shipping a magnetic crane?
– Answer: Lead times can vary, typically ranging from 30 to 60 days for manufacturing. Shipping times depend on the mode of transport (air, sea) and destination.
4. What are the payment terms generally accepted by Chinese suppliers?
– Answer: Common payment terms include T/T (Telegraphic Transfer), L/C (Letter of Credit), and sometimes payment milestones (e.g., 30% deposit and 70% before shipment).
5. Are there customization options available?
– Answer: Yes, many Chinese manufacturers offer customization to suit specific requirements like lifting capacity, dimensions, and control systems. Discuss your needs upfront.
6. How is the crane shipped and packaged to ensure safety?
– Answer: Cranes are usually disassembled and packed in wooden crates or steel frames to prevent damage during transit. Ensure the supplier provides proper packaging.
7. What about after-sales service and support?
– Answer: Confirm whether the supplier offers after-sales services such as installation guidance, warranty coverage, spare parts, and technical support.
8. How can I ensure compliance with local regulations and standards?
– Answer: Ensure the cranes meet international standards like ISO and CE. Check with local authorities on specific regulations and ask the supplier to provide relevant certification.
9. What are the risks associated with sourcing from China, and how can they be mitigated?
– Answer: Risks include quality control issues and delays. Mitigate them by conducting thorough vetting, using verified suppliers, and possibly engaging third-party inspection services.
10. How do warranty and returns work for magnetic cranes from China?
– Answer: Warranties typically range from 1 to 2 years, covering defects in materials and workmanship. Review the supplier’s return policy for defective items and clarify terms before purchasing.





