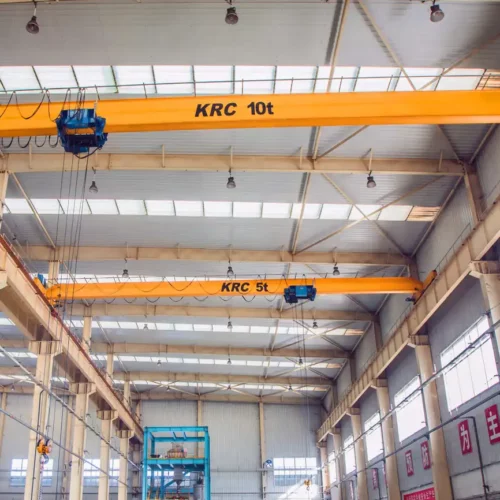
overhead crane Safety Certifications
Ensuring the safety and reliability of overhead cranes requires adherence to specific certifications and standards. Key safety certifications include:
1. OSHA Standards: The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets regulations for the safe operation, maintenance, and inspection of overhead cranes. Notably, OSHA 1910.179 covers general requirements for overhead and gantry cranes in industrial settings.
2. ASME B30 Standards: The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) offers detailed standards, specifically the B30 series, which provide guidelines on various types of cranes and related equipment. ASME B30.2 focuses on overhead and gantry cranes, detailing requirements for construction, installation, inspection, testing, maintenance, and operation.
3. CMAA Specifications: The Crane Manufacturers Association of America (CMAA) publishes specifications for overhead traveling cranes. CMAA Specification No. 70 and No. 74 provide criteria for single and multiple girder cranes, ensuring standardized manufacturing and safety protocols.
4. ISO Standards: International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards like ISO 4301, ISO 9927, and ISO 23815 provide global guidelines for crane classification, inspection, and maintenance requirements, promoting international safety and compatibility.
5. FEM Regulations: The European Federation of Material Handling (FEM) offers standards to ensure the safety and operational efficiency of cranes in Europe. FEM 1.001 outlines rules for crane design, load handling, and stress resistance.
6. NCCCO Certification: The National Commission for the Certification of Crane Operators (NCCCO) certifies crane operators, riggers, and signal persons in the United States. Certification from NCCCO ensures individuals operating cranes are trained, tested, and capable of safely handling equipment.
In addition to compliance with these certifications, regular maintenance and periodic inspections by qualified personnel are critical. Adhering to these certifications helps minimize risks, ensuring the safety of operators and the operational longevity of overhead cranes.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “overhead crane”
Overhead cranes are critical in industrial settings for moving heavy loads with precision and safety. Here are key technical parameters:
1. Load Capacity: Maximum weight the crane can lift, often measured in tons (e.g., 1 ton to 400 tons).
2. Span: The horizontal distance between the crane’s runways. This typically ranges from a few meters to over 30 meters depending on the application.
3. Lift Height: The vertical distance the hook or lifting mechanism can travel, important for clearance levels, often varying from a few meters to over 50 meters.
4. Lift Speed: The rate at which the crane can hoist and lower its load, usually measured in meters per minute. Varies depending on the load and operating conditions.
5. Travel Speed:
– Trolley Travel Speed: Speed at which the trolley moves along the bridge, typically ranging from 20 to 100 meters per minute.
– Bridge Travel Speed: Speed at which the entire bridge moves along the runway, typically 20 to 200 meters per minute.
6. Duty Cycle/Classification: The operational time and frequency the crane can sustain without overheating or wear, categorized as A1 to A8 according to ISO standards or equivalent classifications.
7. Control System:
– Manual Control: Operated via pendant or radio remote.
– Automated Control: Includes programmable logic controllers (PLCs) for precision operations.
8. Power Supply: Voltage and phase of electrical supply, typically 3-phase, ranging from 208V to 460V or higher.
9. Drive Type:
– Single Girder: One main beam, suitable for light to moderate loads.
– Double Girder: Two main beams, offering greater strength for heavier loads and higher lift heights.
10. Safety Features: Includes overload protection, emergency stop controls, limit switches, and anti-collision systems.
11. Environmental Resistance: Adaptations for specific conditions such as dust, extreme temperatures, or corrosive environments.
Understanding these parameters ensures proper crane selection and safe, efficient operation in a variety of industrial applications.
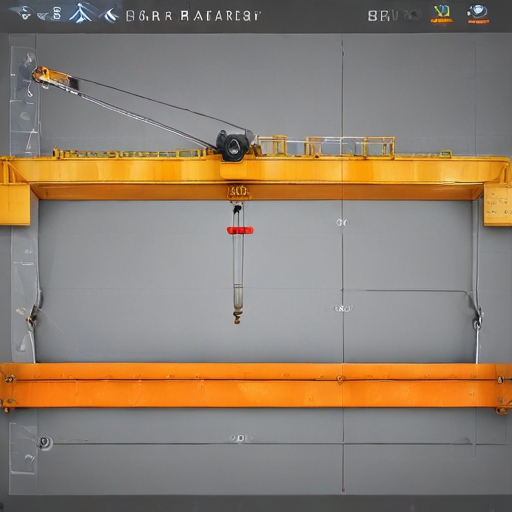
List Product features of “overhead crane”
Certainly! Here are the key product features of an overhead crane:
1. Load Capacity: Overhead cranes come in varying load capacities, typically ranging from 1 to 100 tons or more, enabling the lifting of heavy and bulky items.
2. Span: The span of an overhead crane, which is the distance between the runway rails, can be customized to fit the dimensions of the workspace.
3. Lift Height: These cranes can be designed to accommodate different lift heights, depending on the needs of the facility.
4. Crane Runway: The crane runway can be made of various materials and be of different lengths to suit the operational space, often spanning the entire facility.
5. Hoist: Powered by electricity or hydraulics, the hoist is capable of precise vertical lifting and lowering of loads.
6. Bridge: The bridge is the horizontal beam that spans the gap between the runways and supports the hoist and trolley. It can be single or double girder.
7. Trolley: The trolley moves the hoist along the bridge, facilitating horizontal movement.
8. Control Systems: These can include wired pendants, wireless remote controls, or automated systems for ease of operation.
9. Safety Features: Overhead cranes are equipped with safety mechanisms including emergency stop buttons, limit switches, overload protection, and anti-sway technology.
10. Durability: Constructed with high-strength materials like steel for robust performance and longevity.
11. Customization: Overhead cranes can be tailored to specific industry requirements, such as magnetic lifts for the steel industry or cleanroom standards for pharmaceuticals.
12. Installation and Maintenance: Designed for straightforward installation and routine maintenance to ensure optimal operational uptime.
13. Flexibility: Suited for various applications across industries like manufacturing, construction, warehousing, and shipping.
14. Energy Efficiency: Modern overhead cranes often incorporate energy-saving technologies to reduce energy consumption.
15. Ergonomics: Designed to minimize operator strain and improve workplace safety.
These features collectively enhance the efficiency, safety, and performance of material handling operations in various industrial settings.

List Application of “overhead crane”
Applications of Overhead Cranes
Overhead cranes, also known as bridge cranes, are essential in various industries for lifting and moving heavy loads with precision and safety. Here are some key applications:
1. Manufacturing: Used for moving heavy components across the production line. They’re critical in assembling large machinery, automotive manufacturing, and in heavy equipment plants.
2. Warehousing and Distribution: Overhead cranes help in the efficient handling of large, bulky items, streamlining inventory management and loading/unloading processes.
3. Construction: Involved in transporting heavy construction materials such as steel beams, concrete blocks, and pre-fabricated sections. They ensure timely placement and movement of materials on construction sites.
4. Shipbuilding: Facilitate the movement and placement of massive components such as hull sections, engines, and other critical parts. They are instrumental in dry docks and shipyards.
5. Railway Maintenance: Used for lifting and placing railway components like tracks, engines, and carriages, ensuring maintenance tasks are performed with precision.
6. Steel Mills: Overhead cranes are essential for handling raw materials, transporting molten metal, and moving heavy steel products through various stages of production.
7. Aerospace: Aid in the precise assembly of large aircraft parts, moving heavy and delicate components during production and maintenance.
8. Mining: Used to lift and transport mining equipment and raw materials, facilitating efficient operations within mines.
9. Power Plants: Support in lifting and positioning heavy turbines, generators, and other large-scale equipment during installation and maintenance.
10. Automotive: Essential in moving and positioning heavy dies and molds in automotive plants, and ensuring efficient assembly line production.
11. Paper Mills: Used to handle large rolls of paper and other heavy materials, aiding in the production process.
Through their versatility and capacity to handle substantial weights, overhead cranes are indispensable across diverse sectors, enhancing productivity, safety, and operational efficiency.
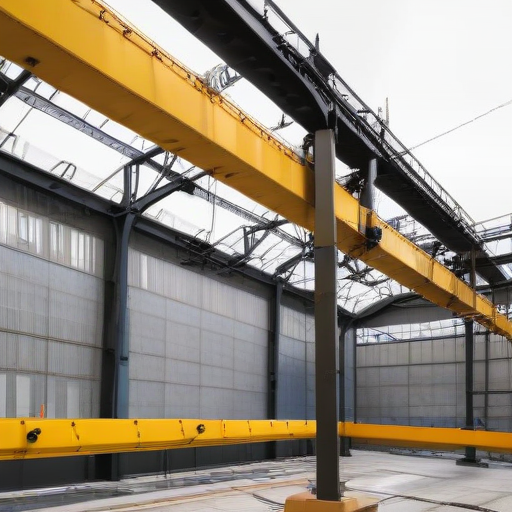

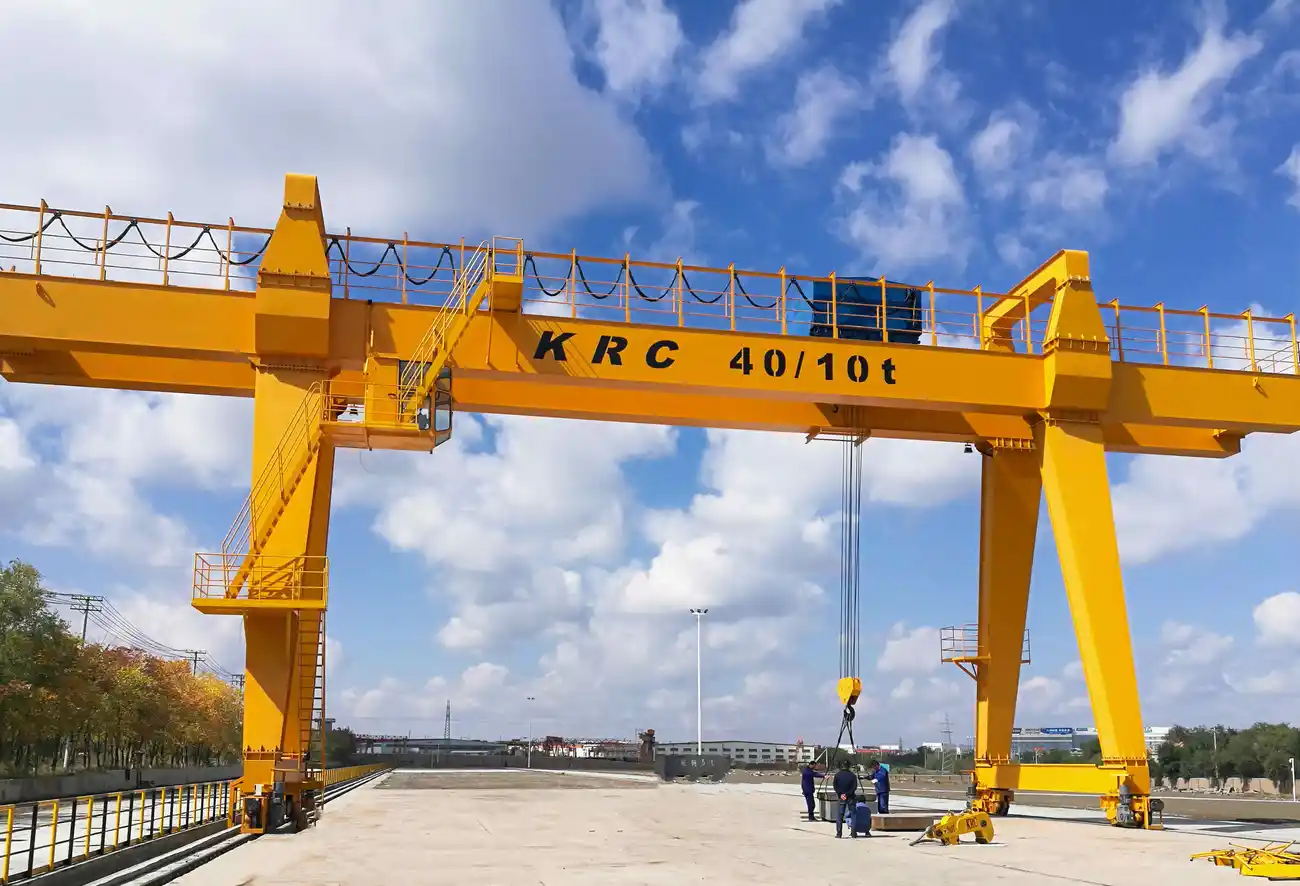
List Various Types of “overhead crane”
Overhead cranes are essential equipment in many industries for lifting and transporting heavy materials. Here are the various types:
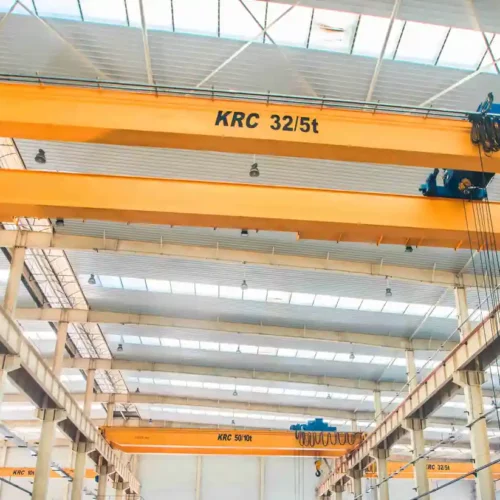
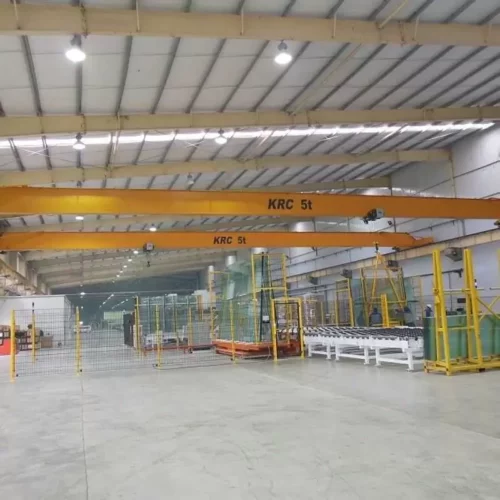
1. Bridge Cranes:
– Single Girder Bridge Crane: Utilizes one girder for support and is ideal for light to moderate lifting.
– Double Girder Bridge Crane: Features two girders for increased strength and capacity, suitable for heavy-duty applications.
– Underhung Bridge Crane: The crane’s runway is attached to the ceiling structure, saving floor space.
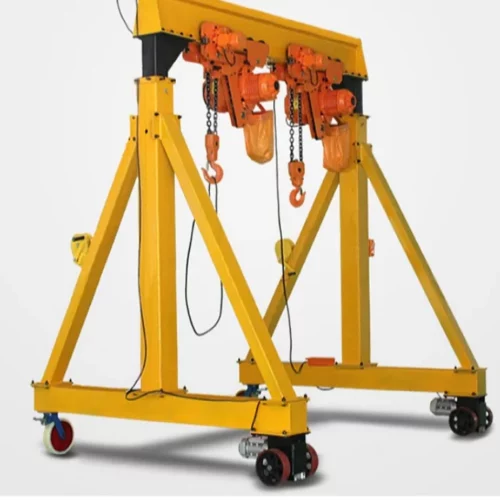
2. Gantry Cranes:
– Full Gantry Crane: Spans the entire width of the work area and is supported by two legs.
– Semi-Gantry Crane: Has one leg on wheels and the other side on a runway.
– Portable Gantry Crane: Smaller and mobile, used for lighter loads and flexible operations.
3. Jib Cranes:
– Freestanding Jib Crane: Installed independently on the shop floor, offers 360-degree rotation.
– Wall-Mounted Jib Crane: Attached to a wall or column, provides a half-circle rotation.
– Articulating Jib Crane: Features multiple arms for increased maneuverability.
4. Monorail Cranes:
– operates on a single runway system, ideal for simple and straightforward material transport along a fixed path.
5. Workstation Cranes:
– Designed for lighter loads with modular setups to suit small to medium workspaces, improving efficiency.
6. Top Running Vs. Under Running Cranes:
– Top Running Cranes: The crane runs on rails mounted on top of the runway beams, suitable for heavier loads and larger spans.
– Under Running Cranes: Runs on the bottom flange of runway beams suspended from the overhead structure, ideal for maximizing floor space.
Each type serves different needs based on load, space, and operational requirements. Understanding these varieties helps in selecting the right crane for specific industrial applications.
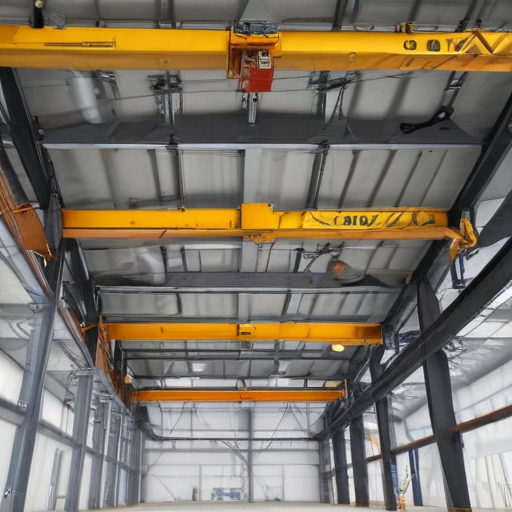

overhead crane Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Overhead cranes are essential for various industrial applications, and accessorizing, upgrading, or customizing them can significantly enhance their performance and lifespan. Here are some key accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options:
1. End Trucks and Trolleys: Upgraded end trucks and trolleys ensure smoother travel and better load distribution, enhancing efficiency and reducing wear and tear.
2. Custom Runs and Spans: Tailoring the crane’s span and runway length to specific operational needs ensures optimal coverage and efficiency within the workspace.
3. Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): VFDs provide better control over crane speed and movement, reducing mechanical stress and improving safety.
4. Remote Controls and Automations: Wireless remote controls and automated systems offer precision, reduce manual labor, and enhance operator safety.
5. Specialized Lifting Attachments: Custom lifting attachments like grab buckets, spreader beams, and magnets can be designed to handle specific materials more effectively.
6. Anti-Sway Technologies: Advanced anti-sway systems minimize load swing, ensuring safer and more precise placement of materials.
7. Load Monitoring Systems: Real-time load monitoring systems improve safety by providing precise measurements and preventing overloads.
8. Weather Protection: For outdoor cranes, weather-resistant coatings and protective covers can extend lifespan and functionality under harsh conditions.
9. Safety Upgrades: Features like emergency stop systems, warning lights, and audible alarms enhance operational safety.
10. Maintenance Walkways and Platforms: Custom walkways and platforms simplify maintenance tasks, ensuring quicker and safer inspections and repairs.
11. Energy-Saving Solutions: Implementing regenerative braking systems or energy-efficient motors can reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
Custom manufacturing options ensure that specific industry needs and spatial constraints are addressed, providing a tailored solution that optimizes productivity and safety. By carefully selecting appropriate upgrades and accessories, businesses can significantly enhance the performance and reliability of their overhead cranes.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “overhead crane”
Quality Control in Overhead Crane Manufacturing:
1. Material Selection:
– Use high-grade steel and components.
– Verify material certificates.
2. Design Verification:
– Utilize CAD software for accurate design.
– Conduct stress and load testing simulations.
3. Supplier Evaluation:
– Select reliable suppliers.
– Inspect incoming materials and components.
4. Precision Machining:
– Use CNC machines for precise manufacturing.
– Conduct dimensional inspections.
5. Welding Quality:
– Employ certified welders.
– Perform non-destructive testing (NDT) such as ultrasonic or radiographic testing.
6. Assembly Inspection:
– Ensure proper alignment of components.
– Check fastening and joining integrity.
7. Functional Testing:
– Run load tests to verify capacity.
– Test safety features like limit switches and brakes.
8. Certification:
– Adhere to relevant standards (e.g., ASME, OSHA).
– Obtain third-party certification if required.
Manufacturing Process of Overhead Crane:
1. Design and Planning:
– Define crane specifications.
– Create detailed blueprints and plan production schedules.
2. Material Procurement:
– Source high-quality steel and other materials.
– Inspect and store materials appropriately.
3. Cutting and Machining:
– Cut steel beams and plates to size using laser cutters or plasma torches.
– Machine components for precise fits.
4. Welding and Fabrication:
– Assemble main girder, end trucks, and other structural components.
– Ensure high-quality welds through robotic or manual welding.
5. Mechanical Assembly:
– Attach trolley, hoist, and other mechanical parts.
– Install motors, gears, and bearings.
6. Electrical Installation:
– Wire control systems and safety mechanisms.
– Install power supply and control panels.
7. Painting and Finishing:
– Apply anti-corrosive coatings.
– Paint according to customer specifications.
8. Testing and Inspection:
– Conduct load and safety tests.
– Perform final inspections to ensure compliance with design and safety standards.
9. Packaging and Delivery:
– Disassemble into transportable sections if necessary.
– Pack securely and arrange for transport to the customer site.
10. Installation and Commissioning:
– Assemble and install at the customer’s facility.
– Perform on-site testing and operator training.
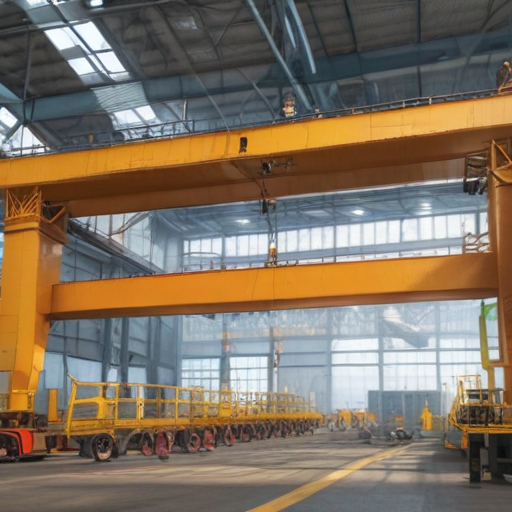

How to use “overhead crane”
Using an overhead crane involves strategically moving heavy or bulky items within a confined space, commonly found in warehouses, factories, and construction sites. Here’s how to use one safely and efficiently:
Preparation
1. Training: Ensure operators are adequately trained and certified.
2. Inspection: Conduct a thorough inspection of the crane, including checking for any visible damages, fluid levels, wiring, and testing the controls.
3. Work Area: Clear the area of any obstructions, and communicate with team members about crane operations.
Operation
1. Control Console: Familiarize yourself with the control panel, which typically includes a joystick or buttons for moving the crane.
2. Hook and Load: Safely attach the load to the crane’s hook using appropriate lifting slings or devices. Double-check the security of the load.
3. Lifting: Gently lift the load a few inches to ensure it’s properly balanced. Make adjustments if necessary.
4. Movement:
– Vertical: Use the control to lift or lower the load vertically.
– Horizontal: Use the control panel to move the crane along the overhead rails to the desired location.
5. Maneuvering: Move slowly to avoid swinging the load, which could become a safety hazard.
Safety Measures
1. Load Limits: Never exceed the crane’s maximum load capacity.
2. Communication: Use hand signals or radios to communicate with team members, ensuring everyone is aware of the crane’s movements.
3. Emergency Stop: Keep hands near the emergency stop button in case you need to halt operations immediately.
4. Observation: Continuously monitor the load and path, making adjustments as needed.
Concluding Operations
1. Unload: Carefully place the load in the designated area and detach it from the crane hook.
2. Shutdown: Turn off the crane and conduct a post-operation inspection.
By following these steps, you can safely and efficiently use an overhead crane.
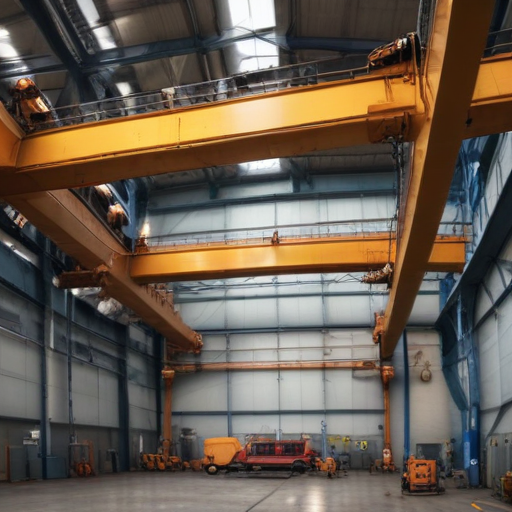

“overhead crane” Comparative Analysis
An overhead crane, often referred to as a bridge crane, is a critical piece of equipment in manufacturing, warehousing, and construction industries, designed for lifting and transporting heavy materials with precision and efficiency. These cranes generally consist of parallel runways with a traveling bridge spanning the gap. Here’s a comparative analysis focusing on three common types: single-girder, double-girder, and gantry cranes.
Single-Girder Overhead Cranes:
– Cost-Effective: Typically less expensive due to simpler construction.
– Application: Suitable for light to moderate lifting (up to 20 tons).
– Structure: One main bridge girder. Easier to install and maintain.
– Space Utilization: Limited hook height due to the hoist being under the girder.
Double-Girder Overhead Cranes:
– Load Capacity: Higher lifting capacity (up to several hundred tons). Better for heavy-duty applications.
– Stability: Greater stability and rigidity due to dual girders.
– Structure: Two parallel girders, allowing the hoist to be placed between them, providing improved hook height.
– Customization: Greater flexibility for custom features and attachments.
Gantry Cranes:
– Mobility: Feature legs on wheels or a rail system, making them versatile for indoor and outdoor use.
– Cost and Installation: Can be more economical as they don’t require a runway structure fixed to building columns.
– Capacity and Span: Available in single and double-girder models, they can handle various capacities and spans.
– Application: Ideal for outdoor applications, such as shipyards and large infrastructure projects.
Conclusion:
The choice between single-girder, double-girder, and gantry cranes depends on specific operational requirements, including load capacity, working environment, and budget considerations. Single-girder cranes offer a cost-effective solution for lighter loads, while double-girder cranes are preferable for heavy-duty lifting due to their enhanced stability and higher capacity. Gantry cranes add flexibility and are particularly advantageous for applications without existing runway structures or for outdoor use. Understanding these differences ensures the selection of an optimal crane type tailored to specific needs.
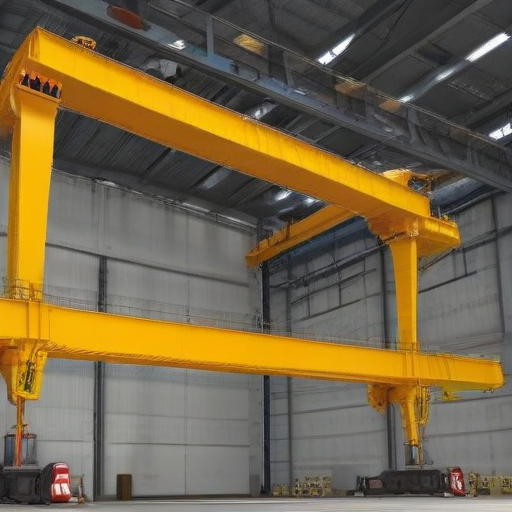

“overhead crane” Warranty and Support
Warranty and Support for Overhead Cranes
Warranty:
Our overhead cranes come with a comprehensive warranty to provide you with peace of mind and ensure the longevity of your investment. We offer a standard warranty period of two years from the date of installation. This warranty covers defects in material and workmanship under normal use and service conditions. Should any component of the crane fail due to a manufacturing defect within this period, we will repair or replace the affected parts at no cost to you.
Key Features:
1. Coverage of all major components, including the hoist, motor, and control systems.
2. Free repairs or replacements for defective parts.
3. Detailed terms and conditions outlined in the warranty document provided at the time of purchase.
Support:
To maximize the efficiency and lifespan of your overhead crane, we offer robust support services that cater to your needs throughout the product’s lifecycle. Our dedicated support team is available 24/7 to assist you with any technical issues or inquiries.
Support Services Include:
1. Installation Assistance: Professional installation services to ensure safe and optimal setup.
2. Routine Maintenance: Scheduled maintenance visits to keep your crane in peak operating condition.
3. Technical Support: Round-the-clock technical support via phone, email, or on-site assistance for troubleshooting and repairs.
4. Training: Comprehensive training programs for your operators and maintenance staff to ensure safe and efficient crane operation.
5. Spare Parts: A readily available inventory of spare parts to minimize downtime in case of repairs.
Our commitment is to provide exceptional customer service and technical support, ensuring your overhead crane operates smoothly and efficiently for years to come. For detailed warranty terms, service plans, and support inquiries, please contact our customer service team or visit our website.

List “overhead crane” FAQ
Certainly! Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about overhead cranes:
1. What is an overhead crane?
An overhead crane is a type of lifting equipment designed to move heavy loads horizontally along overhead rails. They are commonly used in industrial environments like warehouses, manufacturing facilities, and construction sites.
2. What are the main types of overhead cranes?
– Bridge Cranes: Consist of a single or double bridge that spans across two rails, offering wide-area lifting.
– Gantry Cranes: Similar to bridge cranes but supported on legs that move on wheels or rails, suitable for both indoor and outdoor use.
– Jib Cranes: Feature a horizontal jib arm fixed to a wall or floor-mounted pillar, providing localized lifting.
3. What are the primary components of an overhead crane?
– Hoist: The device that performs the actual lifting and lowering.
– Trolley: Moves horizontally along the crane’s bridge, carrying the hoist.
– Bridge: Spans the crane runway and holds the trolley.
– Runway: The rails or track supporting the crane’s movement.
4. What are the benefits of using an overhead crane?
– Efficient Material Handling: Improved workflow and reduced manual labor.
– Enhanced Safety: Minimizes the risk of workplace injuries.
– Space Utilization: Frees up floor space for other operations.
5. How is load capacity determined?
Load capacity is calculated based on the design specifications of the crane and the manufacturer’s guidelines. Always adhere to the specified load limits to ensure safety.
6. What maintenance is required?
– Regular inspections for wear, deformation, and corrosion.
– Lubrication of moving parts.
– Electrical system checks.
– Compliance with the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule and regulatory standards.
7. Are there safety regulations for operating overhead cranes?
Yes, safety regulations are set by organizations like OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) to ensure safe operating procedures.
8. What training is needed for operators?
Operators must undergo specialized training to understand the operation, safety practices, and emergency procedures associated with overhead cranes. Certification may also be required.
9. How can I ensure the longevity of my overhead crane?
Regular maintenance, proper usage, and adherence to load capacities can significantly extend the lifespan of an overhead crane. Investing in quality components and timely upgrades is also beneficial.
This concise overview addresses common questions about overhead cranes, emphasizing their types, benefits, maintenance, and safety considerations.

Top 10 FAQ with answer about overhead crane for Buyer Sourcing from China
Sure, here are the top 10 frequently asked questions (FAQ) for buyers sourcing overhead cranes from China along with concise answers:
1. What Types of Overhead Cranes Are Available?
– Overhead cranes typically come in single-girder and double-girder configurations. They can also be categorized as bridge cranes, gantry cranes, and jib cranes.
2. What Are the Key Specifications to Consider?
– Key specifications include load capacity, span length, lifting height, duty cycle, and power source requirements.
3. Are Chinese Overhead Cranes Compliant with International Standards?
– Many Chinese manufacturers comply with international standards like ISO, DIN, FEM, and ANSI. Always verify the specific certifications of each manufacturer.
4. What Is the Lead Time for Delivery?
– Lead times vary but typically range from 30 to 90 days depending on the crane’s complexity and the manufacturer’s production schedule.
5. What Are the Main Components of an Overhead Crane?
– Main components include the bridge, hoist/trolley, runway, end trucks, and control system. Each part should be considered carefully for quality and compatibility.
6. Can the Cranes Be Customized?
– Yes, Chinese manufacturers often offer customization to meet specific operational needs such as different lifting capacities, spans, and special environmental considerations.
7. What Are the Warranty and After-Sales Service Terms?
– Warranties typically range from 1 to 2 years. Confirm the manufacturer’s policies on spare parts, technical support, and on-site service.
8. How Is Quality Assurance Managed?
– Reputable manufacturers have rigorous QA processes including material inspection, assembly tests, and pre-shipment testing. Request QA documentation for your peace of mind.
9. What Are the Payment Terms?
– Common payment terms include T/T (Telegraphic Transfer), L/C (Letter of Credit), and DP (Documents against Payment). Initial deposits followed by balance payments upon shipment are typical.
10. How Do I Ensure Reliable Shipping and Handling?
– Collaborate with experienced freight forwarders familiar with exporting heavy machinery from China. Confirm insurance and proper packaging to avoid transit damage.
By addressing these fundamental questions, buyers can mitigate risks and ensure a smoother procurement process when sourcing overhead cranes from China.







