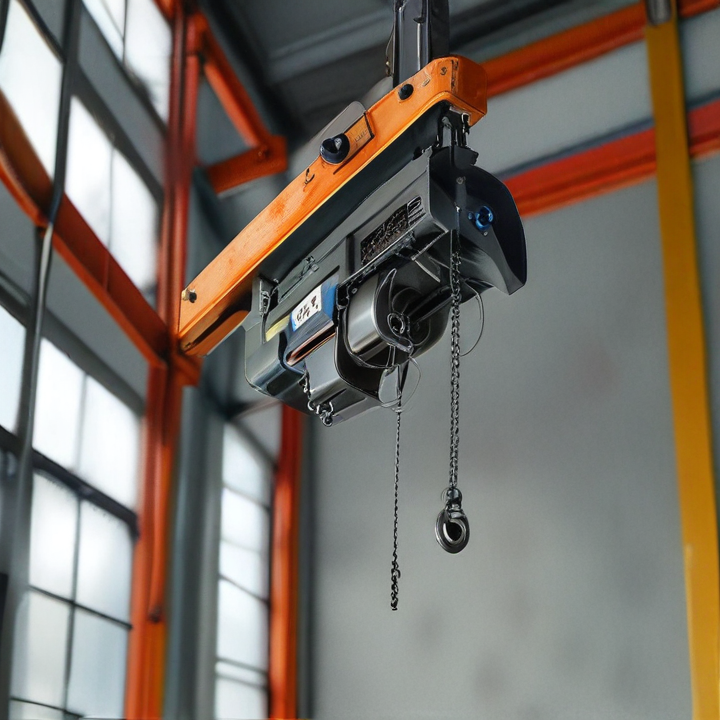
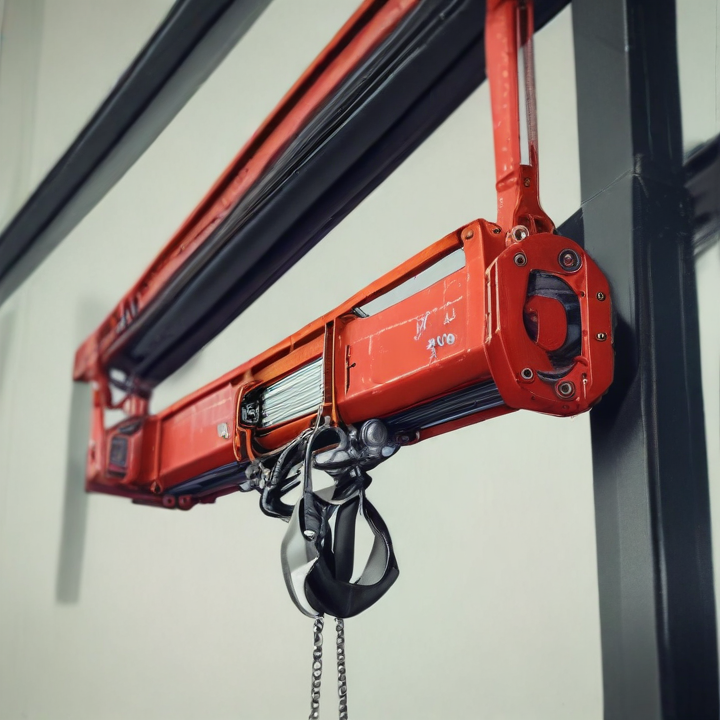
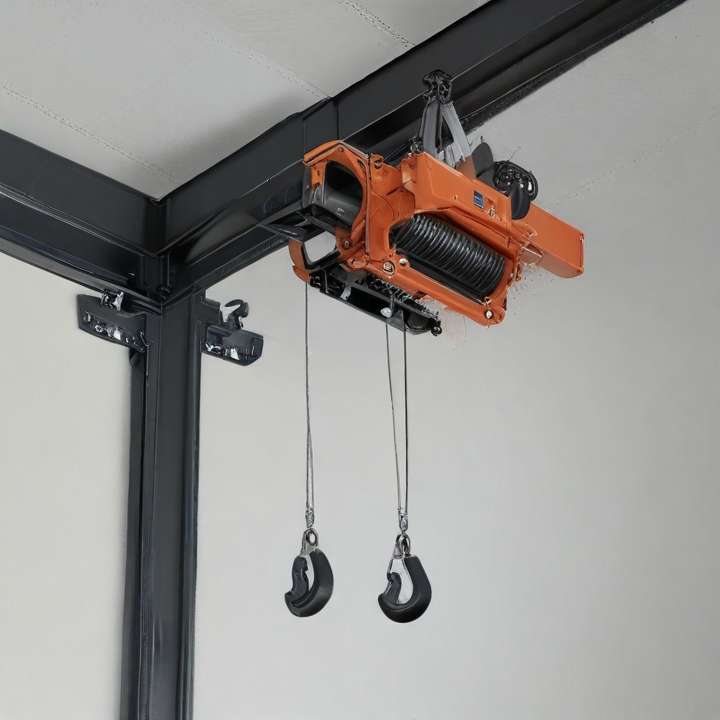
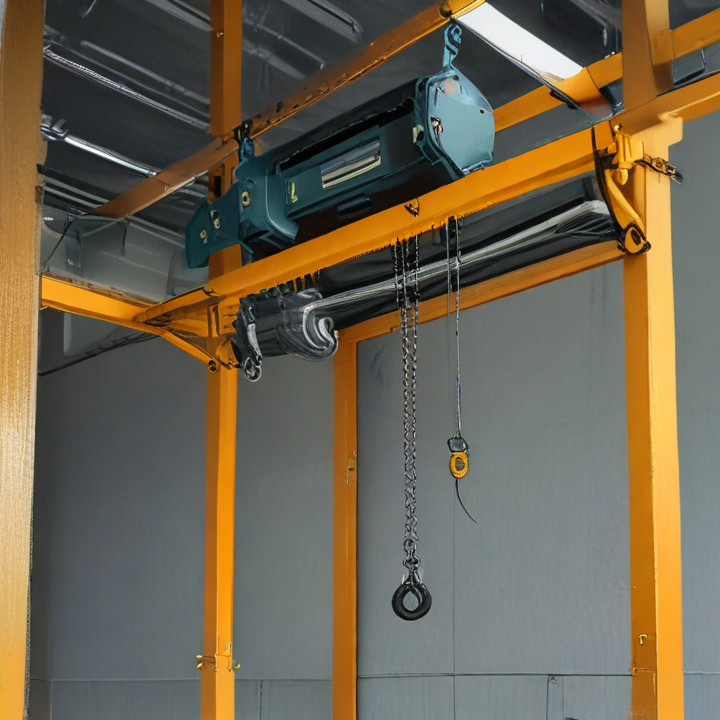
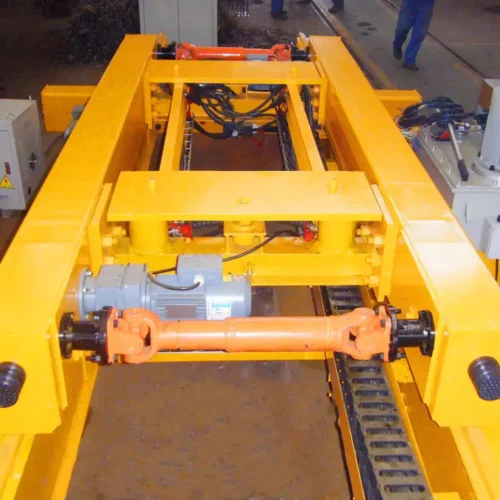
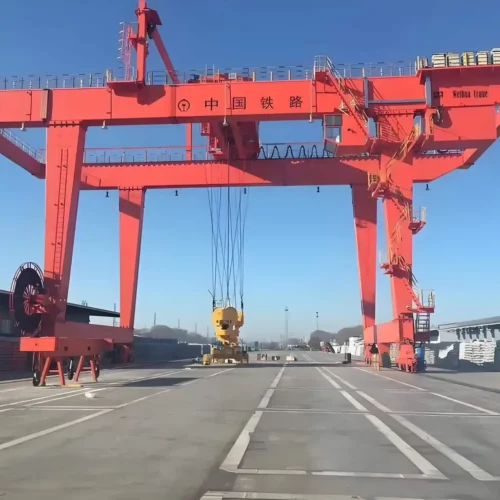
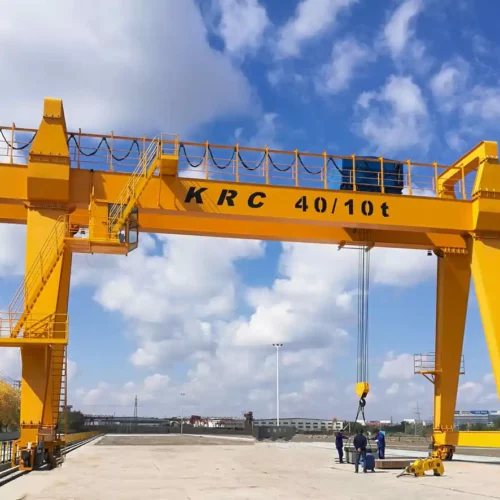
overhead hoist Safety Certifications
Overhead hoists are integral to many industrial applications, making their safety certifications critically important to ensure secure operation. Some primary safety certifications and standards for overhead hoists include:
1. OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration): In the United States, OSHA regulations (such as 29 CFR 1910.179 for overhead and gantry cranes) establish essential safety requirements for overhead hoists. Compliance with OSHA standards is mandatory for workplace safety.
2. ASME B30.16 & B30.17: The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) provides detailed safety standards for overhead hoists, which encompass electric and air-powered hoists (B30.16) as well as hand-operated hoists (B30.17). These standards outline guidelines for design, maintenance, inspection, and operation.
3. ANSI/ASME HST Standards: The HST series provides performance requirements for various types of hoists, including electric (HST-4) and manual (HST-3) models. They specify criteria for load tests, durability, and operational safety.
4. CE Marking: In the European Union, overhead hoists must meet the Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, signified by CE marking. This indicates the equipment complies with EU safety, health, and environmental protection requirements.
5. CSA (Canadian Standards Association): In Canada, CSA standards like CSA B167 regulate the safety of overhead traveling cranes, which cover electrically powered hoists and related equipment.
6. ISO 9001: While not specific to hoists, an ISO 9001 certification for manufacturers indicates adherence to stringent quality management systems, enhancing the reliability and safety of the hoists produced.
Adhering to these certifications ensures that overhead hoists operate safely and efficiently, mitigates risks, and fosters compliance with regional and international safety regulations. Regular training, inspections, and maintenance based on these standards are crucial for ongoing operational safety.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “overhead hoist”
An overhead hoist is a versatile piece of lifting equipment used in various industrial applications to move heavy loads with precision and efficiency. Here are the primary technical parameters for an overhead hoist:
1. Load Capacity: The maximum weight the hoist can lift, typically measured in tons or kilograms, ranging from small capacities (example: 0.5 ton) to heavy-duty capacities (10 tons or more).
2. Lift Height: The vertical distance the hoist can travel, measured in meters or feet. Standard models might offer lift heights from 3 to 30 meters, but custom heights are possible.
3. Lift Speed: The speed at which the hoist can raise or lower the load, usually expressed in meters per minute (m/min). Lift speed can vary widely depending on the model and application.
4. Power Source: The type of power used, which could be electric, pneumatic, or manual. Electric hoists are common in industrial settings, with voltages typically ranging from 110V to 440V, and phases (single-phase or three-phase).
5. Duty Cycle/Class: The hoist’s operational classification, defined by cycles per hour and percentage of time it can operate without cooling down. Common classifications include H2 (light duty), H3 (intermediate duty), and H4 (heavy duty).
6. Motor Power: The power of the hoist’s motor, usually measured in kilowatts (kW) or horsepower (HP), which affects the lifting and lowering speed.
7. Control System: The type of control used, such as pendant control, wireless remote control, or integrated into an automated system.
8. Hook Approach: The minimum distance between the hook and the hoist body or ceiling, affecting the clearance required for operation.
9. Trolley Type: The type of trolley used, which can be manual push, geared, or motor-driven, and whether it runs on a single or double girder setup.
10. Safety Features: Includes overload protection, emergency stop functions, and limit switches to prevent over-travel of the hoist.
11. Environmental Conditions: Specifications regarding operational temperature ranges, humidity levels, and any additional requirements for hazardous or corrosive environments.
These parameters collectively define the capabilities and suitability of an overhead hoist for specific tasks, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
List Product features of “overhead hoist”
An overhead hoist, commonly used in industrial and construction settings for lifting and moving heavy loads, boasts several key features designed to enhance its functionality, safety, and ease of operation:
1. Load Capacity: Ranges from a few hundred kilograms to several tons, accommodating various lifting needs.
2. Lifting Mechanism: Typically includes an electric motor, manual chain, or pneumatic system for efficient lifting and lowering.
3. Durable Construction: Made from robust materials such as hardened steel to withstand heavy use and harsh environments.
4. Hoist Speed: Variable speed options for precise control during lifting and lowering operations.
5. Safety Features: Includes overload protection, emergency stop buttons, and automatic braking systems to prevent accidents and ensure user safety.
6. Height of Lift: Customizable lifting heights to suit specific applications, often up to several tens of meters.
7. Mounting Options: Can be mounted on fixed or adjustable frames, ceiling structures, or integrated into crane systems for flexibility in different settings.
8. Control System: Available with pendant control, wireless remote control, or integrated control panels for user convenience and operational safety.
9. Swivel Hooks: Equipped with 360-degree rotating hooks to facilitate easy attachment and positioning of loads.
10. Compact Design: Space-saving configurations that maximize floor space and enhance maneuverability within confined areas.
11. Ease of Maintenance: Features like accessible components and simplified designs for routine checks and maintenance tasks.
12. Versatility: Suitable for various applications across industries, including manufacturing, warehousing, construction, and more.
13. Noise Reduction: Some models incorporate noise-dampening technology to minimize operational noise for a quieter work environment.
14. Energy Efficiency: Designed to minimize energy consumption while maximizing lifting power and efficiency.
These features collectively ensure that overhead hoists are reliable, user-friendly, and well-equipped to handle demanding lifting operations while prioritizing safety and efficiency.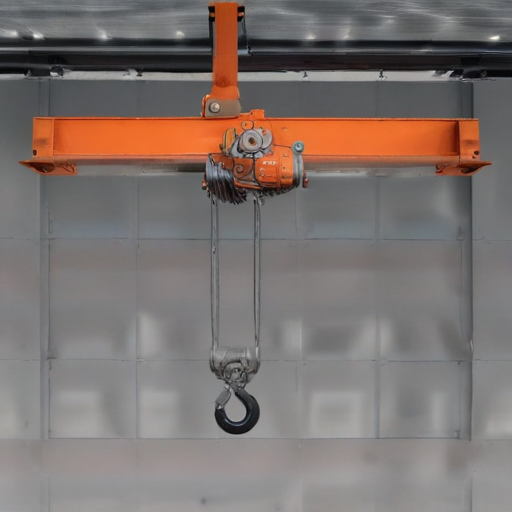
List Application of “overhead hoist”
Overhead hoists are powerful lifting devices used extensively in various industries to enhance efficiency and ensure safety when handling heavy loads. Below are some key applications of overhead hoists:
1. Manufacturing and Assembly Lines: Overhead hoists streamline the movement of heavy components, enhancing productivity and reducing manual labor in assembly processes. They enable precise positioning of parts for assembly, welding, or machining operations.
2. Warehousing and Distribution Centers: These facilities use overhead hoists to move bulky items, pallets, and containers, optimizing space utilization and minimizing the risk of injury during handling.
3. Construction Sites: Overhead hoists are indispensable for lifting heavy construction materials like steel beams, concrete blocks, and other structural components, facilitating safer and faster construction processes.
4. Automotive Industry: In automotive manufacturing and repair, overhead hoists are employed to lift engines, transmissions, and car bodies. This ensures precise and safe movement of heavy parts during assembly and maintenance.
5. Shipyards and Docks: Overhead hoists are used for loading and unloading heavy cargo, components, and ship parts. They assist in maintenance tasks by lifting heavy machinery and structural elements.
6. Mining and Extraction Operations: In mining, overhead hoists transport heavy equipment, extracted minerals, and machinery, contributing to efficient material handling from extraction to processing stages.
7. Energy Sector (Oil, Gas, and Wind Energy): These industries use overhead hoists to lift heavy equipment, such as turbines, generators, and pipelines, enhancing efficiency and safety during installation and maintenance.
8. Aerospace Industry: Overhead hoists assist in the assembly and maintenance of aircraft by positioning large and heavy components, such as wings and engines, accurately and safely.
9. Healthcare: In hospitals and care facilities, overhead hoists are used to assist in patient handling and transfer, reducing the risk of injury to both patients and caregivers.
In summary, overhead hoists find application across multiple industries, promoting safer, more efficient, and precise handling of heavy loads.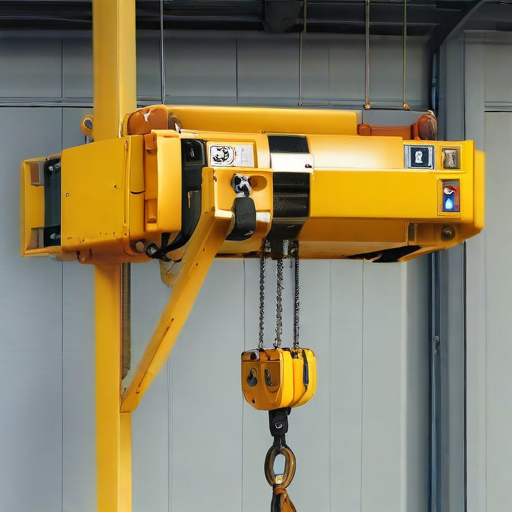
List Various Types of “overhead hoist”
Overhead hoists are crucial tools for lifting and moving heavy loads in various industrial settings. Here are some of the main types of overhead hoists:
1. Electric Chain Hoists:
– Common in both industrial and commercial applications.
– Utilize an electric motor to lift loads via a chain.
– Known for their robustness and efficiency.
2. Electric Wire Rope Hoists:
– Designed for heavier loads and more industrial applications.
– Use a wire rope instead of a chain, offering increased durability and strength.
– Suitable for higher vertical lifts.
3. Manual Chain Hoists:
– Operated by manually pulling a chain.
– Ideal for smaller projects where electrical power is not available.
– Portable and versatile but require more physical effort.
4. Pneumatic Hoists:
– Powered by compressed air.
– Useful in hazardous environments where spark prevention is critical.
– Offer good speed control and are durable in harsh conditions.
5. Lever Hoists:
– Operated using a lever that is manually moved to lift the load incrementally.
– Extremely portable and useful for precise lifting and positioning.
6. Hydraulic Hoists:
– Use hydraulic power to lift loads.
– Common in automotive and heavy manufacturing sectors.
– Offer high load capacity and smooth operation.
7. Explosion-Proof Hoists:
– Designed for environments with flammable gases or dust.
– Constructed with materials that minimize spark risk.
– Often found in chemical plants and refineries.
8. Monorail Hoists:
– Move along a single, fixed path typically on a beam.
– Useful for transporting materials along a linear route in production lines.
9. Trolley Hoists:
– Mounted on trolleys that run on overhead rails.
– Can be manual, electric, or air-powered.
– Provide horizontal mobility in addition to vertical lifting.
10. Jib Cranes with Hoists:
– Consist of a rotating arm (jib) with an attached hoist.
– Offers localized lifting and positioning capability.
– Suitable for workshops and assembly areas.
Each type is selected based on specific needs such as load capacity, application environment, and power source availability.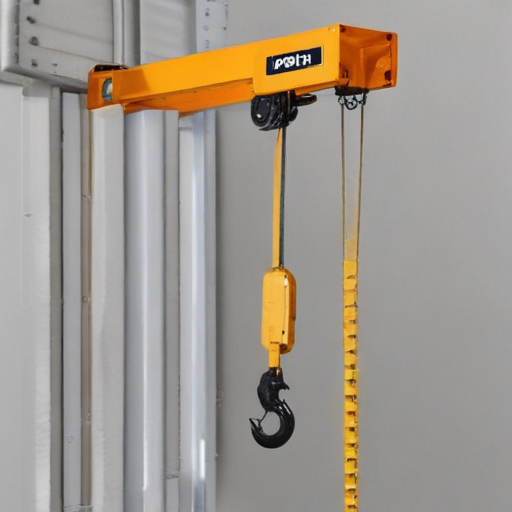
overhead hoist Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Upgrading your overhead hoist with specialized accessories and custom manufacturing options can significantly enhance its performance, safety, and versatility. Here are some key considerations and options for optimizing your overhead hoist:
1. Load Control Accessories:
– Wireless Remote Controls: Offer convenience and enhance operator safety by allowing control from a distance.
– Variable Speed Drives: Provide precise control over hoist speed, improving handling and reducing wear.
2. Safety Enhancements:
– Overload Protection Devices: Prevent hoist operation when the load exceeds safe limits.
– Anti-sway Systems: Minimize load swing, increasing safety and precision.
3. Rigging Attachments:
– Custom Lifting Beams: Engineered for specific tasks, improving load management and distribution.
– Special Hooks and Clamps: Designed for unique lifting requirements, ensuring secure attachment.
4. Environmental Adaptations:
– Weatherproof Enclosures: Protect hoist components from harsh environments.
– Explosion-Proof Designs: Safe operation in hazardous settings, such as chemical plants.
5. Material Handling Integration:
– Automated Systems: Interface with integrated conveyor belts or robotic systems for improved workflow efficiency.
– Custom Trolley Designs: Tailored to the specific layout and load requirements of your facility.
6. Performance Upgrades:
– High-Capacity Hoist Motors: Increase lifting capacity and speed.
– Advanced Control Systems: Implement programmable logic controllers (PLCs) for automated and precise operations.
7. Maintenance and Longevity:
– Lubrication Systems: Automated systems to ensure optimal performance and reduce downtime.
– Wear-Resistant Cables and Chains: Extend the lifespan of critical components.
Investing in these upgrades and accessories not only boosts operational efficiency but also enhances safety and reduces long-term costs. Custom manufacturing options provide solutions tailored to your specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your overhead hoist system.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “overhead hoist”
Quality Control for Overhead Hoists
1. Material Inspection: Ensure that all raw materials, such as steel and alloys, meet industry standards.
2. Dimensional Checks: Verify that all components are machined to precise dimensions.
3. Welding Inspections: Perform radiographic or ultrasonic testing to ensure strong, defect-free welds.
4. Load Testing: Conduct load tests to certify that the hoist can handle specified weights safely.
5. Functionality Tests: Test operational functions like lifting, lowering, and braking.
6. Electrical Testing: Check the integrity and functionality of electrical components, including controllers and motors.
7. Paint and Finish Quality: Inspect paint and finishes for corrosion resistance and adherence.
8. Final Inspection: Conduct a comprehensive check for overall quality and performance.
9. Documentation Review: Ensure all quality control documents are complete and compliant.
Manufacturing Process of Overhead Hoists
1. Design and Engineering: Create detailed designs and simulations using CAD software to meet specific load and operational requirements.
2. Material Procurement: Source high-quality materials that meet engineering specifications and standards.
3. Cutting and Shaping: Use laser cutting, CNC machining, and other methods to shape the raw materials into components.
4. Welding and Assembly: Weld parts together and assemble sub-components, such as the hoist frame and lifting mechanism.
5. Machining: Machine critical parts to precise tolerances, ensuring smooth operation and durability.
6. Electrical Installation: Install electrical systems, including motors, control units, and wiring.
7. Surface Treatment: Apply coatings, paint, or other finishes for corrosion resistance and aesthetics.
8. Quality Assurance: Conduct extensive inspections and tests as outlined in the Quality Control section.
9. Packaging and Dispatch: Carefully package the hoist for storage or shipping, ensuring it is protected from damage.
10. Documentation and Support: Provide detailed manuals and support documents for end-users.
This concise overview ensures both the quality and reliability of overhead hoists, meeting industry standards and customer expectations.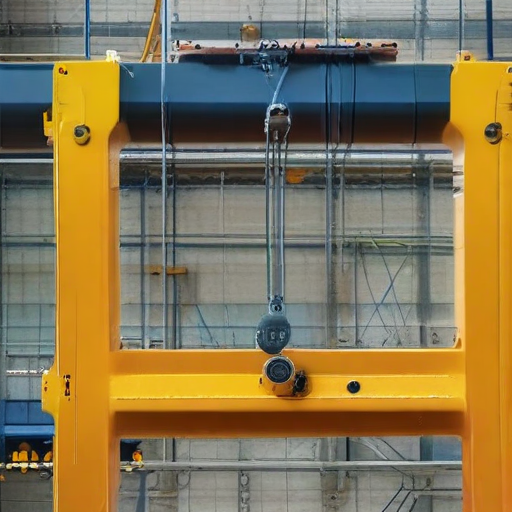
How to use “overhead hoist”
Using an overhead hoist involves several key steps to ensure safety and efficiency:
1. Inspection:
– Check the Hoist: Inspect the hoist mechanism for any signs of wear, damage, or malfunction.
– Assess the Load: Ensure the load is within the hoist’s weight limit.
2. Preparation:
– Position the Hoist: Move the hoist directly above the load.
– Attach Slings: Secure the load with appropriate slings or lifting attachments. Make sure they are properly aligned and fastened.
3. Safety Measures:
– Clear the Area: Ensure that the work area is free from obstacles and that all personnel are at a safe distance.
– Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear appropriate PPE, such as gloves, hard hats, and safety boots.
4. Operation:
– Lift Slowly: Gradually lift the load, ensuring it remains balanced.
– Monitor: Observe the load continuously for any signs of shifting or instability.
– Move with Caution: Carefully move the load to the desired location using the hoist controls.
5. Lowering the Load:
– Position Correctly: Ensure the destination area is ready and clear.
– Lower Slowly: Gradually lower the load into place, ensuring it remains steady.
– Release Safely: Once in place, unhook the slings or lifting attachments.
6. Post-Operation:
– Inspect the Hoist Again: After use, inspect the hoist and attachments for any potential damage or wear.
– Store Properly: Ensure the hoist and accessories are stored in a safe, dry place.
Note: Always consult and follow the manufacturer’s instructions and local safety regulations when using an overhead hoist. Proper training is essential for safe and effective operation.
“overhead hoist” Comparative Analysis
An overhead hoist, pivotal in material handling, enhances operational efficiency across various industries. This comparative analysis delves into different types of overhead hoists, their mechanisms, and ideal applications.
1. Electric Chain Hoists:
Electric chain hoists are renowned for their durability and precision. They utilize an electric motor to lift loads via a chain, making them suitable for repetitive lifting tasks in manufacturing and assembly lines. Their compact design ensures easy installation and minimal maintenance. However, they may struggle with extremely heavy loads compared to wire rope hoists.
2. Wire Rope Hoists:
Wire rope hoists, characterized by their steel rope, offer superior strength and load-bearing capacity. They are ideal for heavy-duty applications such as in construction, shipyards, and large-scale manufacturing. Though bulkier and costlier than chain hoists, their robustness justifies the investment when handling substantial weights.
3. Manual Hoists:
Manual hoists operate without electrical power, relying on human effort to lift loads via a chain or rope. They are cost-effective and useful in remote locations lacking power supply or in applications requiring occasional use. The primary downside is the significant physical effort needed, which limits efficiency for frequent or heavy lifting tasks.
4. Pneumatic Hoists:
Pneumatic hoists, powered by compressed air, excel in environments where electricity poses hazards, such as in petrochemical or mining industries. They provide smooth operation and can handle heavy weights, but the initial setup can be expensive due to the need for an air compressor infrastructure.
Comparison:
– Precision & Speed: Electric chain hoists outperform in precision and speed, making them ideal for assembly lines.
– Load Capacity: Wire rope hoists have the highest load capacities, suited for heavy-duty applications.
– Cost-effectiveness: Manual hoists are the most affordable, fitting for occasional and lighter use.
– Safety in Hazardous Areas: Pneumatic hoists win in safety-critical environments but come with higher initial costs.
In summary, the choice of an overhead hoist hinges on the specific requirements of load capacity, operational frequency, safety needs, and budget considerations. Each type offers distinct advantages tailored for various industrial needs.
“overhead hoist” Warranty and Support
Warranty and Support for Overhead Hoist
#### Warranty:
Our overhead hoists come with a comprehensive warranty designed to provide you with peace of mind. Each hoist is covered by a 5-year warranty from the date of purchase. This warranty includes coverage for any defects in materials or workmanship under normal use conditions. Specifically, the warranty covers:
– Mechanical Components: Gears, brake systems, chains, and other critical mechanical parts.
– Electrical Components: Control panels, motors, and wiring systems.
Please note that the warranty does not cover damage caused by misuse, neglect, unauthorized modifications, or improper maintenance. Wear and tear from regular use and consumables (such as load chains) are also excluded from this warranty.
#### Claim Process:
To make a warranty claim, please contact our customer service team with your purchase details and a description of the issue. Our team may request photos or additional information to better understand the defect. Approved claims will be repaired or replaced at our discretion.
#### Support:
We are committed to providing exceptional support for all our products. Our support services include:
– Customer Service: Our experts are available via phone and email to answer any questions or concerns. Operating hours are Monday through Friday, 8 AM to 6 PM.
– Technical Support: Troubleshooting guidance is available from our experienced technicians who can help diagnose and resolve any issues.
– Maintenance Services: We offer annual maintenance checks and servicing packages to ensure optimal operation and longevity of your overhead hoist.
– User Manuals and Resources: Comprehensive manuals, FAQs, and video tutorials are accessible on our website for your convenience.
For fast and efficient assistance, please refer to your product’s serial number when contacting support. We are dedicated to ensuring your overhead hoist remains reliable and efficient throughout its lifespan.
List “overhead hoist” FAQ
Overhead Hoist FAQ
1. What is an overhead hoist?
An overhead hoist is a mechanical device used for lifting and lowering heavy loads. It operates on an overhead track and is often utilized in manufacturing, warehousing, and construction.
2. What types of overhead hoists are available?
Common types include electric, manual, and air-powered hoists. Electric hoists are popular for their efficiency and ease of use, while manual hoists are typically used for lighter loads or where power is unavailable. Air-powered hoists are preferred in hazardous environments.
3. What is the lifting capacity of an overhead hoist?
Lifting capacities can vary widely, typically ranging from a few hundred pounds to several tons, depending on the model and design.
4. How do I choose the right overhead hoist?
Consider factors such as the required lifting capacity, type of load, lifting height, operating environment, and power source availability.
5. What safety features should I look for?
Key safety features include overload protection, emergency stop buttons, limit switches, and robust hooks. Regular maintenance and inspections are also crucial for safe operation.
6. How often should an overhead hoist be inspected?
Routine inspections should be done daily, with more thorough inspections monthly or annually, depending on usage. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines.
7. Can an overhead hoist be used outdoors?
Yes, some hoists are designed for outdoor use but ensure they are weather-resistant and suitable for your specific environmental conditions.
8. Are there any regulatory standards for overhead hoists?
Yes, in the United States, OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) provide guidelines and standards for safe operation.
9. What should I do if my hoist stops working?
First, consult the user manual for troubleshooting tips. If the issue persists, contact the manufacturer or a certified technician for repair.
10. How can I extend the life of my overhead hoist?
Regular maintenance, proper usage, and adherence to load limits will significantly extend the life of your hoist.
By understanding these FAQ, users can ensure safe and efficient operation of their overhead hoists.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about overhead hoist for Buyer Sourcing from China
Certainly! Here are the top 10 frequently asked questions (FAQ) about sourcing overhead hoists from China:
1. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ)?
– The MOQ varies by manufacturer but generally ranges from 1 to 10 units. Always check with the supplier for specific requirements.
2. What certifications should I look for?
– Look for ISO, CE, and SGS certifications. These ensure that the products meet international quality and safety standards.
3. What is the lead time for delivery?
– Typical lead times range from 30 to 60 days, depending on order size and customization requirements.
4. Can I customize the hoist specifications?
– Yes, most Chinese manufacturers offer customization options for load capacity, lift height, power supply, and other specifications.
5. What kind of warranty do Chinese manufacturers offer?
– Warranties usually last from 1 to 2 years. Verify the warranty terms, including what it covers and the process for claiming it.
6. How does the pricing compare to other markets?
– Pricing is generally more competitive due to lower manufacturing costs. However, consider shipping, duties, and taxes when calculating total costs.
7. Are there reliable suppliers in China?
– Yes, but it’s crucial to conduct thorough research, seek recommendations, and possibly use a sourcing agent for due diligence.
8. What is the quality of Chinese-made hoists?
– Quality varies, but many reputable manufacturers produce high-quality hoists that comply with international standards.
9. How do I handle shipping and customs?
– Most suppliers offer FOB (Free on Board) terms. You can hire freight forwarders to manage shipping and customs clearance.
10. Is after-sales support available?
– Reputable manufacturers offer after-sales support, including spare parts and technical assistance. Confirm the details during negotiations.
Remember, effective communication and due diligence are key to successful sourcing from China.









