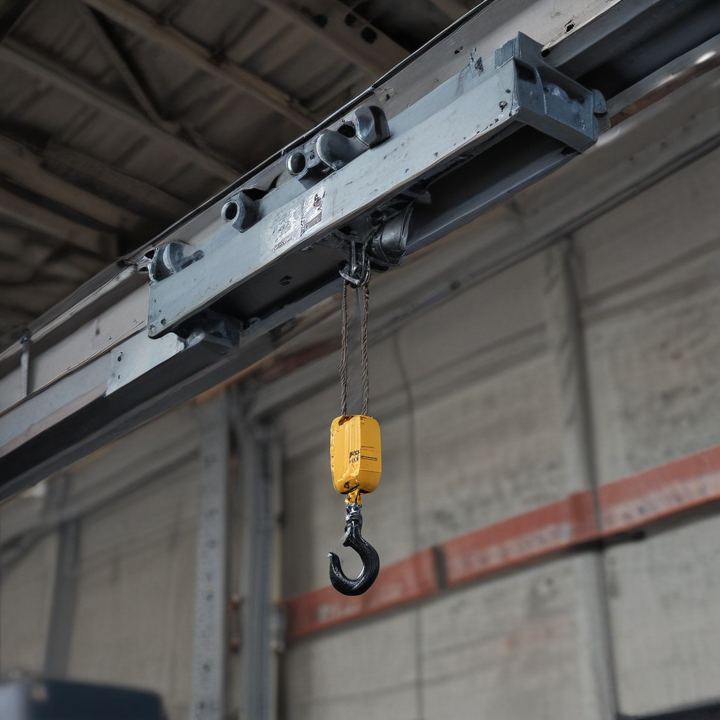
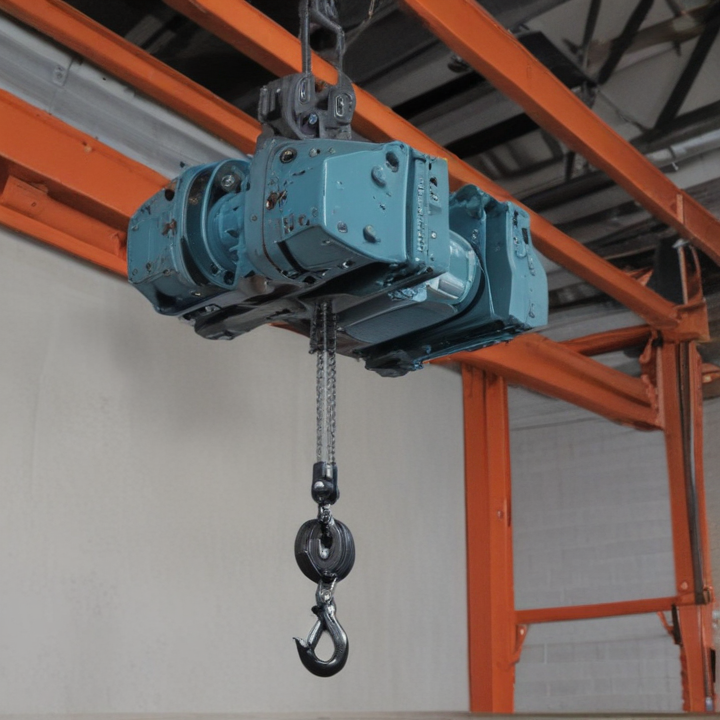
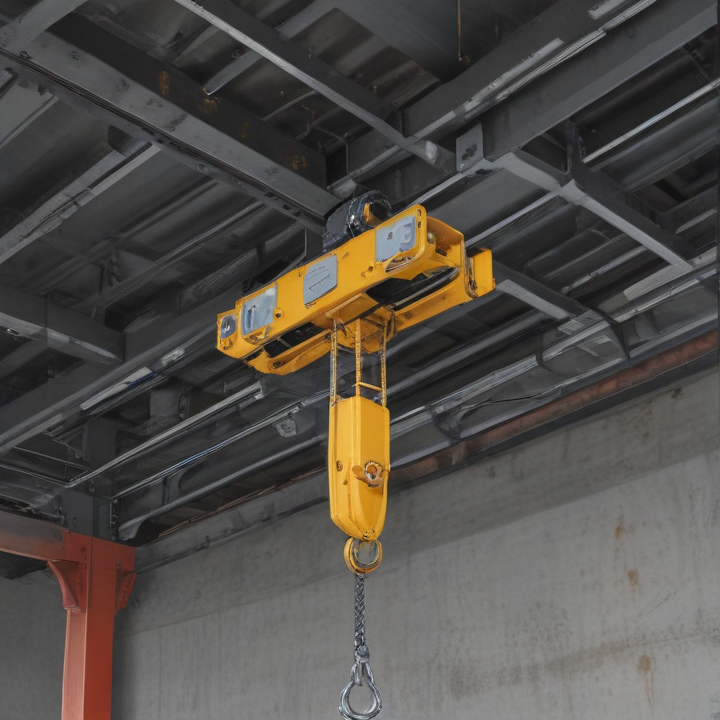
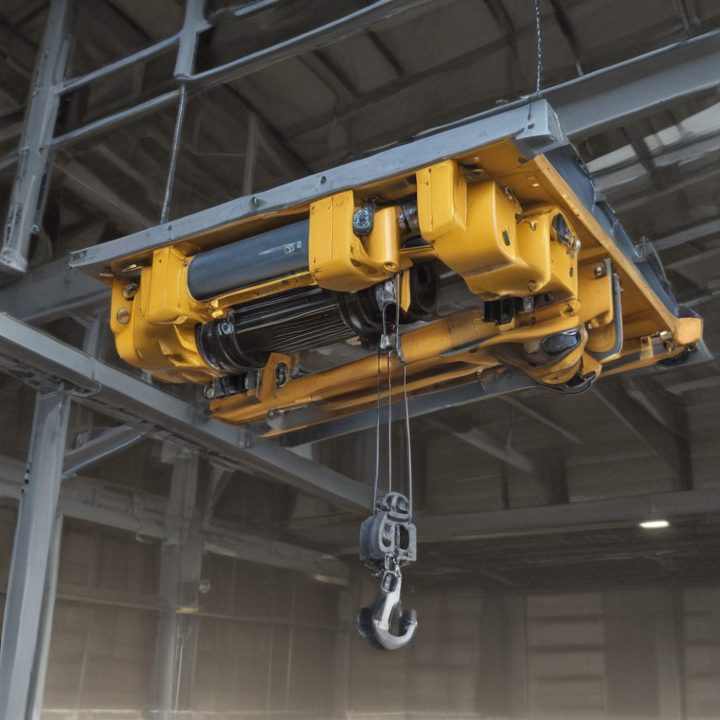
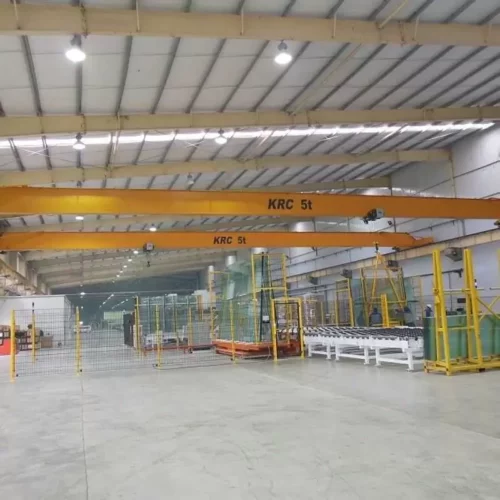
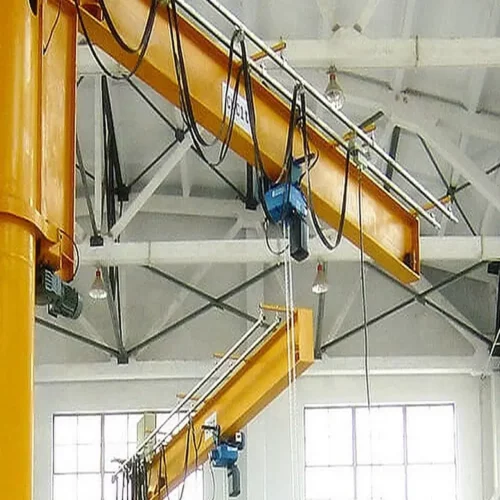
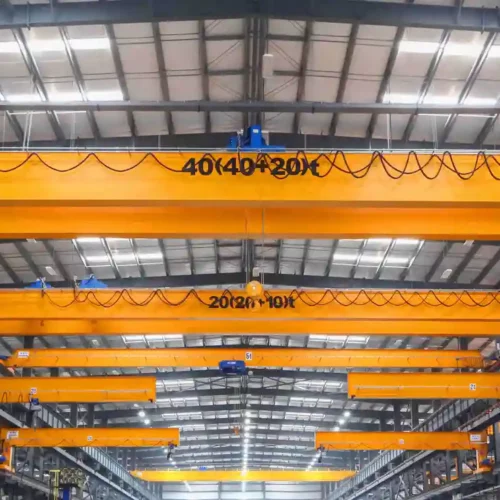
overhead hoist i beam Safety Certifications
Ensuring the safe operation of overhead hoist systems, particularly those utilizing I-beams, is paramount in industrial and construction environments. Several safety certifications and standards govern the use and maintenance of these systems to ensure they meet stringent safety and performance criteria:
1. OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration): OSHA sets and enforces standards to ensure safe and healthy working conditions. OSHA Standard 1910.179 covers overhead and gantry cranes, outlining requirements for design, inspection, testing, maintenance, and operation to ensure safety.
2. ANSI (American National Standards Institute): ANSI/ASME B30.2 is a critical standard for overhead and gantry cranes, detailing construction, installation, inspection, testing, maintenance, and operation safety guidelines.
3. ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers): ASME B30 series, particularly B30.16, applies to overhead hoists, including electric and air-powered types. It sets forth safety practices for operators to prevent accidents and injuries.
4. CMAA (Crane Manufacturers Association of America): CMAA Specification Nos. 70 and 74 offer guidelines for the construction, installation, inspection, and maintenance of overhead traveling cranes, essential for ensuring they operate safely under load conditions.
5. ISO (International Organization for Standardization): ISO 9927 deals with crane inspections, providing global standards for regular and thorough inspections to identify and mitigate potential safety hazards.
6. FEM (European Federation of Materials Handling): FEM 9.755 outlines the principles for the safe use and maintenance of cranes and lifting equipment, fostering consistency across European standards.
Compliance with these standards involves regular training for operators, meticulous maintenance schedules, detailed record-keeping, and routine inspections. These measures not only ensure safe operation but also extend equipment lifespan and enhance productivity by minimizing downtime due to accidents or mechanical failures.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “overhead hoist i beam”
Sure! Below are the key technical parameters for an overhead hoist I-beam:
1. Material Composition:
– Typically made from structural steel (e.g., ASTM A36, ASTM A992).
2. I-Beam Size and Dimensions:
– Flange width (W): Ranges from 3 to 12 inches or more.
– Flange thickness (T): Generally between 0.25 to 1 inch.
– Web height (H): Typically 6 to 30 inches, depending on load capacity.
– Web thickness (tw): Generally between 0.25 to 1 inch.
3. Beam Length:
– Custom lengths based on application, usually ranging from 10 to 60 feet.
4. Load Capacity:
– Defined by weight per linear foot (e.g., W8x24 means 24 pounds per foot), impacting the maximum permissible load.
5. Deflection Criteria:
– Max deflection typically limited by span length and beam material, often L/360 for live loads.
6. Support Spacing:
– Distance between supports (e.g., columns or wall mounts), affecting deflection and load capacity.
7. Camber:
– Curvature in beam to counter deflection, specified when necessary.
8. Connections:
– Methods include bolted or welded connections, critical for installation and stability.
9. Surface Treatment:
– May include galvanizing, painting, or epoxy coatings to prevent corrosion.
10. Compliance Standards:
– Must comply with relevant industry standards like OSHA, ASME, and ANSI.
11. Span to Depth Ratio:
– Often maintained to 15:1 to 24:1 for optimal strength and weight balance.
12. Load Type:
– Static or dynamic loads influence beam selection; dynamic loads require more robust parameters.
13. Usage Environment:
– Indoor vs. outdoor settings can affect material choice and treatment.
14. Environmental Conditions:
– Factors like temperature, humidity, and chemical exposure may necessitate specific material properties or coatings.
These parameters ensure the safe and efficient operation of overhead hoist I-beam systems, tailored to specific industrial needs.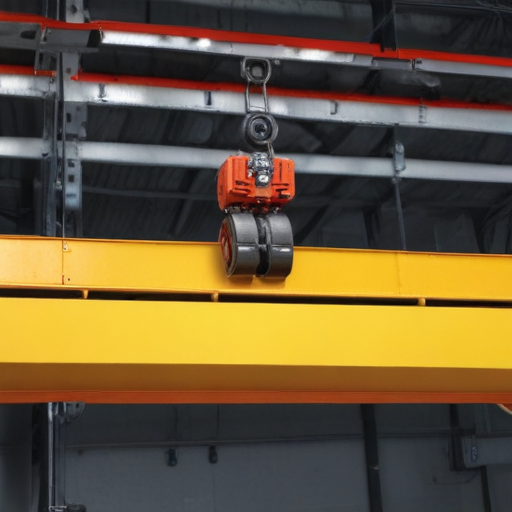
List Product features of “overhead hoist i beam”
An overhead hoist I-beam is a critical component in material handling and lifting systems, particularly in industrial settings. Here are its key product features:
1. Structural Integrity: Made from high-strength steel, the I-beam offers robust structural integrity, ensuring safe and reliable support for heavy lifting operations.
2. Load Capacity: Designed to support various load capacities, ranging from light to extremely heavy loads, depending on the beam size and material specifications.
3. Compatibility: Compatible with various types of hoists, including electric, manual, and pneumatic hoists, providing versatility in different operational settings.
4. Custom Lengths: Available in customizable lengths to fit specific workspace requirements, ensuring optimal use of available space.
5. Durability: Resistant to wear and tear, corrosion, and other environmental factors, ensuring longevity and reduced maintenance costs.
6. Easy Installation: Features standardized dimensions and attachment points for straightforward installation and integration into existing systems.
7. Smooth Operation: Designed for minimal friction during hoist movement, allowing for smoother and more precise lifting.
8. Safety Features: Engineered with safety in mind, often including features like end stops to prevent the hoist from running off the beam.
9. Versatility: Applicable across various domains such as manufacturing, warehousing, construction, and automotive industries.
10. Regulatory Compliance: Meets industry standards and regulatory requirements for safety and performance, ensuring compliance and reliability.
11. Efficient Load Distribution: The I-beam shape ensures efficient distribution of stress and load, minimizing the risk of structural deformation.
These features make the overhead hoist I-beam an essential element for efficient, safe, and reliable overhead lifting solutions.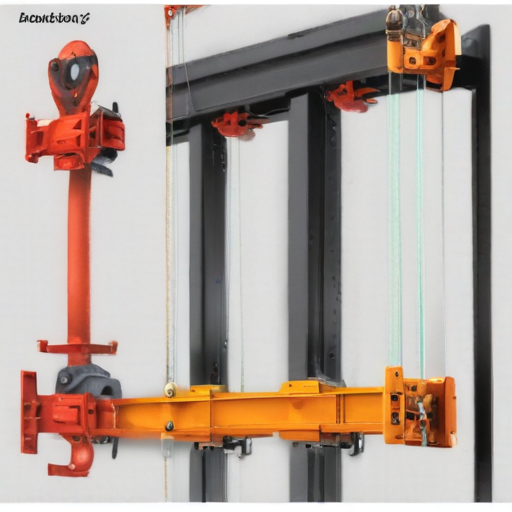
List Various Types of “overhead hoist i beam”
Overhead hoist I-beams come in various designs and configurations to suit different lifting and maneuvering needs in industrial and construction settings. Here are some common types:
1. Standard I-Beam Hoists:
These are conventional I-beams where a hoist trolley is mounted to move horizontally along the beam, lifting loads at various points.
2. Jib Cranes:
Mounted on walls or floors, these I-beam systems rotate to cover semi-circular work areas. They are ideal for localized lifting tasks.
3. Monorail Systems:
These consist of a single I-beam where the trolley and hoist run along a fixed path. They provide streamlined, linear movement and are used in assembly lines and production facilities.
4. Gantry Cranes:
Portable or fixed, gantry cranes feature an I-beam supported by legs. They span across work areas to provide versatile movement over a wider space.
5. Bridge Cranes:
Also known as overhead cranes, these systems include an I-beam suspended between two parallel runways. A trolley and hoist traverse the beam, allowing for multi-directional movement.
6. Track Systems:
Modular in nature, these systems use I-beams arranged in complex track layouts, enabling the movement of hoist trolleys along predetermined paths.
7. Cantilever Cranes:
Partially supported and extending outwards, these I-beam cranes are useful for lifting in confined areas or beyond obstacles.
8. Freestanding Workstation Cranes:
Mounted on a structural framework, these systems use I-beams to provide dedicated lifting capabilities in specific workstations or cells.
Each type caters to distinct operational requirements and spatial constraints, enhancing efficiency and safety in material handling tasks.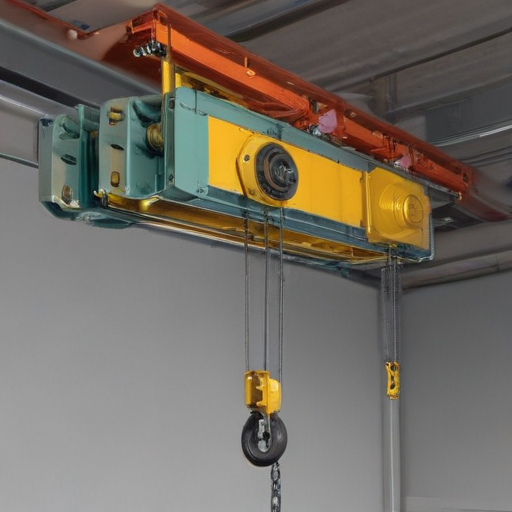
List Application of “overhead hoist i beam”
Overhead hoist I-beams are essential components in various industries for lifting and moving heavy loads efficiently and safely. Here are several applications:
1. Manufacturing Facilities: Used extensively in assembly lines to transport materials, parts, and finished products, improving workflow and reducing manual labor.
2. Warehousing and Distribution Centers: Essential for moving heavy pallets, large items, and bulk materials, optimizing storage and retrieval operations.
3. Construction Sites: Employed to lift and position construction materials such as steel beams, concrete blocks, and heavy machinery, enhancing safety and productivity.
4. Automotive Industry: Crucial for moving engines, transmissions, and other heavy car parts during assembly and maintenance, ensuring precision and reducing physical strain on workers.
5. Shipyards: Used for the assembly and maintenance of ships, moving large components like engines, anchors, and ship parts.
6. Mining Operations: Facilitate the transportation of heavy mining equipment and extracted materials, contributing to operational efficiency.
7. Steel and Metal Fabrication: Enable the handling and positioning of heavy steel sections, improving accuracy and safety during cutting, welding, and assembly processes.
8. Power Plants: Assist in the installation and maintenance of heavy machinery like turbines, generators, and transformers, essential for continuous operation.
9. Aircraft Manufacturing and Maintenance: Used for the precise assembly and repair of aircraft components, including engines, wings, and fuselage sections.
10. Railroad Maintenance: Assist in lifting and repairing heavy train components and tracks, ensuring efficient and safe rail operations.
11. Healthcare Facilities: Some hospitals and rehabilitation centers use hoist systems for lifting patients, reducing the risk of injury to both patients and healthcare providers.
These applications underscore the versatility and importance of overhead hoist I-beams in enhancing operational efficiency, safety, and productivity across various industries.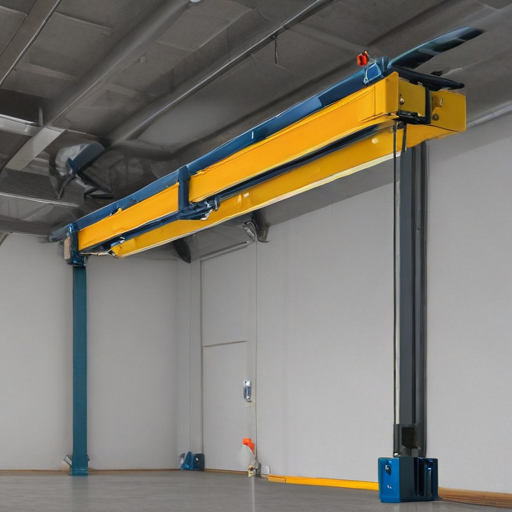
List Buyer Types of “overhead hoist i beam”
When considering the buyer types for “overhead hoist I-beams,” it’s essential to recognize the diverse range of industries and applications that utilize these products. Below are the primary buyer types:
1. Manufacturing Plants:
– Utilize overhead hoists for material handling, assembly lines, and moving heavy components within the facility.
2. Construction Companies:
– Employ hoists for lifting and positioning steel beams, heavy equipment, and building materials on job sites.
3. Warehouses and Distribution Centers:
– Use hoist systems for loading and unloading goods, organizing inventory, and handling bulky products.
4. Automotive Industry:
– Involves lifting engines, car bodies, and other heavy automotive parts during assembly and maintenance.
5. Mining Operations:
– Requires robust hoists for lifting ores, tools, and machinery in underground and surface mining.
6. Shipyards and Maritime Industry:
– Engages overhead hoists to maneuver large ship components, cargo, and maintenance equipment.
7. Utility Companies:
– Utilizes hoists for the installation and maintenance of heavy electrical equipment and infrastructure.
8. Aerospace Industry:
– Involves precise lifting and positioning of aircraft components, engines, and assemblies.
9. Steel Mills and Foundries:
– Demands hoist systems to transport molten metal, heavy castings, and large fabricated structures.
10. Fabrication Shops:
– Uses hoisting equipment to move raw materials and finished products within the shop floor.
Each buyer type has specific requirements based on their operational needs, workspace, and the nature of the materials they handle. Understanding these distinctions helps in tailoring solutions to fit their exact demands, ensuring efficiency and safety in their hoisting operations.
List “overhead hoist i beam” Project Types for Different Industries
Overhead hoist I-beams are integral components in various industries for material handling and lifting heavy loads. These systems enhance safety, efficiency, and productivity. Below are some project types where overhead hoist I-beams are deployed across different industries:
1. Manufacturing
– Assembly Line Transport: Facilitates the movement of large components between workstations.
– Parts Handling: Lifts and transports parts within a manufacturing plant, reducing manual labor.
2. Construction
– Material Hoisting: Elevates heavy building materials to different floors of a construction site.
– Equipment Installation: Assists in positioning large machinery and equipment accurately.
3. Warehousing and Distribution
– Inventory Management: Aids in the organization and retrieval of heavy goods from storage shelves.
– Loading and Unloading: Streamlines the process of loading goods onto shipping vehicles.
4. Automotive
– Engine Assembly: Supports the lifting and positioning of engines during the manufacturing process.
– Component Transportation: Moves various automotive parts along the production line.
5. Shipbuilding
– Hull Assembly: Lifts and places large hull sections precisely.
– Equipment Installation: Facilitates the installation of heavy ship components.
6. Aerospace
– Aircraft Assembly: Supports the transport and assembly of large aircraft components.
– MRO (Maintenance, Repair, Overhaul): Assists in the lifting and maneuvering of heavy aircraft parts for maintenance.
7. Mining
– Load Hauling: Moves mined materials to processing plants.
– Equipment Handling: Assists in lifting and transporting heavy mining equipment.
8. Energy
– Turbine Installation: Facilitates the installation of heavy wind or hydroelectric turbine components.
– Pipeline Construction: Aids in the handling and placement of large pipeline sections.
9. Metal Fabrication
– Raw Material Transport: Moves large metal sheets, rods, and other raw materials.
– Finished Goods Handling: Transports finished products for further processing or shipment.
10. Chemical and Pharmaceutical
– Reactor Charging: Assists in loading raw materials into reactors.
– Equipment Maintenance: Facilitates the maintenance and replacement of heavy machinery.
These varied applications highlight the essential role of overhead hoist I-beams in optimizing operations across multiple sectors.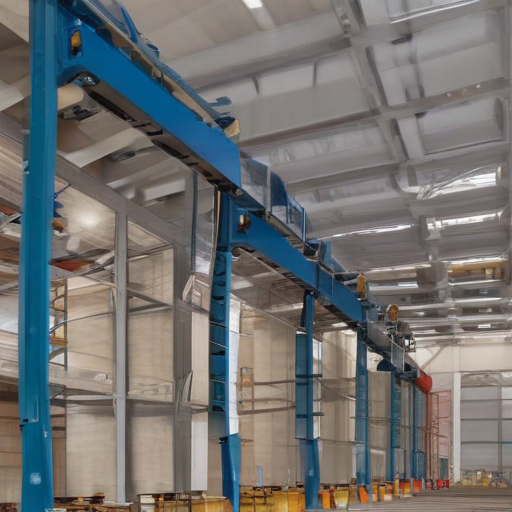
overhead hoist i beam Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Upgrading and customizing your overhead hoist I-beam system can significantly enhance its functionality, safety, and efficiency. Here are some key accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options:
1. End Trucks: Robust end trucks with adjustable features improve load distribution and mobility along the beam.
2. Festoon Systems: Cable and hose management systems maintain order and prevent tangling, ensuring smooth operation.
3. Trolleys: Motorized and manual trolleys provide better load control and ease of movement. Options include low-headroom trolleys for height-restricted areas.
4. Freestanding Support Structures: Customizable support structures compatible with various I-beam sizes ensure stability and flexibility in positioning.
5. Hoist Upgrades: Variable speed controls, anti-sway technology, and advanced braking systems enhance precision, safety, and efficiency.
6. Load Indicators: Integrated load cells and digital readouts provide real-time weight measurements to avoid overloading and ensure safe operation.
7. Protective Coatings: Custom finishes such as galvanization, powder coating, or specific paint types can protect the beam against corrosion and wear, suitable for different environments.
8. Lighting and Signage: Adequate lighting and clear signage improve visibility and safety around the hoist area.
9. Automation Integration: Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and remote controls can automate repetitive tasks, reducing manual intervention and increasing productivity.
10. Custom Fabrication: Tailored I-beam lengths, special alloy materials, or unique configurations may be designed to match specific operational needs and constraints.
These enhancements not only improve operational efficiency but also extend the lifespan of your equipment, ensuring that it meets the specific requirements and challenges of your work environment. By integrating these accessories and custom options, you optimize safety, performance, and productivity in your hoisting operations.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “overhead hoist i beam”
Quality Control and Manufacturing Process of Overhead Hoist I-Beam
Manufacturing Process:
1. Design and Engineering:
– Specifications: Define load capacity, length, material type (typically steel), and standards compliance.
– Blueprints: Create detailed engineering drawings and 3D models.
2. Material Selection:
– Procurement: Source high-quality steel with appropriate tensile strength and durability.
– Inspection: Check raw materials for defects or non-conformance to specifications.
3. Cutting and Shaping:
– Cutting: Use CNC machinery for precise cutting.
– Shaping: Form the steel into an ‘I’ shape using rolling mills.
4. Welding and Assembly:
– Welding: Weld components together, ensuring proper alignment and joint strength.
– Assembly: Assemble the beam with required fixtures like end caps or connection plates.
5. Heat Treatment:
– Stress Relieving: Apply heat treatment to relieve residual stresses.
– Cooling: Control the cooling process to prevent warping.
6. Surface Treatment:
– Cleaning: Remove scale, rust, and debris.
– Coating: Apply protective coatings such as primer and paint to prevent corrosion.
Quality Control:
1. Incoming Inspection:
– Material Testing: Conduct chemical and physical tests on raw materials.
– Certification Verification: Cross-check supplier certificates with industry standards.
2. In-Process Inspection:
– Dimensional Checks: Use calipers, gauges, and measurement tools to confirm dimensions.
– Welding Inspection: Inspect welds using non-destructive testing (NDT) methods like ultrasonic, radiography, or dye penetrant tests.
3. Final Inspection:
– Load Testing: Perform load tests to ensure the beam can bear specified loads.
– Visual Inspection: Check for surface defects, coating continuity, and general workmanship.
– Documentation: Maintain detailed records of inspections and test results.
4. Non-Conformance Management:
– Defect Analysis: Identify and analyze defects.
– Corrective Actions: Implement corrective measures and re-inspect.
5. Certification and Compliance:
– Third-Party Verification: Sometimes involve third-party agencies for final certification.
– Standards Compliance: Ensure the product meets relevant industry standards like ISO, ANSI, or OSHA.
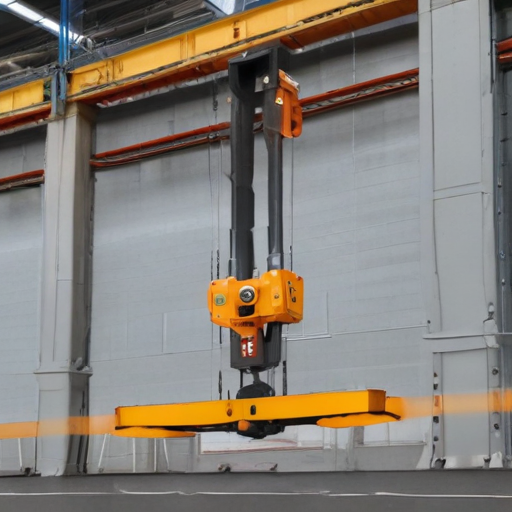

How to use “overhead hoist i beam”
An overhead hoist I-beam system is a common lifting solution used in various industrial settings for moving heavy loads along a defined path. Here’s a concise guide on how to use it effectively:
Preparation:
1. Inspection: Before use, inspect the I-beam and hoist for any signs of damage or wear. Ensure all components are securely fastened.
2. Clear Path: Ensure the path along the I-beam is clear of obstructions and personnel.
Operation:
1. Hoist Attachment: Secure the load to the hoist using appropriate rigging equipment like slings, chains, or hooks. Confirm that the load is within the hoist’s weight capacity.
2. Positioning: Use the control system to position the hoist directly above the load. This ensures vertical lifting, which is safer and prevents swinging.
3. Lifting: Gradually raise the load using the hoist controls. Maintain a slow and steady pace to keep the load stable.
4. Transporting: Move the load along the I-beam to the desired location. Keep the load close to the ground or platform, especially if moving over a significant distance.
5. Lowering: Once in position, slowly lower the load to the ground or the designated area. Make sure to release the load gently to prevent damage or accidents.
Safety Measures:
1. Training: Operators should be trained in the use of the overhead hoist and familiar with safety protocols.
2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear appropriate PPE such as hard hats, safety glasses, and steel-toed boots.
3. Load Limits: Never exceed the rated load capacity of the hoist or the I-beam.
4. Communication: Use clear signals or communication methods when operating the hoist, especially if multiple operators are involved.
Regular maintenance and adherence to safety protocols are crucial to the efficient and safe operation of an overhead hoist I-beam system.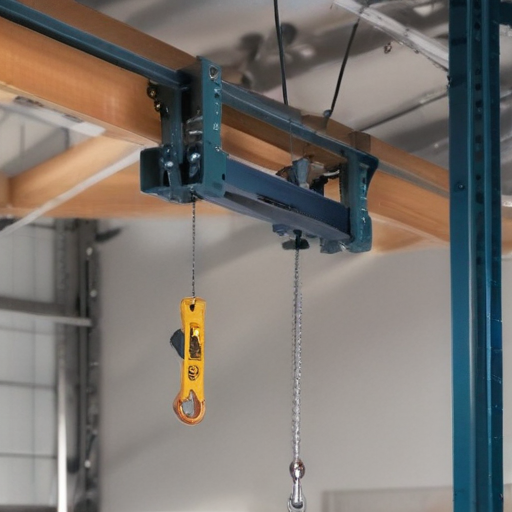
“overhead hoist i beam” Comparative Analysis
Comparative Analysis of Overhead Hoist I-Beam
Overview:
Overhead hoist I-beams are essential components in material handling systems used in various industries for lifting and moving heavy loads. Key factors considered in comparing I-beams for overhead hoists include their load capacity, material, dimensions, cost, and suitability for specific applications.
Load Capacity:
The load capacity of an I-beam is critical and depends on its size, material, and engineering design. Heavier and thicker beams can bear more weight, but they also require stronger supporting structures.
Material:
– Steel: Most common, offering high strength and durability. Suitable for heavy-duty applications.
– Aluminum: Lighter than steel, with a good strength-to-weight ratio. Ideal for applications where weight is a concern but load requirements are moderate.
Dimensions:
I-beams come in various standard sizes, typically defined by the height and width of the beam’s profile. Larger beams with greater cross-sectional areas can support more weight but may require more space and higher structural support.
Cost:
– Steel I-Beams: Generally more expensive due to higher material costs, manufacturing processes, and required support structures.
– Aluminum I-Beams: Typically less expensive in terms of installation due to lighter weight, though raw material cost can vary.
Suitability:
The choice depends on the application’s specific needs:
– Heavy Manufacturing: Steel I-beams are preferred due to their high load-bearing capacity and durability.
– Warehousing and Light Manufacturing: Aluminum I-beams are advantageous because of their lighter weight, ease of installation, and adequate load capacity.
Maintenance and Longevity:
Both types of beams require proper maintenance to prevent wear and damage over time. Steel beams are prone to rusting if not properly coated, whereas aluminum beams are more resistant to corrosion but can still suffer from fatigue under cyclic loading.
Conclusion:
Selecting the right I-beam for an overhead hoist system depends on balancing load requirements, material characteristics, cost, and specific application needs. Steel beams are ideal for heavy-duty, high-load scenarios, while aluminum beams offer benefits in weight-sensitive, moderate-load contexts.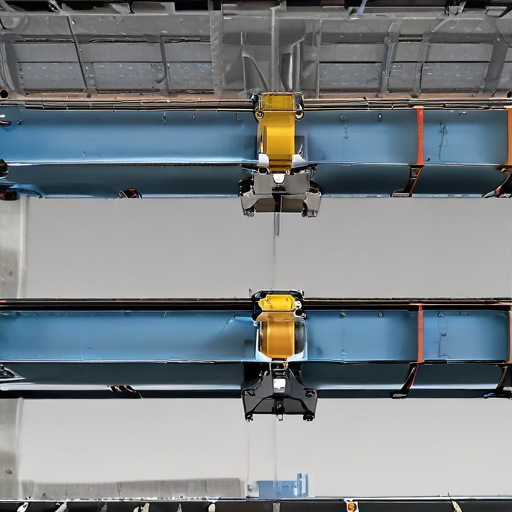
“overhead hoist i beam” Warranty and Support
When investing in an overhead hoist I-beam system, understanding the warranty and available support is crucial for ensuring long-term reliability and performance. Most reputable manufacturers provide a comprehensive warranty that typically covers defects in materials and workmanship. The duration of the warranty may vary, but it’s common to find warranties that range from one to five years. It’s essential to read the warranty terms carefully to understand the coverage, including any conditions or limitations.
Support services are equally important for the seamless operation of your overhead hoist I-beam. Reliable manufacturers usually offer extensive customer support that includes technical assistance, troubleshooting, and maintenance tips. Many companies provide online resources such as user manuals, installation guides, and troubleshooting FAQs accessible on their websites. Additionally, telephone and email support are generally available for more immediate concerns.
Some manufacturers may offer optional service contracts for regular maintenance and inspections to ensure the equipment remains in optimal condition. These services can be invaluable for preventing downtime and extending the life of your hoist system.
In summary, a solid warranty and reliable support are fundamental when selecting an overhead hoist I-beam system. Ensure you understand the warranty details, and take advantage of available customer support services to maximize your investment.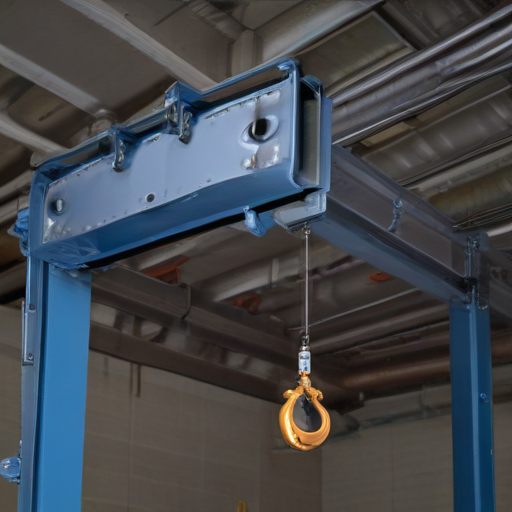
List “overhead hoist i beam” FAQ
Overhead Hoist I Beam FAQ
1. What is an overhead hoist I beam?
An overhead hoist I beam is a structural component used to support a hoist. The hoist travels along the I beam to lift and move heavy loads horizontally.
2. What materials are used for overhead hoist I beams?
I beams are typically made from steel or aluminum. Steel offers higher load-bearing capacity while aluminum is lighter and more resistant to corrosion.
3. How do I determine the right size I beam for my needs?
The size of the I beam depends on the load it needs to carry, the span of the beam, and the distance between supports. Consult engineering guidelines or a structural engineer to make an accurate determination.
4. What is the standard length of an overhead hoist I beam?
Standard lengths vary, commonly ranging from 10 to 40 feet. Custom lengths can also be fabricated based on specific requirements.
5. How is the I beam installed?
Installation involves anchoring the I beam to appropriate supports, often using brackets, clamps, or specially designed trolleys. It’s essential to follow manufacturer guidelines and safety standards.
6. Can an I beam be used outdoors?
Yes, but it should be treated or coated to resist rust and corrosion if it’s made of steel. Aluminum beams are naturally more corrosion-resistant.
7. What kind of maintenance is required?
Regular inspections for wear, deformation, and corrosion are necessary. Ensure that all moving parts are lubricated and that the hoist and beam are aligned properly.
8. What safety precautions should be taken?
Always adhere to load capacity limits, perform regular maintenance checks, and ensure all personnel are trained for safe operation.
9. Are there weight limitations for overhead hoist I beams?
Yes, weight limitations depend on the size, material, and design of the beam. Always consult manufacturer specifications and engineering guidelines.
10. Can overhead hoist I beams be customized?
Absolutely, I beams can be customized in terms of length, material, and load capacity to meet specific operational requirements.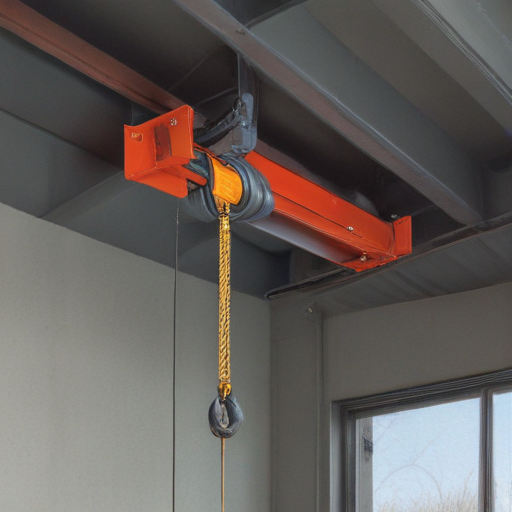
Top 10 FAQ with answer about overhead hoist i beam for Buyer Sourcing from China
Sure, here’s a concise FAQ for buyers sourcing overhead hoist I-beams from China:
1. What materials are used for I-beams?
Most I-beams are made from high-strength steel, like Q235B, Q345B, SS400, S235JR, or other comparable grades.
2. What specifications should I consider?
Key specs include the beam size (height, width, and thickness), material grade, load capacity, and length. Custom dimensions are often available.
3. Are the I-beams certified?
Yes, reputable Chinese manufacturers provide I-beams compliant with international standards such as ASTM, EN, and ISO.
4. What is the typical lead time?
Lead times vary but generally range from 3 to 6 weeks, depending on the order’s complexity and size.
5. How do I ensure the quality of the I-beams?
Request quality certifications, conduct third-party inspections, and check for compliance with international standards.
6. Are samples available?
Many manufacturers can provide samples or small trial orders to verify quality before committing to larger orders.
7. What are the common freight options?
Shipping options include FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight). Be clear about your logistics preferences.
8. What is the payment structure?
Typically, a 30% deposit is required, with the remaining 70% paid before shipment. Terms may vary by supplier.
9. What if I need custom I-beams?
Most manufacturers offer customization services. Provide detailed specifications to get accurate quotes and timelines.
10. Are there minimum order quantities (MOQ)?
MOQ can vary but is usually around 20-50 tons. Some suppliers may negotiate smaller quantities depending on the project.
This should provide a clear overview for buyers looking to source overhead hoist I-beams from China.










