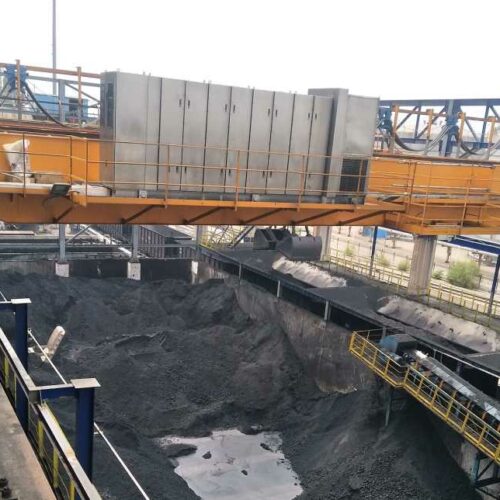
portable hoist crane Safety Certifications
When dealing with portable hoist cranes, adhering to established safety certifications is crucial to maintain workplace safety and operational efficiency. Key safety certifications and standards include:
1. OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration): Adhering to OSHA regulations ensures compliance with safety requirements in the U.S. Portable hoist cranes must comply with OSHA 29 CFR 1910.179 for overhead and gantry cranes.
2. ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers): The ASME B30 series provides guidelines for construction, operation, inspection, testing, and maintenance. Relevant sections include B30.2 (Overhead and Gantry Cranes) and B30.16 (Overhead Hoists).
3. ANSI (American National Standards Institute): ANSI standards, particularly ANSI/ASME B30 series, align closely with ASME recommendations.
4. CE Marking: In Europe, the CE marking indicates that a product complies with the Essential Health and Safety Requirements (EHSR) of the European Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC.
5. ISO (International Organization for Standardization): ISO 9927-1: 2013 provides guidelines for the inspection of cranes to ensure safe working conditions.
6. CSA (Canadian Standards Association): CSA B167-16 standards apply to overhead traveling cranes, gantry cranes, and hoists in Canada, focusing on safety and performance.
To maintain compliance, manufacturers and operators should engage in regular inspection, maintenance, and training. Documentation of safety procedures and adherence to local regulations and international standards is critical. Safety certifications are not just bureaucratic requirements but essential components in protecting workers and ensuring the reliable operation of equipment.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “portable hoist crane”
Certainly! Here are key technical parameters of a portable hoist crane:
1. Load Capacity: Indicates the maximum weight the crane can lift; commonly ranges from 500 kg to 20,000 kg depending on the model.
2. Lift Height: The maximum vertical distance the hoist can raise a load; typical ranges are from 2 meters to 15 meters.
3. Boom Length: Specifies the horizontal reach of the crane’s arm; generally varies between 1 meter to 12 meters.
4. Power Source: Can be electric, manual, pneumatic, or hydraulic. Electric hoists often operate on 110V to 480V systems.
5. Lift Speed: Rate at which the hoist can raise or lower the load; can range from 0.5 meters per minute to 8 meters per minute.
6. Rotation Angle: Some portable hoist cranes feature a rotating boom, often capable of 180 to 360 degrees of rotation for versatile load placement.
7. Control System: Mechanisms include pendant control, wireless remote, or manual lever systems for precision operation.
8. Weight of Equipment: The total weight of the crane, influencing its ease of portability; weights can range from 50 kg to 500 kg.
9. Wheel Base/Type: Determines mobility; options include solid or pneumatic wheels, and size can range from 100 mm to 400 mm in diameter.
10. Construction Material: Commonly made from high-strength steel or aluminum for durability and weight considerations.
11. Safety Features: Includes overload protection, emergency stop, and limit switches to ensure safe operation.
12. Operating Temperature: The range within which the crane can function effectively, often from -20°C to +50°C.
These parameters are critical for selecting the appropriate portable hoist crane that meets specific operational requirements and safety standards.
List Product features of “portable hoist crane”
A portable hoist crane offers a range of versatile and efficient features ideal for various lifting and material handling operations. Key product features include:
1. Portability: Designed for easy transportation and set-up, allowing for quick relocation between job sites or different areas within a facility.
2. Compact Design: Typically lightweight and compact, making it suitable for tight spaces and areas with limited headroom.
3. High Load Capacity: Capable of lifting significant weights, ranging from a few hundred pounds to several tons, depending on the model.
4. Adjustable Height: Features adjustable boom heights to accommodate different lifting needs and ensure optimal performance in varied environments.
5. Durability: Constructed from robust materials, such as high-grade steel or aluminum, to withstand harsh working conditions and ensure longevity.
6. Electric or Manual Operation: Available in both electric and manual versions, providing flexibility for operations with or without readily available power sources.
7. Swiveling Boom: Often equipped with a swiveling or rotating boom for enhanced maneuverability and precision in placing loads.
8. Safety Mechanisms: Includes safety features such as overload protection, emergency stop buttons, and locking brakes to ensure safe operation.
9. Ease of Assembly and Disassembly: Designed for quick assembly and disassembly without requiring specialized tools, facilitating rapid deployment and storage.
10. Versatile Applications: Suitable for a wide range of applications, including construction, warehousing, manufacturing, maintenance, and more.
11. User-Friendly Controls: Intuitive control systems, often with remote control options, to simplify the lifting process and reduce operator fatigue.
12. Stability: Features sturdy bases or adjustable legs for enhanced stability during operation, reducing the risk of tipping or accidents.
13. Customization: Options for customization to meet specific industry requirements, such as different lifting capacities, boom lengths, and accessories.
These features make portable hoist cranes essential tools for various industries, providing flexibility, efficiency, and safety in material handling operations.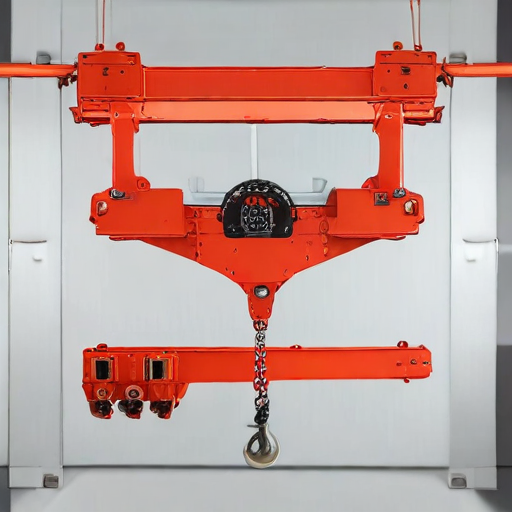
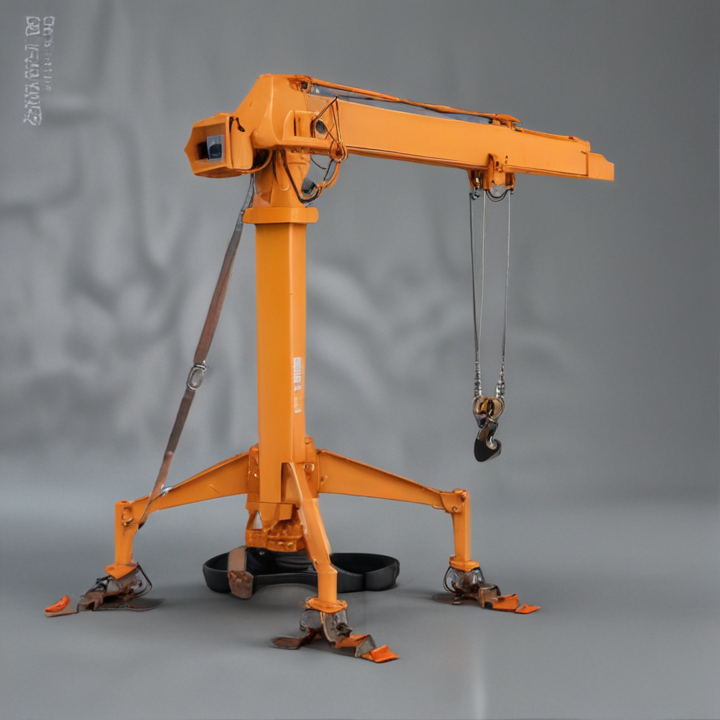
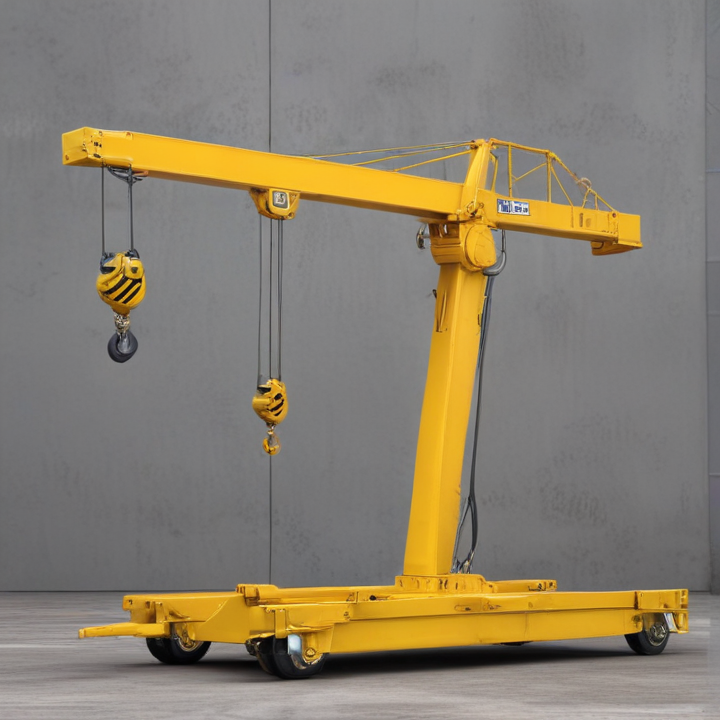
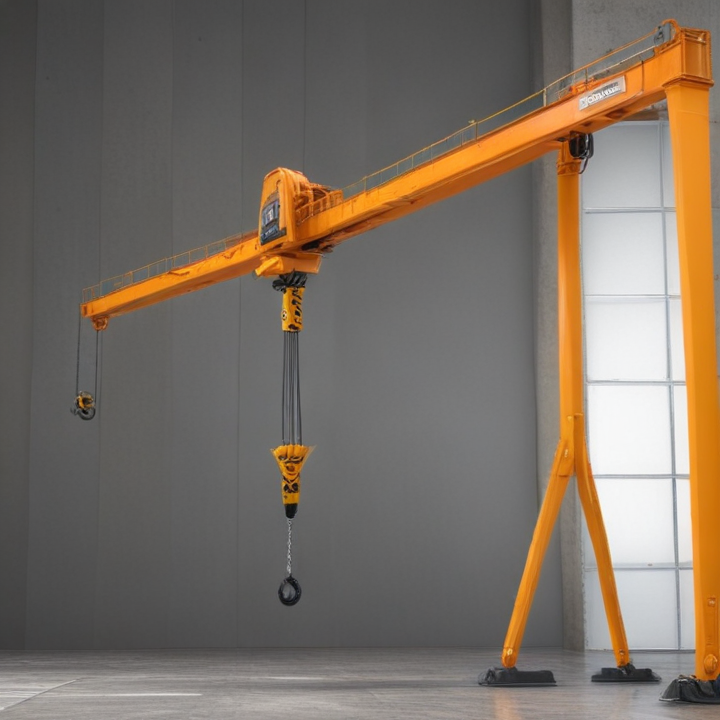
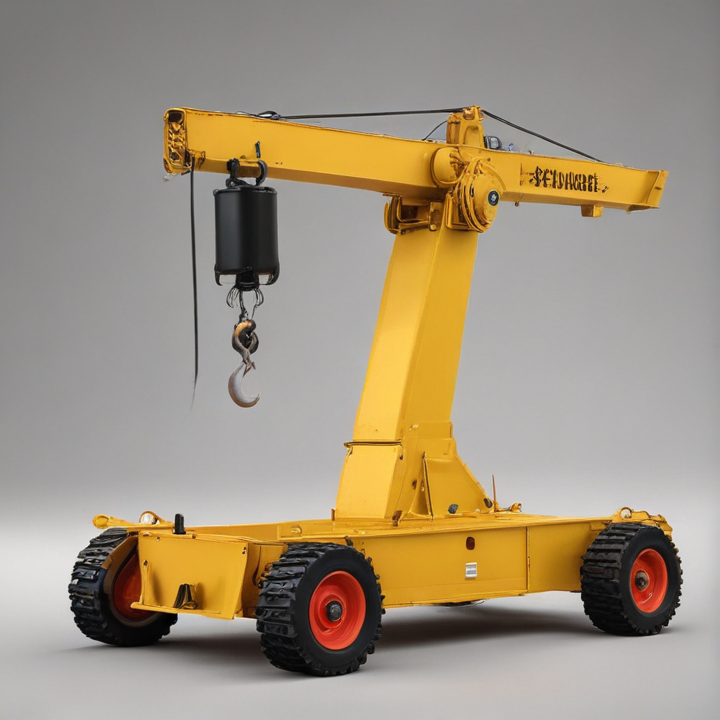
List Various Types of “portable hoist crane”
Portable hoist cranes come in various types, each designed for specific applications and ease of mobility. Here are some common types:
1. Portable Gantry Cranes:
– Adjustable Height Gantry Cranes: Feature adjustable legs, which allow for varying heights to suit different tasks.
– Fixed Height Gantry Cranes: Have a set height designed for consistent, repetitive lifting tasks.
– Foldable Gantry Cranes: Can be folded down for easy transport and storage.
2. Portable Jib Cranes:
– Wall-Mounted Jib Cranes: Attached to walls or columns, providing a rotational lifting range while saving floor space.
– Floor-Mounted Jib Cranes: Standalone units that offer a wide rotational range and can be moved around a workspace as needed.
3. Engine Hoists:
– Often used in automotive and industrial settings, these are compact cranes designed primarily for lifting engines and other heavy machinery components.
4. Air-Powered Hoists:
– Utilize compressed air for lifting, making them suitable for settings where electrical sources are unreliable or hazardous.
5. Electric Hoists:
– Powered by electricity, these hoists simplify heavy lifting with minimal manual effort and are ideal for indoor use where power outlets are readily available.
6. Manual Chain Hoists:
– Operated manually via a chain, these hoists are straightforward and reliable, suitable for smaller loads and areas where power sources are not accessible.
7. Pneumatic Hoists:
– Utilize air pressure for lifting, commonly used in environments where electrical equipment is impractical.
8. Wire Rope Hoists:
– Utilize wire ropes for lifting, providing higher strength and durability compared to chain hoists, suitable for industrial applications.
Each type of portable hoist crane is designed for different environments and lifting needs, offering flexibility, ease of transport, and varied lifting capacities to meet diverse operational requirements.
List Application of “portable hoist crane”
A portable hoist crane is a versatile and mobile lifting solution used across various industries. Here are some key applications:
1. Construction Sites: Essential for lifting and transporting materials like steel beams, concrete blocks, and equipment, simplifying on-site assembly and reducing manual labor.
2. Warehouses: Used for moving heavy inventory, loading and unloading trucks, and optimizing space by stacking items vertically.
3. Manufacturing Plants: Facilitates the movement of raw materials, assembly of large components, and transfer of finished goods, enhancing production line efficiency.
4. Automotive Industry: Assists in engine assembly, removal, and installation, as well as handling heavy vehicle components, improving safety and operational speed.
5. Shipping and Dockyards: Ideal for loading and unloading cargo from ships, managing containers, and transferring heavy goods with ease.
6. Healthcare Facilities: Utilized for moving large medical equipment like MRI machines and aiding in patient transfer in certain scenarios, ensuring safety and comfort.
7. Mining Operations: Essential for transporting extracted materials and heavy machinery in challenging environments, facilitating easier and safer operations.
8. Entertainment Industry: Used in setting up stages, lighting rigs, and other heavy equipment for concerts, theater productions, and events, ensuring timely and safe setups.
9. Utilities and Maintenance: Assists in the installation and maintenance of heavy equipment like transformers, substations, and large machinery in various industrial settings.
10. Emergency Services: Deployed in disaster relief operations for debris removal, rescue operations, and setting up temporary structures quickly.
11. Aerospace Industry: Used for handling aircraft components, engines, and assembly tasks, ensuring precision and safety in high-stakes environments.
These applications underscore the critical role of portable hoist cranes in enhancing efficiency, safety, and productivity across diverse sectors.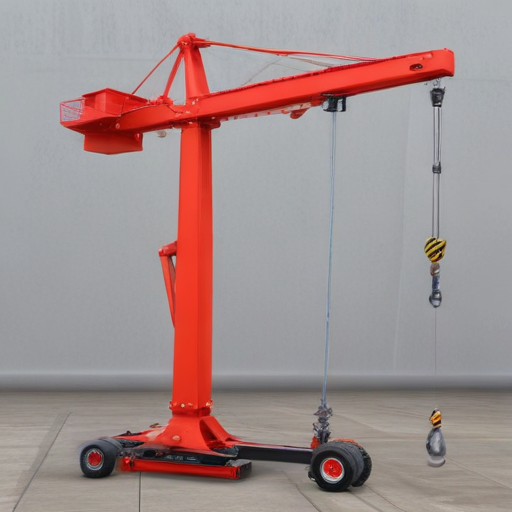
List Buyer Types of “portable hoist crane”
Buyers of portable hoist cranes span a diverse range of industries and applications due to the versatility and adaptability of these lifting devices. Here are the primary buyer types:
1. Construction Companies:
– Use portable hoist cranes for lifting heavy building materials, machinery, and tools on construction sites. Their mobility and ease of setup make them particularly suitable for temporary lifting needs.
2. Manufacturing Plants:
– Essential for lifting and moving heavy components, machinery, or raw materials within the plant. They offer flexibility in assembly lines and production areas where fixed cranes are impractical.
3. Warehousing and Logistics Firms:
– Utilize portable hoist cranes to handle heavy goods in loading and unloading areas, facilitating the movement of large or bulky items within warehouses and distribution centers.
4. Automotive Industry:
– Employed for lifting engines, parts, and assemblies during manufacturing and maintenance processes. Their portability allows for easy repositioning within automotive workshops and assembly lines.
5. Maintenance and Repair Services:
– Ideal for lifting and positioning heavy equipment or machinery during repair operations in various industrial sectors. Their portability ensures they can be brought to different sites as needed.
6. Event Setup Companies:
– Used for rigging and constructing stages, sets, and lighting equipment for concerts, exhibitions, or other events. Their compact size and mobility are advantageous in such dynamic environments.
7. Agriculture and Farming:
– Assist in lifting and transporting heavy agricultural equipment, feed, or produce. Their use is particularly beneficial in handling tasks that require mobility across different areas of a farm.
8. Shipyards and Marine Industry:
– Essential for lifting and moving heavy components, such as ship parts and cargo, within shipyards and docks. A portable hoist crane’s flexibility is crucial for various tasks in marine settings.
9. Mining and Quarrying Operations:
– Utilize portable hoist cranes for handling mining equipment and extracted materials. The cranes provide the necessary lifting power and mobility required in these rugged environments.
These diverse applications underscore the widespread demand and utility of portable hoist cranes across various sectors.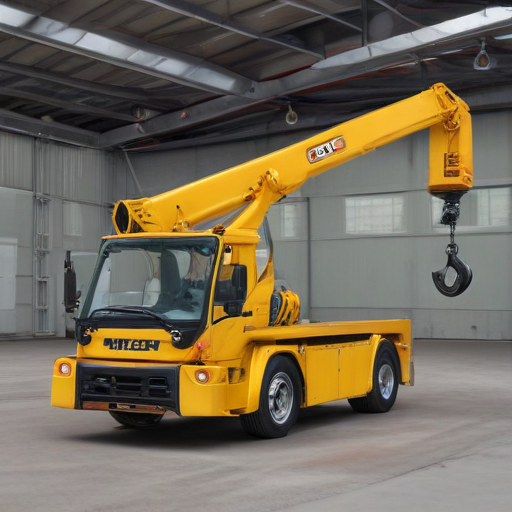
List “portable hoist crane” Project Types for Different Industries
Portable hoist cranes are versatile lifting solutions used across various industries to enhance productivity, improve safety, and streamline operations. Below are some common project types where portable hoist cranes are utilized:
1. Construction Industry:
– Site Assembly: For lifting heavy beams, panels, and construction materials in confined or temporary construction sites.
– Maintenance Tasks: Assisting in the maintenance and repair of machinery and scaffolding within construction environments.
2. Manufacturing Industry:
– Production Line Adjustments: Facilitating the rearrangement or installation of production line equipment.
– Component Lifting: Handling heavy parts and components during the assembly process.
3. Warehousing and Logistics:
– Inventory Management: Moving large or bulky items within warehouses and distribution centers.
– Container Loading/Unloading: Aiding in the efficient loading and unloading of shipping containers.
4. Oil and Gas Industry:
– Site Setup: Erecting and dismantling equipment on drilling sites and platforms.
– Heavy Equipment Maintenance: Assisting in the maintenance of heavy drilling machinery and components.
5. Healthcare Facilities:
– Medical Equipment Handling: Lifting and relocating large medical devices, such as MRI machines or surgical tables.
– Patient Handling: Assisting in the safe transfer of patients within hospitals and care facilities, particularly those with mobility issues.
6. Automotive Industry:
– Vehicle Assembly: Supporting the lifting and placement of heavy automotive parts like engines and transmissions.
– Repair and Maintenance: Facilitating the removal and installation of components during vehicle maintenance.
7. Aviation:
– Aircraft Maintenance: Hoisting engines, wings, and other heavy components during routine or emergency maintenance.
– Cargo Handling: Enhancing the loading and unloading operations of aircraft cargo.
8. Agriculture:
– Farm Equipment Maintenance: Aiding in the repair and upkeep of heavy farm machinery.
– Material Handling: Moving bulk materials such as fertilizer or harvested crops.
9. Utilities:
– Installation Projects: Assisting in the erection of utility poles, transformers, and other infrastructure components.
– Maintenance Work: Supporting routine maintenance and emergency repairs of utility infrastructure.
Each of these industries benefits from the flexibility, ease of use, and portability of hoist cranes, making them an essential tool for diverse operational needs.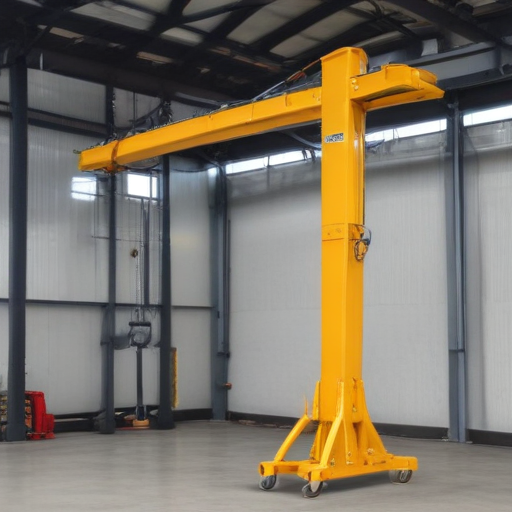
portable hoist crane Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Portable hoist cranes are essential for various industries due to their versatility and ease of use. To maximize their utility, several accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options are available.
Accessories:
1. Lifting Attachments: Slings, chains, and hooks can handle different loads and improve safety.
2. Trolleys: Manual and motorized trolleys enhance maneuverability along the beam.
3. Remote Controls: Wireless remotes allow for seamless operation from a safe distance.
4. Spreader Bars: Ideal for lifting wide or uneven loads, thereby distributing weight evenly.
5. Vacuum Lifters: These are perfect for handling non-porous materials like glass and metal sheets.
Upgrades:
1. Motorized Systems: Converting manual hoist cranes to motorized systems increases efficiency and reduces physical strain.
2. Advanced Braking Systems: Enhanced braking offers better load control and improved safety.
3. Load Sensors: Integrated load sensors provide real-time data for optimal weight handling.
4. Anti-Sway Technology: Reduces load swing for precision placement and increased safety.
5. Power Supply Upgrades: Options for solar power and battery backup systems ensure uninterrupted operation.
Custom Manufacturing Options:
1. Tailored Load Capacities: Custom-built cranes to handle specific weight requirements, from light loads to several tons.
2. Adjustable Heights: Cranes can be manufactured with telescopic or adjustable-height features to suit diverse operational environments.
3. Specific Material Choices: Options to manufacture cranes using materials like high-strength steel or aluminum for weight-sensitive applications.
4. Weatherproofing: Custom coatings and seals for cranes used in harsh weather conditions or corrosive environments.
5. Specialized Designs: Custom designs to fit unique spatial constraints, such as low-clearance areas or tight spaces.
These options transform portable hoist cranes into highly specialized tools, maximizing their efficiency, safety, and lifespan in various applications across multiple industries.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “portable hoist crane”
Quality Control of Portable Hoist Crane
1. Material Inspection: Verify raw materials meet specified quality standards, such as tensile strength and durability.
2. Component Testing: Test individual parts like motors, cables, and gears for functionality, compliance, and load-bearing capacity.
3. Assembly Verification: Ensure all components are correctly assembled to design specifications.
4. Load Testing: Perform rigorous testing under varying loads to ensure safe operation.
5. Operational Testing: Check for smooth functioning, speed control, and emergency stop mechanisms.
6. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Use methods like ultrasonic testing to detect internal flaws.
7. Safety Certifications: Ensure compliance with industry standards such as ISO, ANSI, and OSHA guidelines.
8. Final Inspection: Conduct a thorough final quality check before packaging and shipping.
Manufacturing Process of Portable Hoist Crane
1. Design and Planning: Engineers create detailed blueprints and simulations to ensure the design meets performance and safety criteria.
2. Material Procurement: High-quality materials like steel and aluminum are sourced.
3. Component Fabrication:
– Machining: Parts are shaped using lathes, mills, and CNC machines.
– Welding: Structural components are welded together.
– Painting and Coating: Apply anti-corrosion coatings.
4. Assembly Line:
– Motor Installation: Fit and secure the motor.
– Gearbox and Hoist Mechanism: Assemble and install the lifting mechanism.
– Electrical Wiring: Implement control systems and safety wiring.
5. Pre-Assembly Testing: Test individual components for defects.
6. Full Assembly: Integrate all components into the final product.
7. Quality Control Testing: Perform load tests, operational checks, and NDT.
8. Final Inspection: Ensure the entire unit meets the design and safety requirements.
9. Packaging and Shipping: The crane is packaged securely for transport to prevent damage.
Each stage is designed to ensure the portable hoist crane meets rigorous safety and performance standards, providing reliability and safety to the end-user.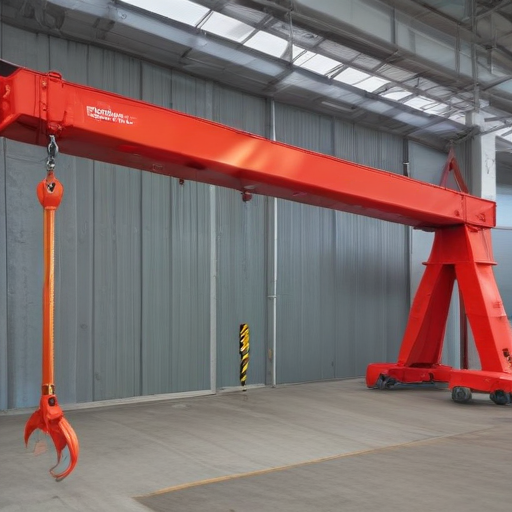
How to use “portable hoist crane”
A portable hoist crane is a device used for lifting and moving heavy loads. Here’s a quick guide on how to use it safely and efficiently:
1. Site Preparation:
– Ensure the ground is stable and level.
– Clear obstructions from the working area.
– Mark the operating area to keep unauthorized personnel out.
2. Crane Setup:
– Position the crane in the desired location.
– Lock the wheels if the crane has them to prevent movement.
– Assemble any parts according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
3. Pre-Operation Checks:
– Inspect the crane for any damage or wear.
– Ensure all bolts and nuts are tightened.
– Check the hoist mechanism and load chain for proper operation.
4. Load Preparation:
– Determine the weight of the load to ensure it does not exceed the crane’s capacity.
– Securely attach the load to the hoist hook using appropriate slings or chains.
– Ensure the load is balanced and stable.
5. Lifting:
– Use the control mechanism to slowly lift the load.
– Pause lifting if the load swings or shifts, and adjust as necessary.
– Continue lifting smoothly, keeping the load under control.
6. Moving the Load:
– If the crane has wheels, carefully push or pull it to the desired location.
– If the crane is stationary, use the control mechanism to rotate or reposition the load.
– Move slowly to prevent the load from swaying or tipping over.
7. Lowering the Load:
– Gradually lower the load to the specified location.
– Guide the load into place to ensure it lands squarely and safely.
– Once the load is secure, detach the lifting equipment.
8. Post-Operation:
– Inspect the crane for any signs of wear or damage.
– Perform any needed maintenance.
– Store the crane in a secure location.
Safety Tips:
– Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
– Never exceed the crane’s lifting capacity.
– Maintain clear communication with any assisting personnel.
By following these steps, you can safely and efficiently use a portable hoist crane.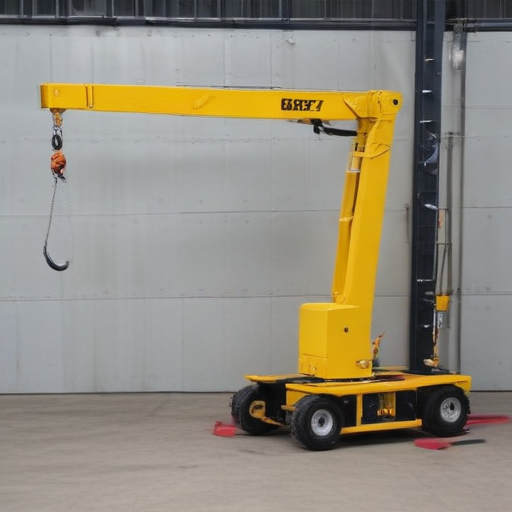
“portable hoist crane” Comparative Analysis
A portable hoist crane, also referred to as a mobile hoist, is a versatile lifting device designed for ease of transportation and deployment across various job sites. Here is a comparative analysis of portable hoist cranes concerning their types, advantages, and limitations.
Types
1. Mobile Floor Cranes: These are typically on wheels and can be manually pushed or motorized. Ideal for indoor use, such as workshops and warehouses.
2. Portable Gantry Cranes: Consist of a robust frame on wheels with an adjustable height beam, suitable for larger loads and outdoor use.
3. Engine Hoists: Often used in automotive shops, these are specifically designed to lift heavy components like car engines.
4. Mini Cranes: Compact and highly maneuverable, making them suitable for constrained spaces and diverse terrains.
Advantages
– Flexibility: Portable hoist cranes can be moved to various locations as required, making them perfect for projects that require temporary lifting solutions.
– Cost-Effective: Eliminates the need for multiple permanent installations, reducing infrastructure and maintenance costs.
– Ease of Use: Typically easy to set up and operate, reducing downtime and operational complexity.
– Versatility: Capable of handling a variety of loads with different attachments and configurations. Suitable for a range of industries, from construction to shipping and repair shops.
Limitations
– Load Capacity: Portable hoist cranes generally have lower load capacities compared to fixed cranes, which may limit their use for very heavy lifting.
– Stability Issues: Being mobile, they may be less stable than permanent installations, particularly on uneven ground or under high wind conditions.
– Operational Range: The range of movement and lift height may be limited compared to larger, fixed cranes, affecting their utility in some scenarios.
Conclusion
Portable hoist cranes offer significant advantages in terms of flexibility, cost-efficiency, and ease of use, making them a valuable asset for various applications. However, their load capacity and operational limitations should be carefully considered to ensure they meet the specific needs of the task at hand.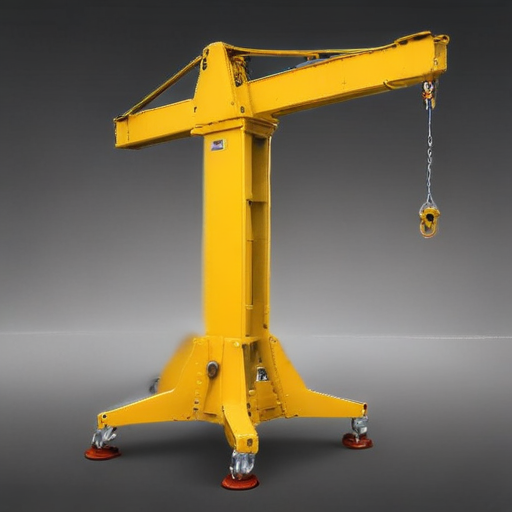
“portable hoist crane” Warranty and Support
Portable Hoist Crane Warranty and Support
When investing in a portable hoist crane, it’s crucial to understand the warranty and support services that come with your purchase to ensure the longevity and reliable performance of the equipment.
Warranty
Most reputable manufacturers offer a comprehensive warranty on portable hoist cranes, often ranging from 1 to 3 years. This warranty typically covers defects in materials and workmanship. However, it’s important to check the specifics, as conditions and exclusions may apply. For instance, warranties often do not cover damage resulting from improper use, lack of maintenance, or accidents. Some manufacturers also offer extended warranty options for added peace of mind.
Support
Customer support is an essential aspect to consider. Reliable manufacturers provide robust support services, including:
– Technical Assistance: Access to expert advice for troubleshooting and maintenance queries. This support can be accessed via phone, email, or live chat.
– Spare Parts Availability: Easy access to genuine spare parts to ensure quick repairs and minimal downtime.
– Service Centers: Authorized service centers or technicians for conducting repairs and maintenance. Some companies even offer on-site assistance.
– Documentation: Comprehensive manuals and instructional videos to guide you through installation, operation, and routine maintenance.
After-Sales Training
Some manufacturers go a step further by offering after-sales training sessions. These training programs can be invaluable for ensuring that your team knows how to operate and maintain the hoist crane safely and efficiently.
Conclusion
A robust warranty and comprehensive support services are crucial for ensuring the effective and long-term operation of your portable hoist crane. Always review the warranty terms and support options before making a purchase to safeguard your investment and ensure you receive the necessary help when needed.
List “portable hoist crane” FAQ
Portable Hoist Crane FAQ
1. What is a portable hoist crane?
A portable hoist crane is a versatile lifting device designed for easy mobility and setup. It is commonly used for transporting heavy loads in workshops, factories, and construction sites.
2. What are the types of portable hoist cranes?
Types include manual portable hoist cranes, electric portable hoist cranes, and hydraulic portable hoist cranes. Each type offers different advantages based on the required lifting capacity and application.
3. What is the lifting capacity of portable hoist cranes?
Lifting capacities vary widely, ranging from a few hundred pounds to several tons. Always check the specifications of the model to ensure it meets your needs.
4. How do I choose the right portable hoist crane?
Consider factors like load capacity, lifting height, power source (manual, electric, or hydraulic), and portability requirements. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific recommendations.
5. Are portable hoist cranes easy to transport?
Yes, they are designed for ease of transport, often featuring wheels and telescoping legs for easy movement and storage.
6. What safety measures should I follow?
Always follow the manufacturer’s safety guidelines, inspect the crane before each use, and never exceed the rated capacity. Use proper personal protective equipment (PPE) and ensure a stable, level setup area.
7. Can I use a portable hoist crane outdoors?
Many models are suitable for outdoor use, but it’s essential to check the manufacturer’s specifications for weather resistance and environmental limitations.
8. How do I maintain a portable hoist crane?
Regular maintenance includes inspecting for wear and tear, lubricating moving parts, and following the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule. Keep the crane clean and stored in a protected area when not in use.
9. Where can I buy a portable hoist crane?
They can be purchased from industrial equipment suppliers, specialized retailers, and online marketplaces. Always buy from a reputable source.
10. How much does a portable hoist crane cost?
Prices vary based on capacity, features, and brand. Entry-level models may start from a few hundred dollars, while advanced models can cost several thousand dollars.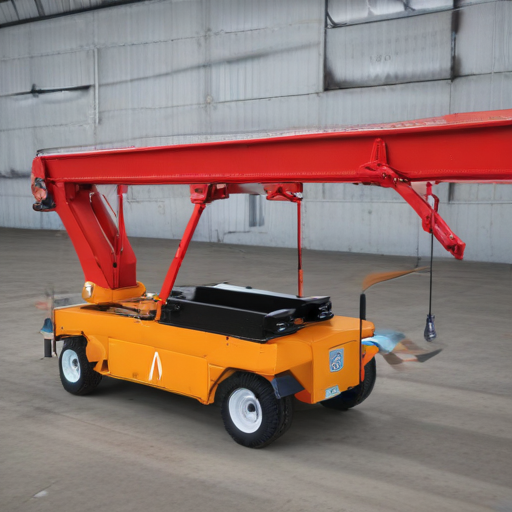
Top 10 FAQ with answer about portable hoist crane for Buyer Sourcing from China
Top 10 FAQ about Sourcing Portable Hoist Cranes from China
1. What is a Portable Hoist Crane?
– A portable hoist crane is a flexible, mobile lifting device designed for temporary or short-term lifting tasks. They are often used in construction, warehouses, and manufacturing settings.
2. Why Source Portable Hoist Cranes from China?
– China is renowned for its cost-effective manufacturing capabilities, advanced technology, and extensive supply chain networks, making it possible to get quality products at competitive prices.
3. What Specifications Should I Consider?
– Key specifications include the lifting capacity, lifting height, power source (manual, electric, or pneumatic), material of construction, and mobility features like wheels or tracks.
4. How to Ensure Product Quality?
– Look for certifications (ISO, CE), request samples, and consider third-party inspections. Manufacturers with a good track record and positive reviews are generally more reliable.
5. What are the Shipment Options and Costs?
– Depending on urgency and budget, options include air freight, sea freight, and express courier services. The cost varies with the weight, dimensions, and shipping route.
6. What Payment Terms are Common?
– Typical payment methods include T/T (Telegraphic Transfer), L/C (Letter of Credit), and PayPal. Upfront deposits (30%–50%) are customary, with the balance paid before shipment.
7. How Long is the Delivery Time?
– Delivery times can range from 15-45 days based on order complexity and quantity. Customized orders might take longer due to additional manufacturing requirements.
8. What After-Sales Services are Provided?
– Reliable suppliers offer warranties ranging from 1-3 years and provide free spare parts or replacements for faulty components within the warranty period.
9. Can I Customize the Crane?
– Yes, most Chinese manufacturers offer customization options, including custom lifting capacities, heights, and additional features to meet specific needs.
10. How to Verify Manufacturers’ Legitimacy?
– Conduct due diligence by checking business licenses, company certifications, and customer reviews. Use sourcing platforms like Alibaba or Made-in-China, which offer verification services.






